Categorías
- iridología (226)
- Lectura ocular (24)
- software QR (15)
- Blog (304)
- Ilustración de iridología (35)
- curso en línea de iridología (54)
- iridología (59)
- Exhibición (2)
- Noticias (424)
Iridology Chart How to Read-Understanding the human body can be tough, but the right tools help. The iridology chart is one such tool. It analyzes the iris to spot health issues.
Interpreting iridology charts means knowing the iris’s zones and body parts. Learning how to read these charts helps find hidden health problems. It also helps take steps towards better health.
Gráfico de iridología cómo leer-Iridology is an ancient practice that’s still valuable today. It helps in diagnosing and treating health issues. By learning to read these charts, both healthcare pros and individuals can find new ways to help their health.
Iridology is a holistic way to understand health, dating back centuries. It has roots in ancient civilizations. Over time, it has grown into a complex tool for health assessment.
Iridology studies the iris to reveal health information. It has ancient roots in Egypt, China, and Europe. In the 19th century, Ignatz von Peczely, a Hungarian doctor, developed the first iridology chart.
The philosophy of iridology sees the iris as a map of the body. Practitioners believe it shows health issues and imbalances. Though not a medical science, it’s used as a complementary therapy to enhance health understanding.
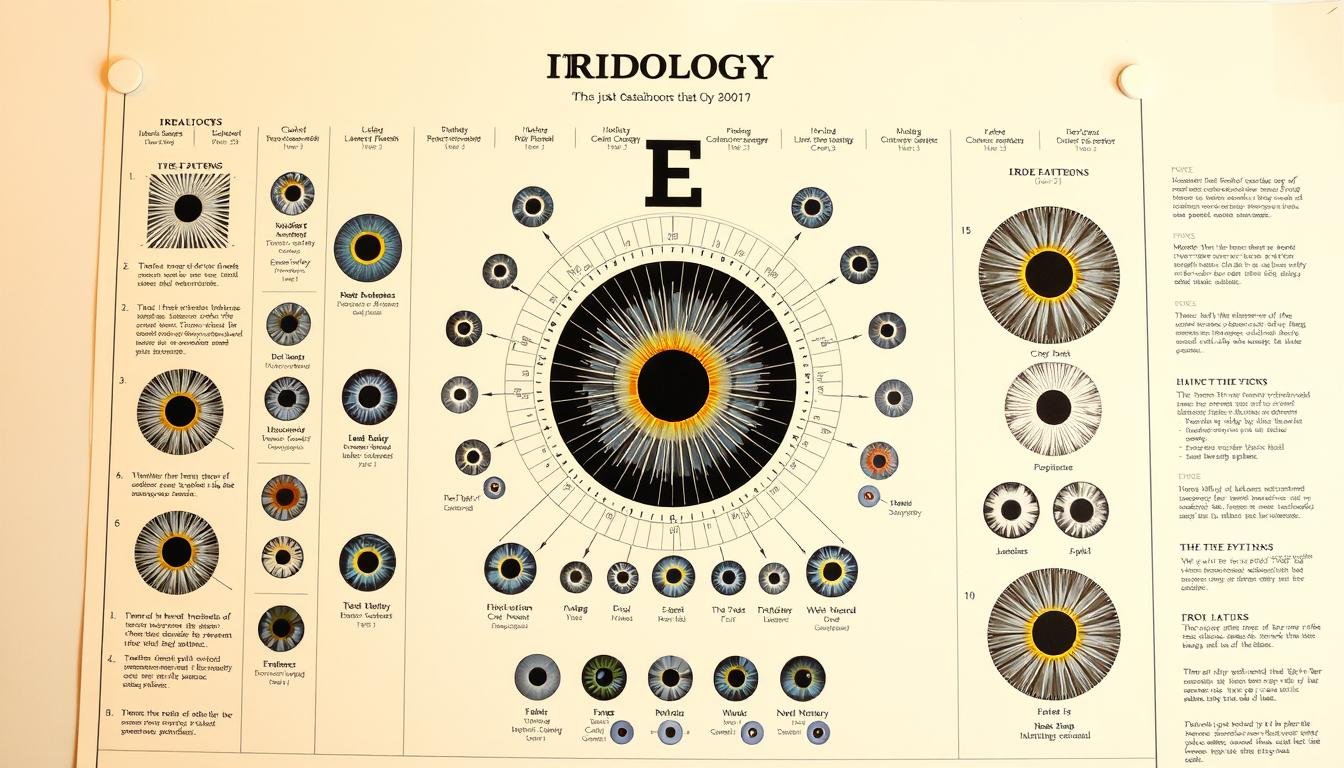
The iridology chart is a detailed map of the iris. It shows different parts of the body, helping to spot health issues. The chart is split into zones and sections, each for a specific organ or system.
An iridology chart has several key parts. The iris is divided into zones like the digestive and respiratory areas. Each zone has markings like spots and lines, showing health conditions.
The chart also has sections for different body parts. For example, the stomach and intestines are in the lower iris. The upper iris might show the brain and nervous system.
| Posición de reloj | Ojo izquierdo (refleja el lado izquierdo del cuerpo) | Ojo derecho (refleja el lado derecho del cuerpo) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 en punto - 2 en punto | Cuello izquierdo: Órganos reproductivos (útero/ovarios/testículos) | Cara derecha: Órganos reproductivos (útero/ovarios/testículos) |
| 2 en punto - 3 en punto | Pulmón izquierdo: salud respiratoria | Garganta Derecha: Salud de las articulaciones (rodillas, caderas, codos, hombros) |
| 3 en punto - 4 en punto | Tórax izquierdo: salud de la columna, flexibilidad, alineación | Parte superior derecha de la espalda: salud de la columna, flexibilidad, alineación |
| 4 en punto - 5 en punto | Abdomen superior izquierdo: vejiga, sistema urinario. | Vejiga derecha: refleja la vejiga y el sistema urinario del lado izquierdo. |
| 5 en punto - 6 en punto | Área Pélvica Izquierda: Colon, intestino delgado, salud digestiva | Área Pélvica Derecha: Colon, intestino delgado, salud digestiva |
| 6 en punto - 7 en punto | Abdomen inferior izquierdo: Riñón derecho (filtración, desintoxicación) | Abdomen inferior derecho: Riñón izquierdo (filtración, desintoxicación) |
| 7 en punto - 8 en punto | Abdomen superior izquierdo: estómago, órganos digestivos. | Abdomen superior derecho: estómago, órganos digestivos. |
| 8 en punto - 9 en punto | Tórax izquierdo: Hígado, desintoxicación, producción de bilis. | Tórax derecho: Hígado, desintoxicación, producción de bilis. |
| 9 en punto - 10 en punto | Pulmón izquierdo: salud cardiovascular, circulación | Pulmón Derecho: Salud cardiovascular, circulación |
| 10 en punto - 11 en punto | Cuello Izquierdo: Salud de las articulaciones (rodillas, caderas, codos) | Cuello Derecho: Salud de las articulaciones (rodillas, caderas, codos) |
| 11 en punto - 12 en punto | Cerebro izquierdo: función cognitiva, salud mental | Cerebro derecho: función cognitiva, salud mental |
| 12 en punto - 1 en punto | Cerebro izquierdo: función cognitiva, salud mental | Cerebro derecho: función cognitiva, salud mental |

There are many iridology charts, each with its own use. Some focus on specific health areas, while others give a full health view.
Practitioners choose charts based on their training and client needs. Some charts are detailed in certain areas, like the digestive system. Others give a broader health overview.
Knowing about different charts is key for good iridology map interpretation y reading iridology iris charts. Practitioners use this knowledge to offer insights into someone’s health and well-being.
Reading iris patterns is more than just looking. It needs the right tools. People who study iridology use special equipment to understand iris diagrams well.
Seeing the iris’s small details is key. Practitioners use magnifying glasses or digital microscopes to zoom in. Buena iluminación is also important. It helps see iris features clearly. Soft, natural light or special lamps are best.
Choosing between digital and physical charts depends on what you like and need. Digital charts are easy to store and analyze with software. Physical charts feel real and can be written on by hand. Some like both for their practice.
| Herramienta | Ventajas | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Lupa | Portable, Easy to Use | Limited Magnification |
| Digital Microscope | High Magnification, Image Capture | Expensive, Requires Technical Knowledge |
| Gráficos digitales | Easily Stored, Analyzed with Software | Requires Digital Literacy |
| Physical Charts | Tactile Experience, Hand Annotation | Space-Consuming, Prone to Damage |
Knowing what each tool does best helps practitioners choose well. This way, they can serve their clients best.
Knowing how the iris works is key to reading iridology charts right. The iris has many layers and zones. These parts give clues about a person’s health.
The iris has several layers, each with its own role in iridology. The stroma is the front layer, giving the iris its color. Underneath is the pigmented epithelium, also with pigment cells. The dilator and sphincter muscles control the pupil’s size.
The layers in the iris are important in iridology. They show health issues. For example, changes in color or markings can point to health problems.
The iris is split into zones and regions, each linked to a body part. Iridologists use these to spot health issues and check overall health. The zones are divided into outer, middle, and inner circles, showing different organ systems.
Seven Iridology rings organized into a table format:
| Ring Number | Nombre | Ubicación | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stomach Ring | Junction between the Iridology and the pupil | Represents the stomach; used to assess digestive health and potential issues within the stomach region. |
| 2 | Intestinal Ring | Occupies the outer one-third of the Iridology surrounding the stomach ring | Indicates intestinal health, including absorption and elimination functions. |
| 3 | Autonomic Nerve Ring | Closely adjacent to the intestinal ring | Acts as a boundary separating intestinal health from other organs, showing nervous system control over digestion. |
| 4-5 | Visceral Organ Reflex Rings | Located outside the autonomic nerve ring | Reflects the condition of internal organs, such as the liver, heart, and lungs. |
| 6 | Lymphatic Metabolic Ring | Between the visceral organ ring and the skin metabolic ring | Indicates lymphatic and metabolic processes, highlighting how toxins are processed and eliminated. |
| 7 | Skin Metabolic Ring | Outermost ring of the Iridology | Represents the body’s skin and metabolism, reflecting how well the skin eliminates waste and maintains health. |
Iridology experts say, “The iris is a mini map of the body. It shows the health of organs and systems through its zones and markings.”
“The eyes are the windows to the soul, and the iris is a map that reveals the state of our bodily health.”
By learning about the iris’s layers, zones, and regions, experts can use iridology charts to check health. They can spot potential health problems.
Reading an iridology chart needs a careful method to unlock its secrets. To get accurate iris readings, you must prepare well and pay close attention to details. First, learn the basics of iridology and the tools needed for chart interpretation.
Before starting with the iridology chart, prepare the setting and the person being checked. Make sure the room is well-lit and use magnification tools to see the iris clearly. Knowing the person’s health history and current condition is also key.
Identifying the iris type is a vital step in reading iridology charts. The iris can be classified by its color, texture, and other features. Knowing the iris type helps tailor the interpretation to the person’s unique traits.
After identifying the iris type, map the iris to body systems. This means linking different iris zones to specific organs and systems. This way, practitioners can understand the person’s health and any imbalances.
By following this guide, you can improve your skills in reading iridology charts. You’ll learn to uncover important health information.
Analyzing iris patterns is key in iridology. It gives insights into a person’s health. The colors and patterns in the iris show different health conditions and tendencies. This makes it a useful tool for health experts.
The iris color is a basic part of iridology. Different colors mean different health traits. For example, blue eyes suggest a sensitive nervous system. Brown eyes mean a strong constitution.
Basic Iris Colors and Their Meanings:
| Color del iris | Rasgos asociados |
|---|---|
| Azul | Sensitive nervous system, prone to stress |
| Marrón | Robust constitution, resistant to disease |
| Verde | Mix of blue and yellow traits, potentially indicating a detoxifying liver |
| Phase | Color Change in Iridology | Indication | Surface Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory Phase | Golden Yellow | Indicates the presence of inflammation within the body. | Raised surface |
| Sub-Inflammatory Phase | Tea Brown | Suggests that the inflammation is below the surface, showing a less intense stage of inflammation. | Below the surface |
| Chronic Phase | Marrón oscuro | Reflects a decline in function of the organ/system corresponding to that area. | Sunken surface |
| Degenerative Phase | Deep Black | Indicates significant loss of function in the corresponding organ/system, potential tissue degeneration, or tumor formation. | Deeply sunken surface |
Changes in iris color can show health issues. A “anillo de sodio” around the iris might mean high sodium or lymphatic problems. It’s important to understand these changes for deciphering eye chart markings correctly.
Color changes also show how the body reacts to treatments or health changes. Watching these changes over time helps see if treatments are working.
density Iridology fibers is another crucial factor in iridology. more dense Iridology, stronger and more resilient constitution, while more loose or less dense Iridology can point to person’s vulnerability or tendency to develop health problems.
| Density Level | Descripción | Body Manifestation |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Silk-like, tight and shiny | The fibers are tightly arranged, smooth surface, reflecting strong immunity and excellent overall health. |
| Level 2 | Cotton-like density, average shine | The fibers are moderately tight, indicating general health stability with a moderately strong immune system, but some mild imbalances may exist. |
| Level 3 | Coarse fabric-like, loose, lack of shine | Fibers are more loosely arranged, reflecting a less resilient immune system. It suggests possible mild chronic issues or predispositions to illness. |
| Level 4 | Linen-like, darker in color | Fibers appear disordered and darker, indicating a weaker immune response. Potential chronic conditions or long-term imbalances may be present. |
| Level 5 | Very loose, cloudy, fibers twisted, lack of shine | Fibers are disorganized and lack clarity, signifying a very poor immune system, low resilience, and possible genetic health defects. |
| Level 6 | Extremely relaxed, fibers are sparse, showing vulnerability to diseases, difficult to overcome | The fibers are loose and disordered, often showing gaps or cavitations. This reflects a severely compromised immune system, and genetic defects or chronic health conditions are evident. |
Iris signs and markings are key to understanding health through iridology. Practitioners use these signs to check overall health and spot potential issues.
The iris shows different signs and markings, each with its own meaning. These can be simple color changes or complex patterns and shapes.
Many common signs are seen in iridology readings. These include:
Different markings on the iris can point to various health issues. For example:
Iridology Learning Guide organized into a table format, using the key points from the original text:
| Topic | Detalles |
|---|---|
| Origin of Iridology | Developed in Europe approximately 200 years ago; the practice reportedly originated from observing an owl’s eye after an injury. |
| Holistic Body Reflection | Iridology reflects the whole body, with each part of the iris corresponding to various organs and systems. Nerve conduction works through frequencies that manifest visually in the iris. |
| Health Assessment Approach | Iridology allows for a full-body health evaluation through iris analysis, helping identify underlying health causes and providing a path to preventive care. |
| Iris Symmetry | Each side of the iris reflects the corresponding side of the body; the left iris relates to the left body side, and vice versa. |
| Iris Density Levels | Iris fiber density is divided into six levels. Tighter, silk-like fibers (Level 1) indicate strong immunity, while loose, irregular fibers (Levels 5-6) suggest hereditary or chronic weaknesses. |
| Iris Defects | Iridologists look for patterns like pits, cracks, and spots, which can indicate health issues in specific organs. |
| Iris Zones | The iris is divided into seven rings, each reflecting different areas of the body: stomach, intestines, autonomic nerves, visceral organs, lymphatic system, and skin metabolism. |
| Color Changes by Disease Stage | – Inflammatory stage: Golden-yellow in iris areas with raised surfaces. – Sub-inflammatory stage: Tea-brown beneath the surface. – Chronic stage: Dark brown and sunken areas. – Degenerative stage: Deep black with deep indentations, indicating tissue loss and potential tumors. |
| Organ Reflex Zones | The iris zones are divided based on proximity to the pupil and sclera. Key reflex areas include the stomach ring, intestinal ring, nerve ring, and lymphatic ring, all contributing to holistic health analysis. |
| Digestive System Clues | The stomach ring and intestinal zones often show early signs of health issues like poor digestion, excess stomach acid, or ulcer risk. Disruptions in these rings suggest toxin buildup or organ stress. |
| Skin and Immune System | The outermost iris ring corresponds to the skin and detoxification processes. Signs such as blackened or thickened skin zones may indicate psoriasis, poor detoxification, or chronic inflammation. |
| Color and Phase Interpretation | Light-colored changes suggest acute or mild issues, while darker shades signal chronic or severe conditions. White represents the acute phase, light gray the sub-acute phase, dark gray the chronic phase, and black the degenerative phase. |
| Learning Recommendations | Mastery of iridology requires diligent study, observation of hundreds of cases, and continuous hands-on practice to interpret iris patterns effectively. |
Understanding these signs and markings is key for accurate Análisis de la tabla de iridología. By
decoding these indicators, practitioners can offer valuable insights into an individual’s health. They can also suggest the right steps to take.
Decoding iridology diagrams needs a deep understanding of the signs and their meanings. This knowledge helps practitioners guide people on keeping their health in check. They can also help address issues before they get worse.
Understanding iris zones is key for accurate iridology chart interpretation. The iris has distinct zones that match different body systems. This map helps practitioners check health conditions.
The iris is split into three main zones: inner, middle, and outer. The inner zone, or autonomic wreath, is around the pupil. It shows the state of the stomach and intestines.
El middle zone is linked to the heart and lungs. The outer zone is about the skin and nerves.
Practitioners link iris zones to body systems to spot health issues. For example, the inner zone might show digestive problems. The outer zone could point to skin or nerve issues.
Knowing these connections helps practitioners understand a person’s health. They can then suggest ways to prevent or treat problems.
In iridology, the right and left iris can give us clues about a person’s health. Each iris is seen as a unique window into the body’s health and potential issues.
The right and left irises show different health aspects. The right iris is linked to the left side of the body. The left iris is connected to the right side. This means each iris can show info about the opposite side of the body.
Key differences:
Gender also affects iridology readings. Some think men and women’s irises are different or interpreted differently. This is because of physiological and hormonal differences.
| Gender | Iris Characteristics | Interpretación |
|---|---|---|
| Male | Typically more dense | May indicate a stronger constitution |
| Female | Often more delicate | May suggest a more sensitive nervous system |
Understanding these differences helps practitioners give more accurate and personalized insights. This makes iridology readings more precise.
Understanding constitutional types is key in iridology. It helps practitioners spot a person’s health predispositions. A constitutional type shows an individual’s inherent traits that can affect their health.
Practitioners look at the iris’s color, texture, and markings to figure out a person’s type. Knowing a person’s type reveals their natural strengths and weaknesses. It also shows potential health risks.
Figuring out a person’s constitutional type involves a close look at their iris. Practitioners search for specific traits likeiris color,texture, ymarkings. For example, certain iris colors might link to specific types.
There are many ways to find a person’s type. Practitioners might mix different methods. Some common ones include:
Knowing a person’s constitutional type greatly influences health readings. It lets practitioners give more precise and personal health checks.
For instance, some types might face certain health problems more often. By spotting these tendencies, practitioners can suggest ways to prevent or lessen these risks.
Also, understanding types helps tailor health advice to fit each person’s needs. This makes health advice more effective.
Los expertos dicen que “Knowing a person’s constitutional type is a strong tool in preventive care.” This method makes health readings more accurate. It also helps people take better care of their health.
Learning to read iridology charts takes time and effort. It’s a journey that requires patience and persistence. To unlock iridology’s secrets, you need to practice and analyze carefully. Understanding the right techniques and tools is key to improving your skills.
To master the iridology eye chart guide, start by practicing often. Here are some tips to help you begin:
Keeping an iridology journal is vital for tracking your progress. It helps you refine your skills. By recording your observations and insights, you can:
By practicing regularly and keeping detailed records, you’ll improve quickly in iridology chart reading.
To improve iridology, practitioners need to learn advanced techniques. They must understand various indicators that reveal a person’s health.
Pupil tonus shows how well the pupil reacts to light and other things. A skilled iridologist can use this to see how the nervous system works and overall health. For example, if the pupil doesn’t react fast, it might mean there’s a problem with the autonomic nervous system.
The sclera, or the white part of the eye, also holds health clues. Certain marks or colors on the sclera can show specific health problems, like inflammation or toxins. Practitioners should know how to spot and understand these signs.
One top technique in iridology is using many indicators together. This means looking at iris patterns, pupil tonus, and sclera signs to understand health better. By doing this, practitioners can spot health issues early and help their patients better.
For instance, when looking at iris patterns, a practitioner might see a mark that suggests a health condition. By also checking pupil tonus and sclera signs, they can confirm this and give a more precise diagnosis.
Reading iridology charts can be tough for many. The iris is full of signs and markings, making it hard to understand. Even experts find it challenging.
One big challenge is figuring out what the charts mean. To get better, practitioners can try a few things:
Dr. Bernard Jensen, a famous iridologist, said, “The eyes are the windows to the body, and the iris is the map that reveals the underlying health conditions.”
“The eyes are the windows to the body, and the iris is the map that reveals the underlying health conditions.”
Misreading charts is a big worry in iridology. To avoid mistakes, practitioners should:
| Strategy | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Consider multiple factors | Look at all the signs and markings, not just one. |
| Stay up-to-date with the latest research | Keep learning about new findings in iridology. |
| Use a holistic approach | Think about the person’s whole health and life when reading the chart. |
Knowing these challenges and how to tackle them can help practitioners. They can then give better care to their clients.
Iridology readings have many uses and are becoming more popular in health care. They help in understanding an individual’s health better. This is especially true in complementary and alternative medicine.
Iridology charts are useful for health professionals. They help in spotting health problems early. This way, treatments can start sooner, leading to better health outcomes.
It’s about understanding iridology charts and seeing patterns. For example, certain iris marks can show digestive or stress issues.
| Health Aspect | Indicador de iris | Potential Health Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Salud Digestiva | Markings in the digestive zone | Digestive issues, such as IBS |
| Niveles de estrés | Radial or circular furrows | High stress, anxiety |
| Función hepática | Color changes or spots | Liver dysfunction, toxicity |
Iridology works well with other health practices. It gives a deeper look into a patient’s health. This is when iridology map interpretation is used with other tests.
For instance, using iridology with nutrition or herbal medicine. It helps make treatment plans that fit the person’s health needs.
Case studies in iridology chart readings show how this ancient practice is used today. They help us understand how iridology is used to check health conditions.
An individual’s iridology chart showed signs of digestive problems. Mark and patterns in the iris pointed to inflammation and toxicity in the digestive tract. These signs matched the person’s symptoms and medical history.
The practitioner suggested dietary changes and supplements to help with digestion. This shows how iridology can guide holistic health plans.
Another case study looked at stress signs in the iris. The chart showed patterns and colors linked to stress and anxiety. By analyzing iris patterns, the practitioner found signs of adrenal fatigue and suggested stress management.
This example shows iridology’s role in spotting stress effects. It helps in finding ways to improve overall health.
Practitioners of iridology must be aware of the ethical considerations and limitations. Iridology is not a substitute for medical diagnosis or treatment. It’s crucial to understand the boundaries of iridology to provide responsible care.
Iridology should be used with other health tools for a full health picture. Practitioners must see iridology as a supporting tool, not a replacement for medical checks.
Knowing when to refer clients to doctors is key. If an iridology reading shows a health issue beyond the practitioner’s scope, the client should be advised to seek medical attention. Dr. Bernard Jensen said, “Iridology is not a diagnostic method, but rather a tool for assessing the body’s overall health and detecting potential imbalances.”
“The eyes are the windows to the soul, and the iris is a map of the body’s health.”
By knowing iridology’s limits and ethics, practitioners can offer valuable health insights. They ensure clients get the right medical care when needed.
Learning to read an iridology chart is a valuable skill. It helps understand a person’s health and well-being. By studying the iris’s patterns and colors, one can learn about their body’s health.
In this article, we covered the basics of iridology. We talked about the iris’s anatomy, different charts, and how to read them. These insights help people understand their health better and take steps to improve it.
Mastering iridology takes practice and dedication. With more learning and practice, one can better understand the iris and the body’s systems. It’s not just about reading charts; it’s about unlocking the body’s secrets for wellness.
 Gráfico de iridología cómo leer
Gráfico de iridología cómo leer
Iridology is a way to check your health by looking at your iris. It looks for signs in the iris that might show health problems. This method uses colors and patterns in the iris to find out about your body’s systems.
To read an iridology chart, first find the different parts of the iris. Then, look for signs and colors. These signs tell about your health, helping to find any issues.
There are many iridology charts, like the Bernard Jensen and Iris Diagnostik charts. Each has its own special features. Practitioners might use one or more charts, based on what they need and the person’s health.
Iris colors and changes can show health issues. For example, blue irises might mean a sensitive nervous system. Dark spots could mean toxins. It’s important to look at the whole health picture when seeing iris colors.
The iris has zones that match different body parts. By looking at these zones, practitioners can find health problems. This helps them see how well different body systems are working.
The right and left irises are different. The right iris is about the body, and the left is about emotions and mind. Practitioners need to understand these differences when reading the irises.
Constitutional types are about a person’s natural traits, shown in their iris. Knowing a person’s type helps practitioners understand their health tendencies. This information helps in creating health plans that fit the person.
To get better at reading iridology charts, practice often. Keep a journal of your progress. Learning about iris features and their meanings is also key.
Challenges include hard interpretations and mistakes. To deal with these, know your limits, stay updated with research, and keep practicing. This will help improve your skills.
Iridology can work with nutrition, herbalism, and acupuncture. This gives a full view of someone’s health. Using iridology with other methods helps create better health plans and improves overall health.
SOFTWARE DE IRIDOLOGÍA MAIKONG Instalación y funcionamiento
