El iris humano (la parte coloreada del ojo) ha fascinado a los profesionales de la salud durante siglos. Más allá de su belleza, algunos creen que contiene un mapa de la salud de todo el cuerpo. Los iridólogos son profesionales que estudian los patrones, colores y características del iris para identificar posibles problemas de salud. Si bien la medicina convencional sigue siendo escéptica, la iridología ha ganado popularidad como método de evaluación alternativo. Esta guía explora lo que hacen los iridólogos, cómo practican y lo que usted debe saber antes de considerar una lectura del iris.¿Qué es un iridólogo y cómo ejerce?
Un iridólogo es un médico que se especializa en examinar el iris del ojo para evaluar el estado de salud de una persona. En lugar de diagnosticar enfermedades específicas, los iridólogos identifican áreas de posible debilidad o estrés en el cuerpo. Creen que cada sección del iris corresponde a diferentes órganos y sistemas corporales, creando un mapa detallado que refleja su salud general.

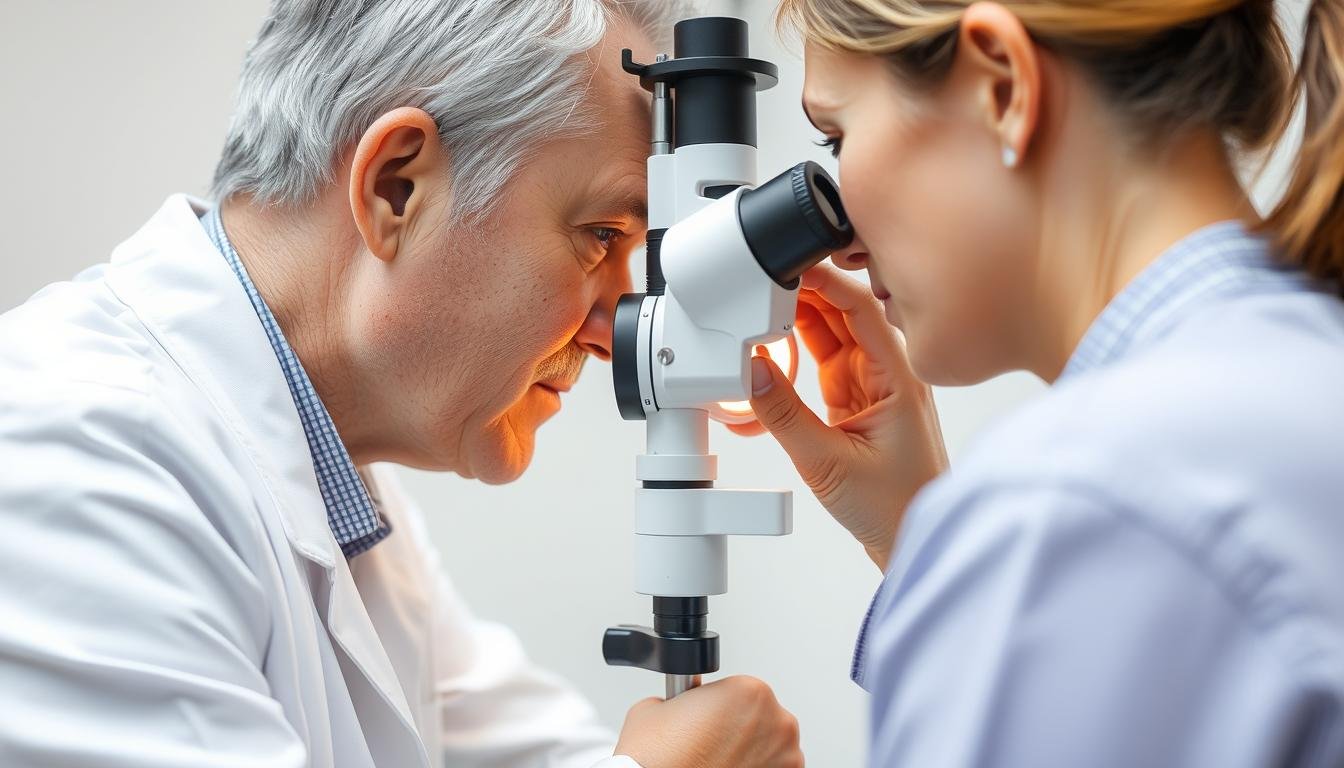
Un iridólogo realizando un examen del iris utilizando equipos de aumento especializados.
Durante una sesión típica, un iridólogo utilizará herramientas especializadas para examinar su iris en detalle. Buscan marcas específicas, variaciones de color y patrones que creen que indican el estado de las partes correspondientes del cuerpo. Después del examen, brindan una evaluación de posibles problemas de salud y pueden sugerir cambios en el estilo de vida, ajustes en la dieta o suplementos para abordar estos problemas.
Es importante tener en cuenta que los iridólogos no pretenden diagnosticar afecciones médicas. En cambio, identifican áreas de preocupación que podrían beneficiarse de atención. Muchos iridólogos recomiendan que los clientes también trabajen con médicos convencionales, especialmente para problemas de salud graves.
Principios básicos detrás del análisis del iris
La iridología se basa en varios principios fundamentales que guían cómo los profesionales interpretan lo que ven en el iris. Comprender estos principios ayuda a explicar cómo un iridólogo aborda su práctica.

Vista detallada de las fibras del iris y los patrones estudiados por los iridólogos.
Estructura de la fibra del iris
Los iridólogos examinan las fibras del iris, las diminutas estructuras en forma de hilos que irradian desde la pupila. Creen que las roturas, separaciones o patrones inusuales en estas fibras indican daño o debilidad del tejido en las áreas correspondientes del cuerpo. Las fibras densas y distribuidas uniformemente se consideran signos de buena salud, mientras que las fibras escasas o dañadas pueden sugerir problemas potenciales.
Análisis de color
El color del iris y cualquier variación dentro del mismo son importantes para los iridólogos. Analizan tanto el color base como cualquier mancha, nube o decoloración. Por ejemplo, un tinte amarillento podría sugerir problemas en el hígado o la vesícula biliar, mientras que las áreas blancas podrían indicar inflamación o acidez en regiones específicas del cuerpo.




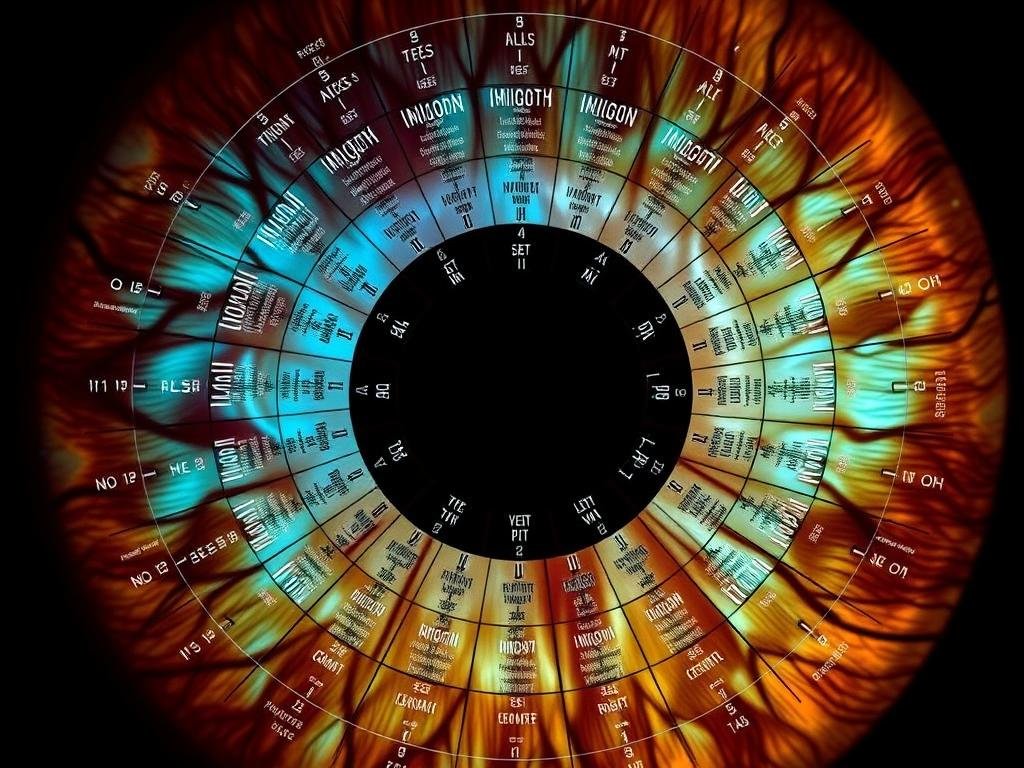
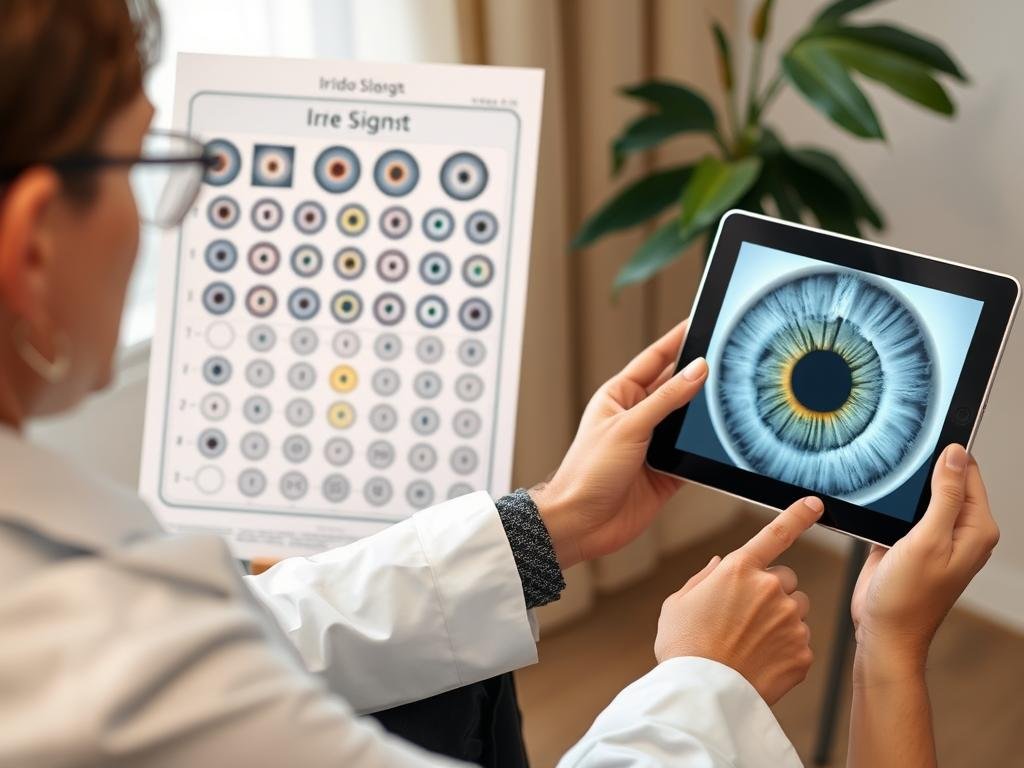
Mapeo de la tabla de iridología Mapeo de las zonas de iris a los órganos y sistemas del cuerpo correspondientes
Zonas del iris y mapeo
Iridólogos Utilice gráficos que dividan el iris en aproximadamente 60 zonas, cada una correspondiente a diferentes partes del cuerpo. Se cree que el iris izquierdo representa el lado izquierdo del cuerpo, mientras que el iris derecho corresponde al lado derecho. Estos mapas guían a los profesionales para identificar qué sistemas del cuerpo podrían verse afectados en función del lugar donde aparecen las marcas en el iris.
Evaluación constitucional
Los iridólogos creen que pueden determinar las fortalezas y debilidades inherentes de una persona (su composición constitucional) examinando el iris. Esta evaluación ayuda a identificar áreas que pueden requerir atención o apoyo especial para mantener una salud óptima.
Formación y Certificación para Iridólogos
A diferencia de los médicos u optometristas, los iridólogos no tienen un sistema de licencias estandarizado en la mayoría de los países. Sin embargo, existen varios caminos para quienes buscan convertirse en profesionales calificados.

Estudiantes en un programa de certificación de iridología aprenden técnicas de análisis.
Caminos Educativos
Aquellos interesados en convertirse en iridólogos suelen seguir una de estas rutas educativas:
- Programas de certificación a través de escuelas de salud holística (normalmente de 100 a 200 horas)
- Diplomados de institutos especializados en iridología.
- Tutoría con profesionales establecidos.
- Formación continua para profesionales sanitarios (naturópatas, quiroprácticos, etc.)
Organizaciones profesionales
Varias organizaciones brindan certificación y educación continua para iridólogos:
- Asociación Internacional de Practicantes de Iridología (IIPA)
- Asociación Nacional de Investigación en Iridología (NIRA)
- Gremio de Iridólogos Naturópatas (GNI)
- Instituto Canadiense de Iridología
Estas organizaciones generalmente requieren que los miembros completen programas de capacitación aprobados, aprueben exámenes y participen en educación continua para mantener la certificación.

Certificaciones y credenciales profesionales exhibidas en el consultorio de un iridólogo.
Educación complementaria
Muchos iridólogos mejoran su práctica con formación adicional en:
- Nutrición y dietoterapia.
- Medicina herbaria
- Anatomía y fisiología.
- Otras modalidades de curación natural.
Condiciones que los iridólogos afirman identificar
Los iridólogos creen que pueden identificar diversas afecciones de salud examinando signos específicos en el iris. Si bien la validación científica sigue siendo limitada, los profesionales informan correlaciones entre los signos del iris y estos problemas de salud:

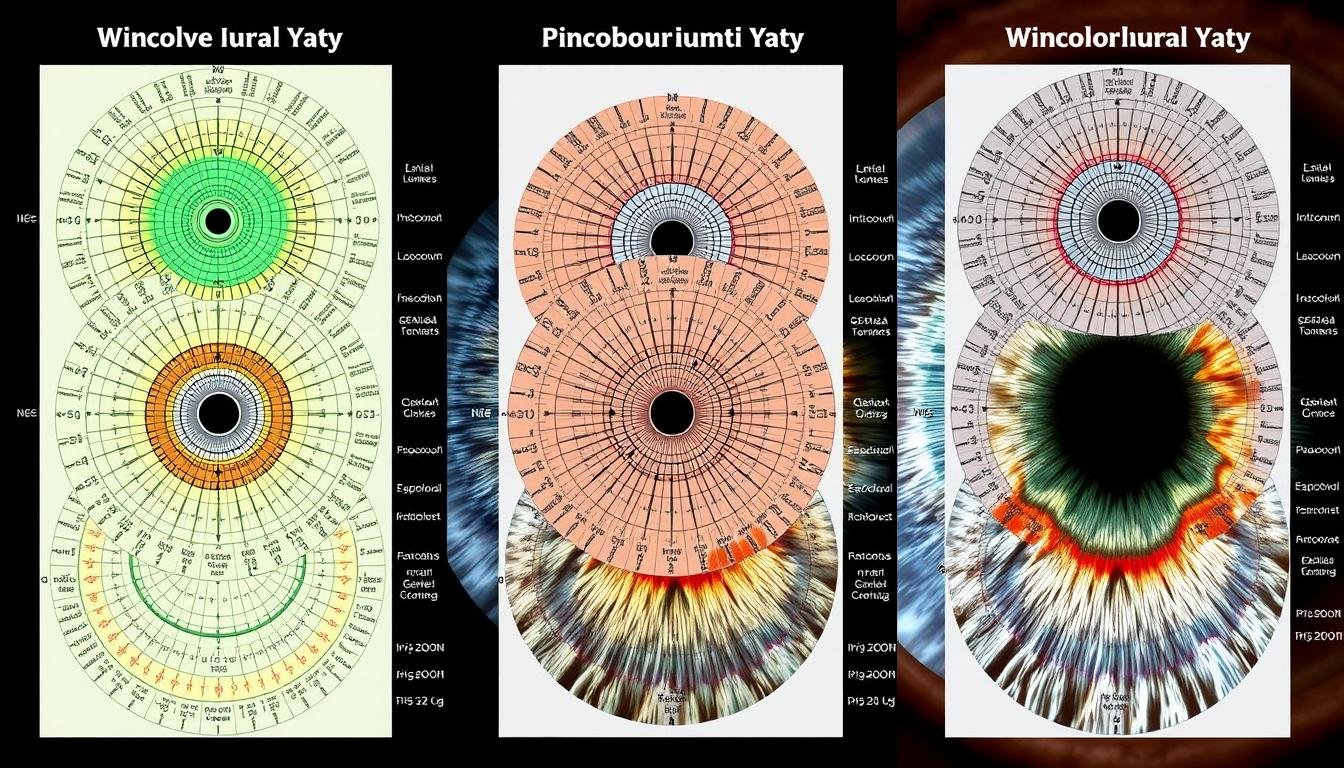
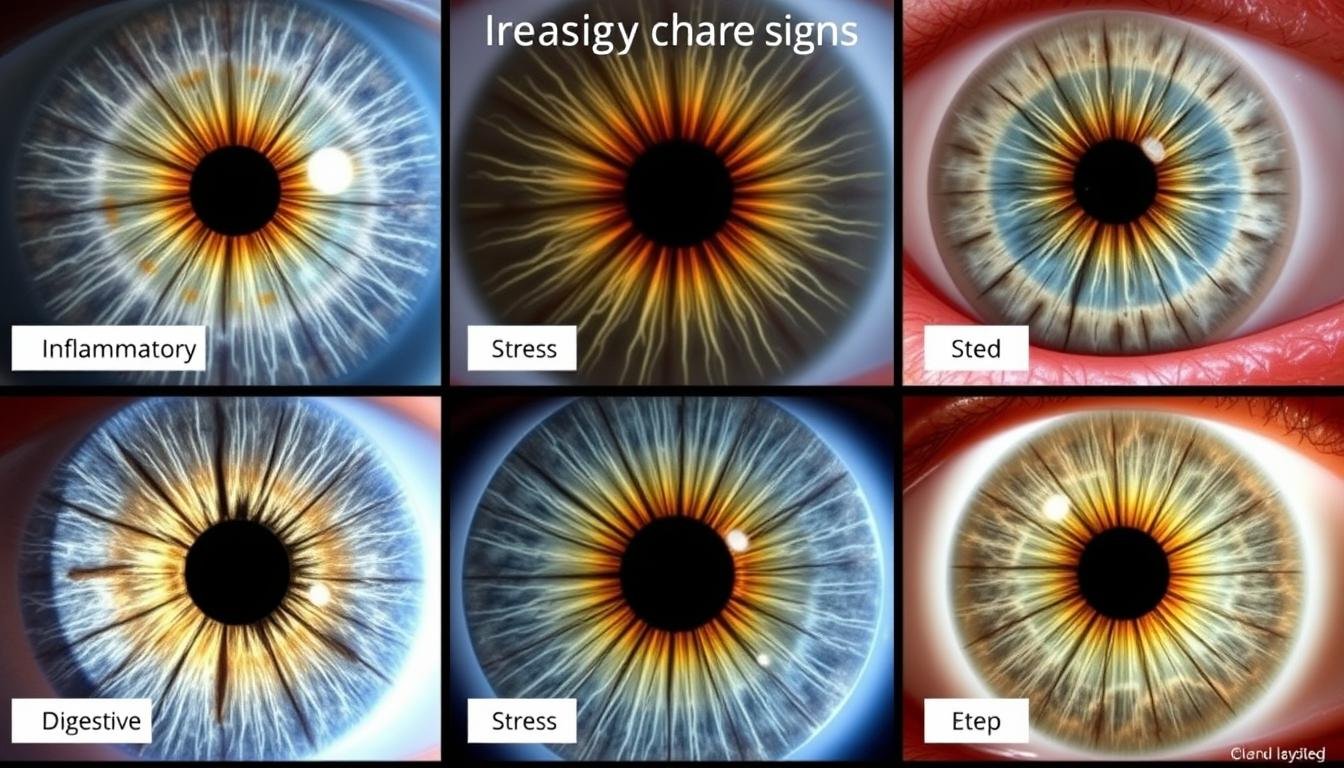
Comparación de diferentes signos del iris y sus correspondientes indicaciones de salud en iridología.
Problemas del sistema digestivo
Los iridólogos suelen identificar problemas digestivos a través de signos específicos del iris. Las marcas oscuras en el área intestinal del gráfico del iris pueden indicar inflamación, mala absorción o afecciones del intestino irritable. Los médicos buscan cambios de color, manchas o anomalías estructurales en estas zonas para evaluar la salud digestiva.
Patrones de inflamación y estrés
fibras blancas o “anillos de estrés” en el iris se interpretan como signos de inflamación o tensión en las zonas correspondientes del cuerpo. Estas marcas pueden aparecer como anillos concéntricos o líneas radiales y se cree que indican respuestas de estrés crónico o afecciones inflamatorias que pueden beneficiarse de enfoques antiinflamatorios.

Signos del iris que los iridólogos asocian con problemas de función hepática
Función del hígado y la vesícula biliar
Las decoloraciones amarillentas o las manchas marrones en zonas específicas del iris se asocian con disfunción del hígado o de la vesícula biliar. Los iridólogos pueden sugerir que estos indican acumulación de toxinas, capacidad de desintoxicación reducida o posible formación de cálculos biliares, lo que lleva a recomendaciones de hierbas que apoyan el hígado o cambios en la dieta.
Congestión del sistema linfático
Nublado o “turbio” Las áreas en el iris pueden interpretarse como signos de congestión linfática o mala eliminación de desechos. Se cree que estos patrones indican áreas donde los procesos naturales de desintoxicación del cuerpo pueden verse comprometidos, lo que podría contribuir a problemas del sistema inmunológico.
Salud cardiovascular
Ciertas marcas en el corazón y las zonas circulatorias del iris están asociadas con problemas cardiovasculares. Un anillo pronunciado alrededor del iris (conocido como anillo de sodio) a menudo está relacionado con la presión arterial alta o desequilibrios minerales que afectan la función cardíaca.

Un iridólogo explicando los signos identificados del iris a un paciente durante una consulta
Desequilibrios del sistema nervioso
anillos nerviosos o “anillos de estrés” que aparecen como líneas circulares en el iris se interpretan como indicadores de tensión del sistema nervioso. Estos pueden estar asociados con ansiedad, alteraciones del sueño o desequilibrios del sistema nervioso autónomo que podrían beneficiarse de técnicas de reducción del estrés.
Desequilibrios hormonales
Los cambios en zonas específicas del iris correspondientes a las glándulas endocrinas pueden sugerir desequilibrios hormonales. Los médicos buscan variaciones de color, cambios estructurales o marcas en áreas asociadas con la tiroides, las glándulas suprarrenales o los órganos reproductivos para identificar posibles problemas hormonales.
Pros y contras de la iridología
Como cualquier método de evaluación de la salud, la iridología tiene beneficios y limitaciones potenciales. Comprenderlos puede ayudarle a decidir si este enfoque podría ser valioso para su viaje hacia la salud.
Beneficios potenciales de la iridología
- Evaluación no invasiva: Los exámenes de iridología no implican agujas, extracciones de sangre ni procedimientos incómodos.
- Perspectiva holística: Considera la interconexión de los sistemas corporales en lugar de aislar los síntomas.
- Enfoque preventivo: Puede identificar áreas de debilidad antes de que se desarrollen los síntomas, lo que permite tomar medidas de salud proactivas.
- Herramienta complementaria: Puede trabajar junto con la medicina convencional para proporcionar información adicional sobre los patrones de salud.
Limitaciones y preocupaciones
- Validación científica limitada: Pocos estudios revisados por pares respaldan la eficacia de la iridología para identificar con precisión las condiciones de salud.
- Interpretaciones inconsistentes: Diferentes sistemas de iridología pueden proporcionar análisis contradictorios del mismo iris.
- No es una herramienta de diagnóstico: No puede diagnosticar definitivamente condiciones médicas ni reemplazar las pruebas médicas adecuadas.
- Potencial de retraso en el tratamiento: Depender únicamente de la iridología podría retrasar la búsqueda de atención médica adecuada para afecciones graves.

Un enfoque integrador: el paciente habla sobre su salud tanto con un iridólogo como con un médico
Preguntas frecuentes sobre iridólogos
¿Está científicamente validada la iridología?
La comunidad científica generalmente no reconoce iridología como método de diagnóstico validado. Varios estudios controlados no han logrado demostrar que los iridólogos puedan identificar consistentemente condiciones de salud mediante el examen del iris. Un estudio notable publicado en el Journal of the American Medical Association encontró que los iridólogos no podían detectar de manera confiable la enfermedad renal al examinar fotografías de iris.
Sin embargo, sus defensores argumentan que estos estudios a menudo ponen a prueba las capacidades de diagnóstico en lugar del propósito previsto de la iridología de identificar debilidades y tendencias constitucionales. Algunas investigaciones preliminares sugieren posibles correlaciones entre ciertas características del iris y condiciones de salud específicas, pero se necesita una investigación científica más rigurosa.
¿En qué se diferencia la iridología de la optometría?
Los optometristas son profesionales de la salud autorizados que examinan, diagnostican y tratan afecciones oculares y problemas de visión. Completan una amplia formación médica y pueden recetar lentes correctivos y medicamentos. Su atención se centra específicamente en la salud ocular y la visión.
Los iridólogos, por el contrario, examinan el iris no para evaluar la salud ocular sino para evaluar el estado de otros sistemas del cuerpo. No diagnostican ni tratan afecciones oculares, no prescriben lentes correctivos ni realizan cirugías oculares. Mientras que los optometristas utilizan métodos científicamente validados para evaluar la visión y la salud ocular, los iridólogos utilizan enfoques alternativos que generalmente no son aceptados en la medicina convencional.
Es importante tener en cuenta que los problemas de salud ocular siempre deben ser abordados por profesionales cualificados del cuidado de la visión, como optometristas u oftalmólogos, no por iridólogos.
¿Cuánto cuesta generalmente una sesión de iridología?
El costo de una sesión de iridología varía ampliamente según la experiencia del profesional, la ubicación y la profundidad de la evaluación. Las consultas iniciales suelen oscilar entre 0 y 0, y las sesiones de seguimiento suelen costar menos. Algunos profesionales incluyen la iridología como parte de una evaluación de salud holística más amplia, lo que puede afectar los precios.
La mayoría de los planes de seguro médico no cubren las sesiones de iridología, ya que se consideran enfoques alternativos o complementarios a la atención médica convencional.
¿Puede la iridología detectar afecciones médicas graves?
Los iridólogos generalmente no pretenden diagnosticar enfermedades específicas, sino identificar áreas de posible debilidad o estrés en el cuerpo. Si bien algunos médicos sugieren que pueden ver signos de enfermedades graves como cáncer o enfermedades cardíacas en el iris, estas afirmaciones no están respaldadas por evidencia científica.
Para problemas de salud graves, es esencial buscar una evaluación médica adecuada por parte de proveedores de atención médica calificados que puedan realizar las pruebas de diagnóstico adecuadas. La iridología no debe utilizarse como sustituto del diagnóstico médico convencional, especialmente en afecciones potencialmente mortales.
Tomar decisiones informadas sobre la iridología
La iridología ofrece una perspectiva intrigante sobre la evaluación de la salud a través del examen de los patrones del iris. Si bien muchos encuentran valor en este enfoque holístico, es importante mantener una visión equilibrada de sus capacidades y limitaciones. La práctica continúa evolucionando y algunos profesionales integran tecnología e investigaciones modernas para mejorar sus evaluaciones.
Si está considerando consultar a un iridólogo, aborde la experiencia con una mente abierta y un saludable escepticismo. Busque profesionales con formación integral y certificaciones profesionales. Lo más importante es considerar la iridología como un complemento potencial, en lugar de un reemplazo, de la atención médica convencional.

Adoptar un enfoque equilibrado: investigar perspectivas de salud tanto convencionales como alternativas
Ya sea que se sienta atraído por la iridología por curiosidad o en busca de información adicional sobre su salud, recuerde que su bienestar se respalda mejor con un enfoque integral que considere múltiples perspectivas y prácticas basadas en evidencia.
¿Interesado en aprender más sobre la salud ocular?
Descubra recursos integrales para el cuidado de la vista y encuentre profesionales calificados que puedan ayudarlo a mantener una visión y una salud ocular óptimas.
Explore los recursos para la salud ocular