Categorías
- iridología (226)
- Lectura ocular (24)
- software QR (15)
- Blog (304)
- Ilustración de iridología (35)
- curso en línea de iridología (54)
- iridología (59)
- Exhibición (2)
- Noticias (424)
 Continúe leyendo para saber cómo los iridólogos examinan el iris, qué signos buscan y qué condiciones de salud comúnmente dicen que una lectura puede resaltar.
Continúe leyendo para saber cómo los iridólogos examinan el iris, qué signos buscan y qué condiciones de salud comúnmente dicen que una lectura puede resaltar.En el centro de la práctica de la iridología se encuentra un gráfico del iris, un mapa que los profesionales utilizan al examinar los iris. Mayoría gráficos de iridología divida cada iris en numerosas zonas (muchos gráficos hacen referencia aproximadamente a entre 80 y 90 áreas), y cada zona está vinculada a un órgano, glándula o sistema corporal en particular. Cuando un iridólogo examina sus ojos, compara marcas y colores con este mapa para sugerir qué parte del cuerpo puede estar bajo estrés o mostrar cambios tempranos. Estas interpretaciones son utilizadas por los iridólogos y no sustituyen a las pruebas médicas (consulte las preguntas frecuentes).
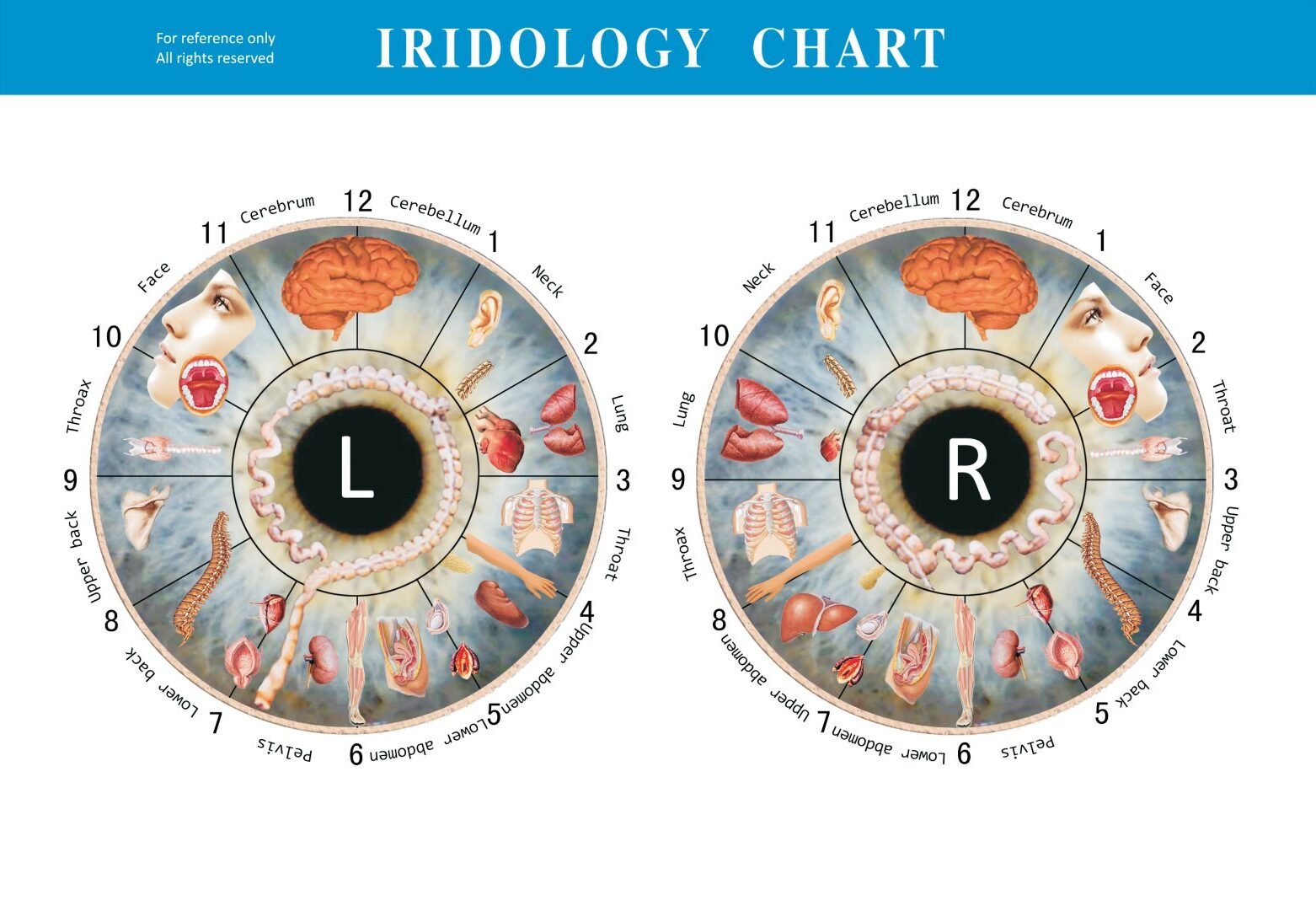

Gráfico de iridología que mapea diferentes zonas del iris con los sistemas corporales correspondientes (nota: el iris izquierdo a menudo refleja los órganos del cuerpo del lado izquierdo; el iris derecho a menudo refleja los órganos del cuerpo del lado derecho)
Para que el diagnóstico sea más preciso, tabla de iridología A menudo se utiliza junto con otros métodos de diagnóstico.

ojo derecho reflejes lado derecho cuerpo.
| Posición del reloj (ojo derecho) | Corresponde órgano/sistema | Detalles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 en punto - 2 en punto | Cara derecha | Corresponde a los órganos reproductivos izquierdos, incluyen útero, ovarios (hembras) o testículos (hombres). |
| 2 en punto - 3 en punto | Garganta | Ringflects Health Juntas izquierdas, incluye rodillas, caderas, codos y hombros. |
| 3 en punto - 4 en punto | Espalda superior derecha | Corresponde a la columna vertebral, la salud espinal, la alineación y la flexibilidad. |
| 4 en punto - 5 en punto | Vejiga | Ringflects Bladder y Sistema urinario del lado derecho. |
| 5 en punto - 6 en punto | Pélvico derecho | Anlingpresents izquierda colon, intestino delgado y salud digestiva. |
| 6 en punto - 7 en punto | Abdomen inferior derecha | Ringflects izquierdo de riñón, se centra en la filtración, la desintoxicación y el equilibrio de fluidos. |
| 7 en punto - 8 en punto | Abdomen superior derecho | Ringflects estómago y órganos digestivos en el lado izquierdo. |
| 8 en punto - 9 en punto | Tórax derecho | Corresponde al hígado del lado izquierdo, la desintoxicación responsable y la producción de bilis. |
| 9 en punto - 10 en punto | Pulmón derecho | Los ritmo del corazón del lado izquierdo, afectan la salud y la circulación cardiovascular. |
| 10 en punto - 11 en punto | Cuello derecho | Ringflects Left Lunm, salud respiratoria y función Brea. |
| 11 en punto - 12 en punto | Cerebro derecho | Corresponde al cerebro del hemisferio izquierdo, la salud mental y las funciones cognitivas. |
| 12 en punto - 1 en punto | Cerebro derecho | Corresponde al cerebro del hemisferio izquierdo, la salud mental y las funciones cognitivas. |
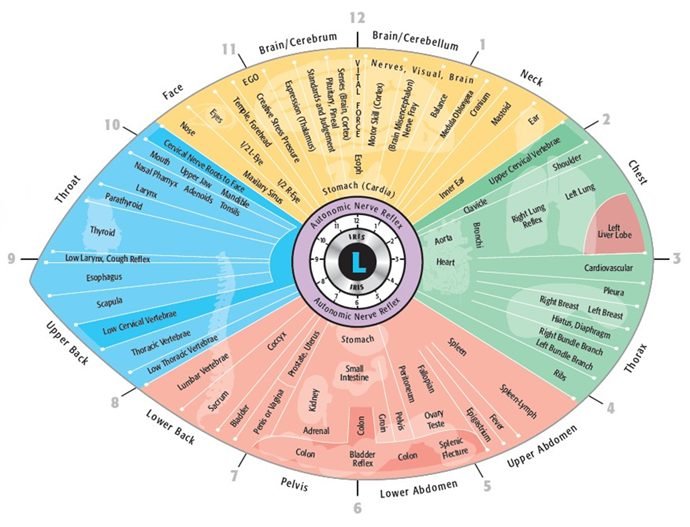
ojo izquierdo reflejes lado izquierdo cuerpo.
| Posición del reloj (ojo izquierdo) | Corresponde órgano/sistema | Detalles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 en punto - 2 en punto | Cuello izquierdo | Corresponde a los órganos reproductivos derecho, incluyen útero, ovarios (hembras) o testículos (macho). |
| 2 en punto - 3 en punto | Pulmón izquierdo | Ringflects Health Right Junks, incluyen rodillas, caderas, codos y hombros. |
| 3 en punto - 4 en punto | Tórax izquierdo | Corresponde a la columna vertebral, la salud espinal, la alineación y la flexibilidad en el lado derecho. |
| 4 en punto - 5 en punto | Abdomen de la parte superior izquierda | Ringflects Bladder y Sistema urinario del lado izquierdo. |
| 5 en punto - 6 en punto | Abdomen inferior izquierdo | Anillo de anillo de colon derecho, intestino delgado y salud digestiva. |
| 6 en punto - 7 en punto | Pélvico izquierdo | Ringflects riñón derecho, se centra en la filtración, la desintoxicación y el equilibrio de fluidos. |
| 7 en punto - 8 en punto | Izquierda hacia atrás | Ringflects estómago y órganos digestivos en el lado derecho. |
| 8 en punto - 9 en punto | Izquierda de la parte superior de la espalda | Corresponde al hígado del lado derecho, la desintoxicación responsable y la producción de bilis. |
| 9 en punto - 10 en punto | Garganta izquierda | Antes de anillo del corazón del lado derecho, afectan la salud y la circulación cardiovascular. |
| 10 en punto - 11 en punto | Cara izquierda | Ringflects pulmón derecho, salud respiratoria y función Brea. |
| 11 en punto - 12 en punto | Cerebro izquierdo | Corresponde al cerebro del hemisferio derecho, la salud mental y las funciones cognitivas. |
| 12 en punto - 1 en punto | Cerebro izquierdo | Corresponde al cerebro del hemisferio derecho, la salud mental y las funciones cognitivas. |
La interpretación del color y las marcas son herramientas fundamentales en el enfoque de un iridólogo. Las convenciones profesionales comunes incluyen:
El análisis del patrón de fibras es otro elemento importante. Las fibras de colágeno que forman la estructura del iris pueden parecer tensas o sueltas; los profesionales interpretan las fibras tensas y bien definidas como un indicador de una resiliencia constitucional más fuerte, mientras que las fibras más laxas y caóticas pueden interpretarse como sugerencias de áreas de debilidad genética o constitucional que podrían necesitar apoyo. Por ejemplo, un médico podría notar una estructura de fibra más suelta en el anillo de la pupila (examinando el área de la pupila del iris) y recomendar una evaluación digestiva o cambios en la dieta como siguiente paso (interpretación del médico).
Los iridólogos utilizan herramientas sencillas (una lupa o una cámara digital especializada) para fotografiar y estudiar ambos iris. Como ocurre con muchos enfoques alternativos, las interpretaciones varían según el médico y deben considerarse como información que puede guiar pruebas adicionales o conversaciones con sus proveedores de atención médica.
Lea la siguiente sección sobre 5 beneficios clave para conocer lo que los profesionales de la iridología comúnmente dicen que una lectura puede revelar sobre su salud y sus patrones de estrés.
— Nota histórica: los métodos modernos de iridología a menudo se remontan a Ignatz von Peczely, quien ayudó a popularizar la idea en el siglo XIX.
Un beneficio de lectura de Iridología comúnmente citado es la capacidad de señalar tendencias heredadas antes de que aparezcan los síntomas. Los iridólogos buscan signos característicos del iris que interpretan como marcadores constitucionales: patrones que pueden sugerir la predisposición de una persona a ciertas condiciones para que se puedan tomar medidas preventivas.
Lo que muestra el iris: marcadores estructurales estables o formaciones de fibras que los profesionales interpretan como patrones heredados.
Lo que un iridólogo podría recomendar: cambios específicos en el estilo de vida o en la dieta, un seguimiento más estrecho o pruebas de detección convencionales si se sospecha un problema hereditario.
Nivel de evidencia: interpretación basada en profesionales; Validación clínica limitada. Confirme siempre con su proveedor de atención médica.
“El iris revela patrones heredados que pueden indicar qué sistemas del cuerpo pueden necesitar apoyo adicional.” explica María Collins, iridóloga certificada con 15 años de experiencia. “Esto brinda a los pacientes la oportunidad de abordar posibles problemas de salud de manera proactiva en lugar de reactiva.”
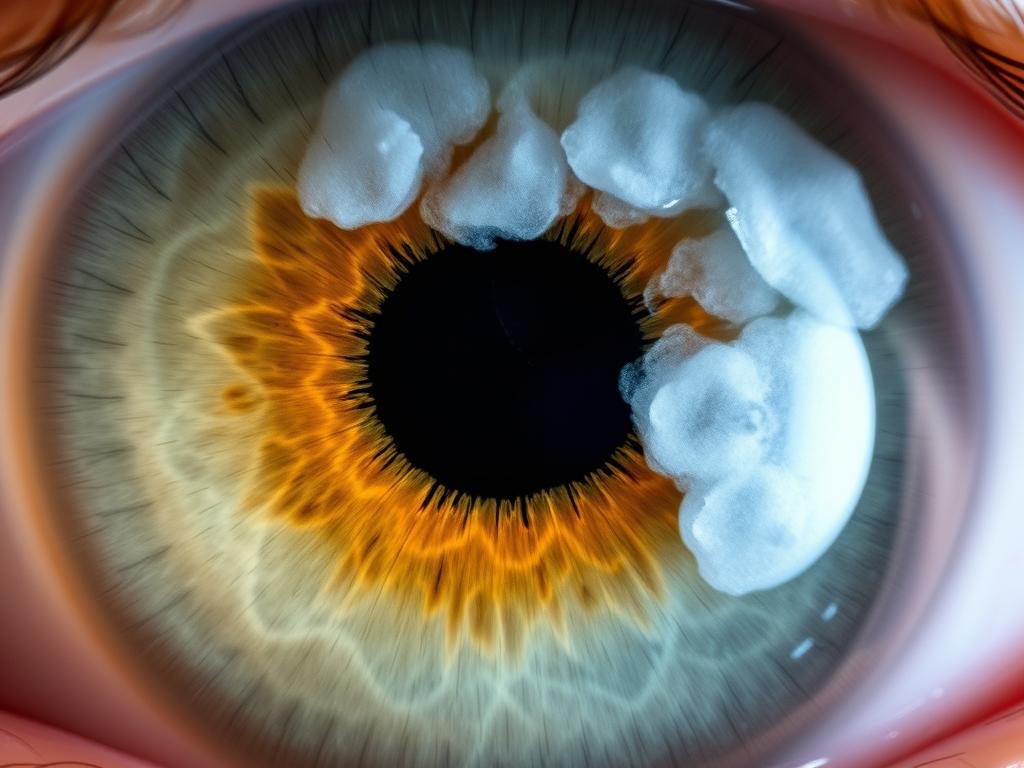
Los profesionales de la iridología suelen utilizar cambios de color del iris y opacidad para sugerir una inflamación localizada en el cuerpo. Si bien no son diagnósticos, estos signos pueden impulsar una mayor investigación.
Lo que muestra el iris: marcas blancas o nubosidad (a menudo leídas como inflamación aguda) y marcas más oscuras (a menudo leídas como congestión crónica).
Lo que un iridólogo podría recomendar: análisis de sangre de seguimiento (p. ej., marcadores inflamatorios), cambios dietéticos específicos o derivación a un médico especialista si se justifica.
Nivel de evidencia: mezclado. Algunos estudios (por ejemplo, investigaciones publicadas en revistas de medicina complementaria) han encontrado correlaciones entre ciertos signos del iris y marcadores inflamatorios, pero los hallazgos son preliminares y requieren ensayos más amplios y rigurosos.
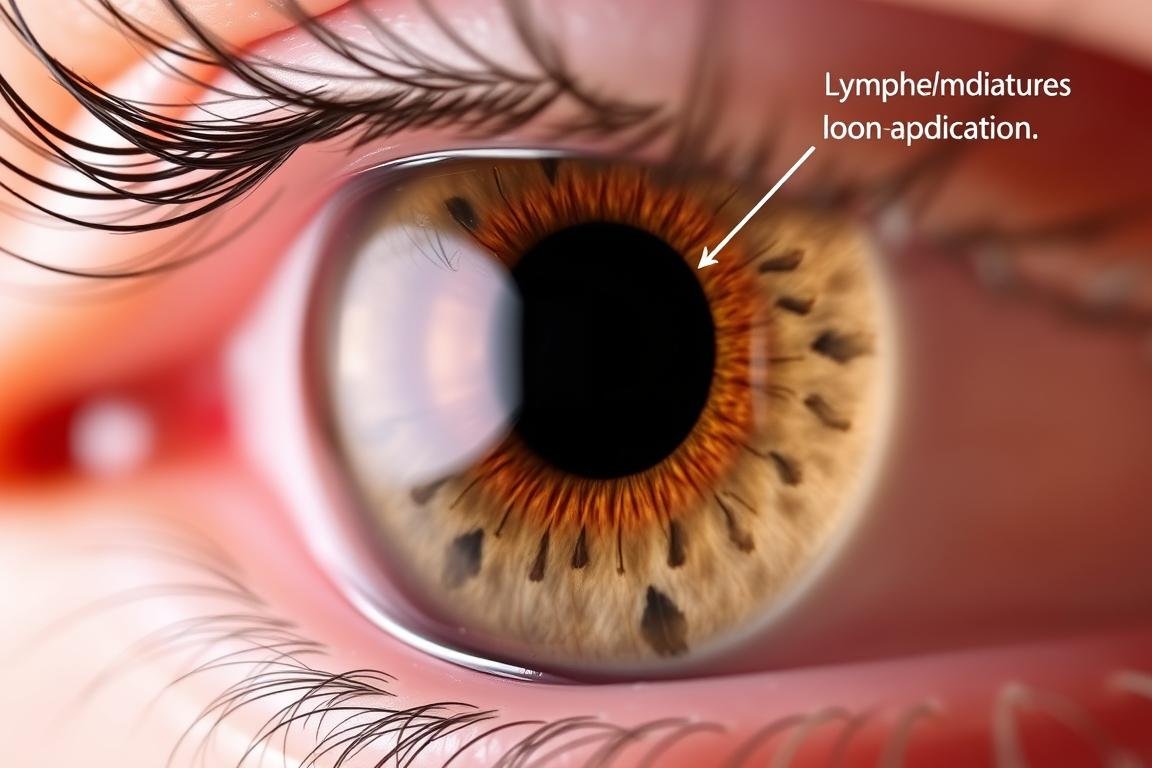
El borde exterior del iris se asocia comúnmente con la función linfática en los gráficos de iridología. Los signos en esta área pueden llevar a los médicos a considerar la congestión linfática como un factor que contribuye a las quejas de hinchazón o baja energía de una persona.
Lo que muestra el iris: anillos o marcas blancas cerca del borde exterior del iris que los médicos interpretan como lentitud linfática.
Lo que un iridólogo podría recomendar: cambios en la dieta y el estilo de vida para apoyar el drenaje linfático (hidratación, movimiento, alimentos específicos) y, cuando sea apropiado, derivación a un médico o profesional de la salud aliado.
Nivel de evidencia: beneficios anecdóticos y observados por los profesionales; investigación limitada revisada por pares.
Programe una consulta con un iridólogo certificado para conocer las fortalezas de su cuerpo y las áreas potenciales que necesitan apoyo.
Los iridólogos suelen interpretar los anillos nerviosos y los patrones de contracción como indicadores de cómo el estrés afecta al sistema nervioso. Estos signos pueden resaltar la tensión crónica o el desequilibrio autónomo que puede afectar el bienestar general.
Lo que muestra el iris: anillos nerviosos concéntricos o surcos de contracción comúnmente asociados con la respuesta al estrés.
Lo que un iridólogo podría recomendar: estrategias de reducción del estrés (respiración, higiene del sueño, intervenciones específicas en el estilo de vida) y, cuando corresponda, evaluación por parte de profesionales de la salud en caso de sospecha de problemas del sistema nervioso.
Nivel de evidencia: limitado; Algunos estudios relacionados con la neurociencia han explorado vínculos entre los patrones del iris y la función autónoma, pero se necesita más investigación.
El anillo interior alrededor de la pupila se lee comúnmente como la zona digestiva en las cartas de iridología. Los cambios en esta área pueden llevar a los profesionales a considerar ineficiencias digestivas, sensibilidades alimentarias o problemas de absorción de nutrientes.
Lo que muestra el iris: Las irregularidades o decoloración cerca del anillo pupilar a menudo se interpretan como signos de la zona digestiva.
Lo que un iridólogo podría recomendar: ajustes dietéticos específicos, ensayos de eliminación para sensibilidades sospechadas o pruebas digestivas convencionales si los síntomas son significativos.
Nivel de evidencia: patrones observados por el practicante; debe corroborarse con pruebas convencionales para decisiones clínicas.
“La zona digestiva del iris a menudo revela problemas antes de que aparezcan los síntomas tradicionales.” dice Jennifer Marks, nutricionista holística y practicante de iridología. “Esto nos permite hacer recomendaciones dietéticas específicas que pueden prevenir el desarrollo de problemas digestivos más graves.”

Si bien la iridología nunca debe reemplazar las pruebas o diagnósticos médicos convencionales, los profesionales utilizan las observaciones del iris para proporcionar información sobre posibles condiciones y desequilibrios de salud. A continuación se detallan algunas de las condiciones y problemas de salud que los iridólogos comúnmente dicen que una lectura puede ayudar a detectar, junto con los próximos pasos prácticos que puede seguir si surge una inquietud.
Diferentes patrones de iris pueden indicar diversas condiciones de salud según la práctica de iridología
Qué hacer si una lectura de iridología genera una inquietud:
Ejemplo de caso (anónimo): una persona de mediana edad tenía una lectura del iris que sugería una decoloración de la zona del hígado. Su médico ordenó pruebas de seguimiento de la función hepática e imágenes; Se confirmaron cambios leves en el hígado graso no alcohólico, lo que llevó a intervenciones dietéticas y de ejercicio. Este ejemplo ilustra cómo una visión iridológica puede impulsar una evaluación convencional (anecdótica y que no sustituye al diagnóstico médico).
La Dra. Lisa Thompson, médica naturópata, señala: “Si bien no utilizamos la iridología para diagnosticar enfermedades específicas, a menudo nos guía hacia áreas que necesitan más investigación mediante pruebas convencionales. Muchos pacientes descubren que la evaluación del iris se alinea con los síntomas que han estado experimentando pero que no habían relacionado.”
Esta tabla resume las diferencias clave entre una lectura de iridología y un examen de la vista tradicional. Está pensado como una referencia rápida; consulte las secciones Perspectivas científicas y Preguntas frecuentes para obtener detalles sobre la evidencia, las limitaciones y cuándo consultar a los profesionales de la atención para obtener un diagnóstico médico.
| Aspecto | Lectura de iridología | Examen de la vista tradicional |
| Propósito principal | Evaluar la salud y el bienestar general del cuerpo a través de los signos del iris | Evaluar la salud ocular, la agudeza visual y las enfermedades oculares. |
| Lo que examina | Patrones, colores y marcas del iris interpretados como indicadores de condiciones sistémicas. | Estructuras oculares, presión intraocular, retina y función de la visión. |
| Facultativo | Iridólogo, naturópata o practicante holístico (práctica complementaria) | Oftalmólogo u optometrista (especialistas médicos) |
| Validación científica | Validación científica limitada; generalmente considerado complementario/alternativo por la medicina convencional | Amplia validación y protocolos estandarizados en la práctica clínica. |
| Equipo utilizado | Lente de aumento o cámara de iris digital especializada (herramienta para documentar signos) | Lámpara de hendidura, tonómetro, foróptero, OCT y otros dispositivos oftálmicos |
| Cobertura de seguro médico | Por lo general, no está cubierto por un seguro de salud | A menudo están cubiertos total o parcialmente por un seguro médico o planes de visión. |
Descargue nuestra guía completa de gráficos de iridología: incluye un gráfico de muestra, un glosario de signos del iris y consejos sobre cómo elegir un médico calificado y discutir los hallazgos con su equipo de atención médica.
La iridología tiene una validación científica limitada en la medicina convencional. Algunos estudios han informado correlaciones entre signos específicos del iris y ciertas condiciones de salud, pero la evidencia es preliminar y no definitiva. Considere la iridología como una herramienta complementaria que puede proporcionar información para investigaciones futuras en lugar de un método de diagnóstico independiente. Si tiene problemas de salud, consulte a los profesionales de la atención para obtener las pruebas y el diagnóstico adecuados.
Una sesión típica de iridología dura entre 30 y 60 minutos. Durante ese tiempo, el médico examinará ambos iris, a menudo fotografiándolos con una cámara especializada o usando una lupa, luego revisará las observaciones y los posibles próximos pasos. Las sesiones de seguimiento suelen ser más breves y se centran en realizar un seguimiento de los cambios a lo largo del tiempo. Si tiene problemas de salud continuos, un médico puede recomendar controles más frecuentes.
No, la iridología no debe utilizarse para diagnosticar enfermedades específicas como el cáncer. Si bien los médicos pueden notar signos de estrés tisular o inflamación en áreas del iris que corresponden a ciertos órganos, estas observaciones no son diagnósticas. Siempre busque una evaluación médica de su proveedor de atención médica si tiene problemas de salud graves y siga los protocolos de detección recomendados.
La mayoría de los profesionales recomiendan una lectura inicial seguida de seguimientos cada 6 a 12 meses para controlar el bienestar. Para las personas que abordan problemas de salud específicos, se pueden programar lecturas con mayor frecuencia (por ejemplo, cada 3 a 6 meses) para rastrear los cambios y las respuestas a las intervenciones. Utilice fotografías y notas del iris para comparar los cambios a lo largo del tiempo y analice los resultados con su proveedor de atención primaria cuando le sugieran pruebas o derivaciones.
Si un iridólogo señala una posible preocupación: 1) valide: solicite una explicación clara y fotografías documentadas del iris, 2) consulte: lleve los hallazgos a su proveedor de atención primaria o a un especialista relevante para las pruebas adecuadas, y 3) realice un seguimiento: mantenga fotografías fechadas y notas de síntomas para detectar cambios tempranos y medir el progreso. Trate la iridología como una indicación para una evaluación adicional, no como un diagnóstico clínico.

“Si bien la medicina convencional sigue siendo escéptica respecto de la iridología, algunas investigaciones sugieren posibles correlaciones entre las características del iris y ciertas condiciones fisiológicas. El campo se beneficiaría de una investigación científica más rigurosa.”
Investigaciones recientes han explorado posibles vínculos entre los signos del iris y aspectos de la salud sistémica, pero los diseños de los estudios y los tamaños de las muestras varían y los hallazgos siguen siendo preliminares. La correlación no es igual a la causalidad: los trabajos existentes destacan patrones interesantes en la estructura y el color del iris, pero no establecen la iridología como método de diagnóstico.
Los estudios y revisiones representativos incluyen:
Cómo leer estos hallazgos: busque el tipo de estudio (piloto versus controlado), el tamaño de la muestra y si los análisis fueron cegados; se necesitan estudios más grandes, replicados y metodológicamente sólidos antes de que la iridología pueda considerarse un enfoque de diagnóstico validado.
Nota: Si bien se están realizando investigaciones sobre los signos del iris, estos estudios no validan la iridología para el diagnóstico médico. Consulte a profesionales de la salud calificados si tiene alguna inquietud médica o prueba de diagnóstico.
La iridología ofrece una perspectiva sobre la salud general al examinar el iris y los iris en busca de patrones que los profesionales interpretan como pistas de desequilibrios, predisposiciones genéticas o áreas del cuerpo que experimentan estrés o inflamación. Como práctica complementaria y no invasiva, puede aportar información útil para las personas que buscan salud y bienestar holísticos cuando se utiliza junto con la atención sanitaria convencional.
Dicho esto, la iridología no reemplaza el diagnóstico médico. Utilice los hallazgos del iris como guía para una evaluación adicional en lugar de respuestas definitivas. Para obtener los mejores resultados, combine los conocimientos de iridólogos certificados con pruebas y consejos de profesionales de atención médica que puedan proporcionar diagnósticos y tratamientos basados en evidencia.
Próximos pasos que puedes seguir:
Descubra lo que sus ojos pueden revelar sobre su salud con una lectura de iridología profesional. Al elegir un profesional, busque credenciales verificadas y pregunte sobre su enfoque y experiencia.

SOFTWARE DE IRIDOLOGÍA MAIKONG Instalación y funcionamiento
