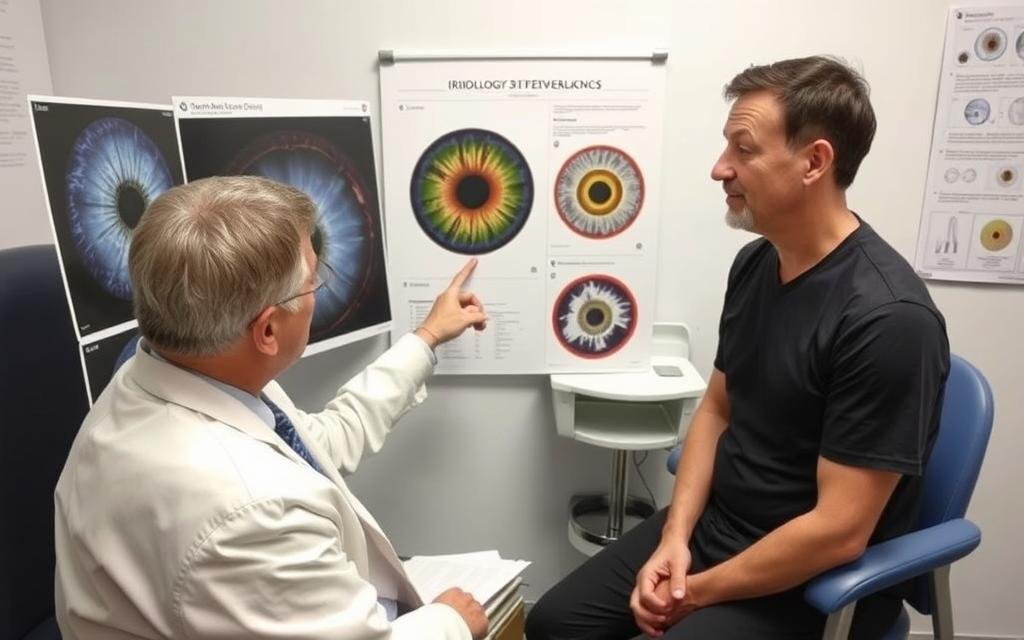
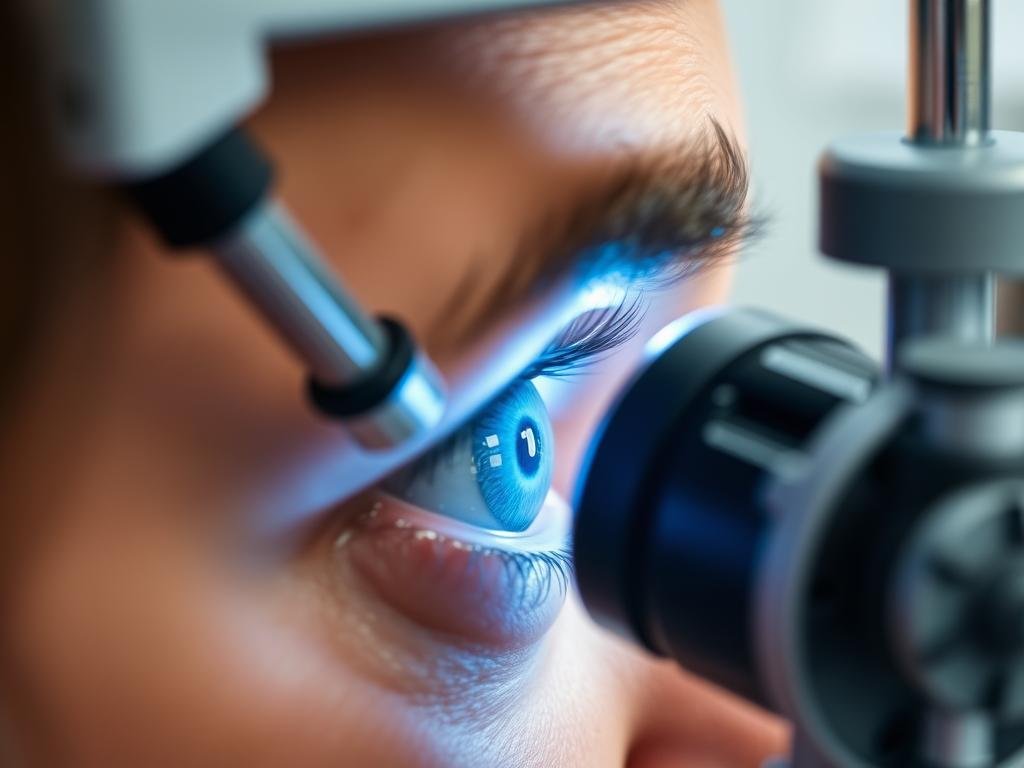
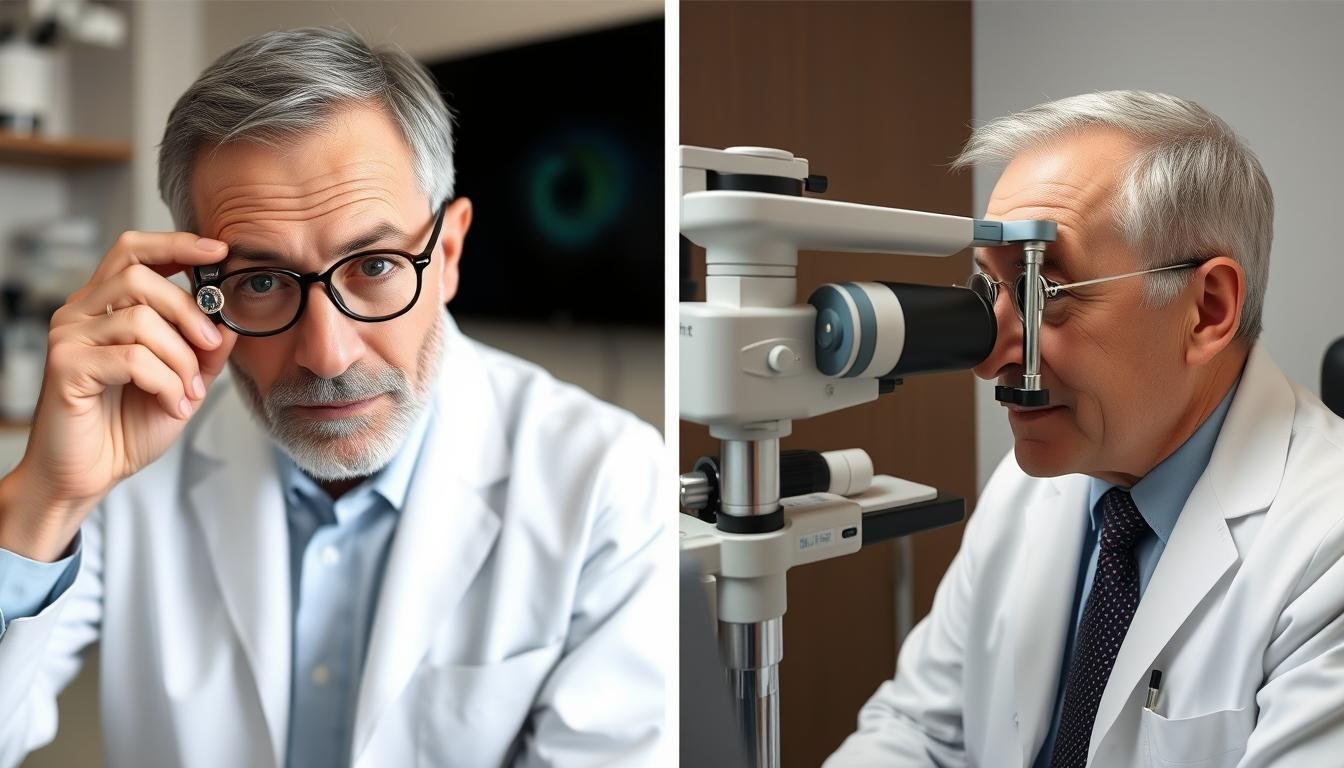
An iridologist is a practitioner who studies the patterns, colors, and other characteristics of the iris—the colored part of the eye—to evaluate a person’s health status. This alternative health practice is based on the theory that each area of the iris corresponds to different organs and systems within the body, potentially revealing information about one’s physical condition. While controversial in conventional medicine, iridology has gained followers worldwide as a complementary approach to health assessment.
Definition and Core Responsibilities of an Iridologist
هڪ ارڊولوجسٽ is a practitioner who specializes in analyzing the iris to identify potential health issues before physical symptoms appear. Unlike ophthalmologists or optometrists who diagnose eye diseases, iridologists focus on using the eye as a diagnostic tool for the entire body.
The core responsibilities of an iridologist typically include:
- Examining the iris using specialized equipment like iridology cameras
- Identifying patterns, colors, and markings in the iris
- Correlating these observations with specific body systems using iridology charts
- Suggesting lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, or supplements
- Monitoring changes in the iris over time to track health progress
Iridologists often work in holistic health centers, alternative medicine clinics, or maintain private practices. Many practitioners combine iridology with other complementary health approaches such as naturopathy, herbalism, or nutritional counseling.
The Historical Development of Iridology
The practice of iridology has roots that stretch back centuries, though modern iridology emerged in the 19th century. Understanding its historical development provides context for how this alternative practice evolved.
Early Origins
Some historical accounts suggest that forms of iris analysis existed in ancient Egypt, China, and India over 3,000 years ago. However, documented evidence of systematic iris examination for health assessment begins much later.
Modern Foundations
Dr. Ignaz von Peczely, a Hungarian physician, is widely credited as the founder of modern iridology in the 1860s. According to popular accounts, as a child, von Peczely noticed changes in an owl’s iris after the bird suffered a broken leg. This observation sparked his interest in the connection between iris markings and physical trauma or disease.
In 1881, von Peczely published his first iris chart, mapping regions of the iris to different parts of the body. Around the same time, Swedish homeopath Nils Liljequist independently developed similar theories after observing changes in his own iris following medical treatments.
Bernard Jensen, an American chiropractor, significantly popularized iridology in the United States during the 1950s. Jensen refined existing iris charts and developed teaching methods that continue to influence iridology practice today.
Techniques and Tools Used by Iridologists
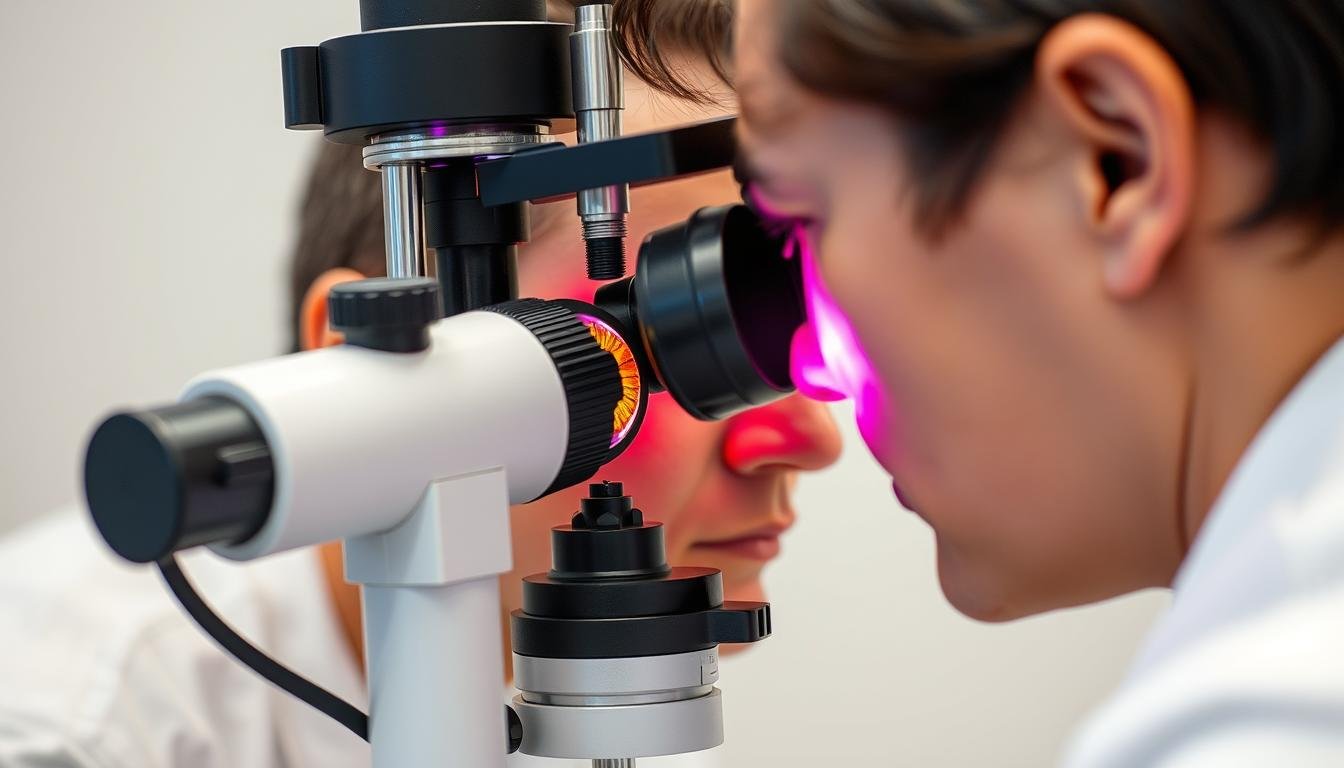
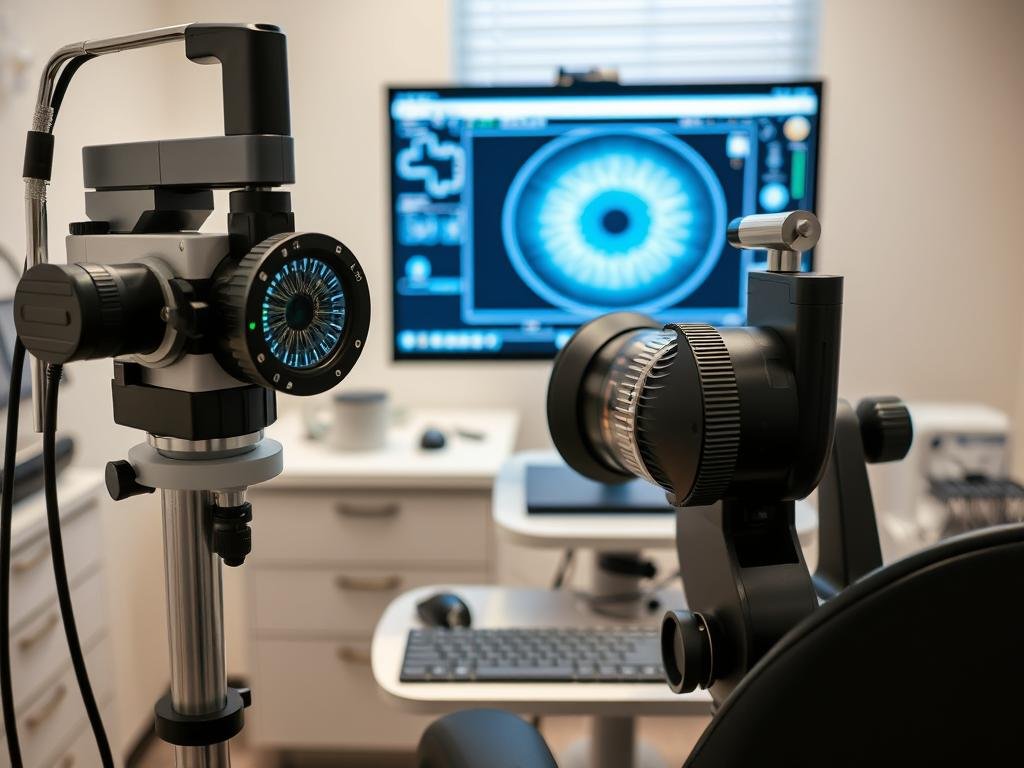
Iridologists employ various specialized tools and methodologies to examine and interpret iris patterns. These techniques have evolved from simple magnifying glasses to sophisticated digital imaging systems.

Examination Equipment
- Penlight and Magnifier: Basic tools used for simple examinations
- Iridology Camera: Specialized high-resolution camera that captures detailed images of the iris
- Slit Lamp: Provides magnified, illuminated view of the eye structures
- Digital Imaging Software: Programs that enhance and analyze iris photographs
During a typical examination, the iridologist will position the client in good lighting, then use specialized equipment to observe or photograph the iris. The practitioner looks for specific features including:
- رنگ جي تغيرات ۽ رنگن جون تبديليون
- Structural patterns and fiber arrangements
- Dark or light spots and markings
- Rings, clouds, or other formations
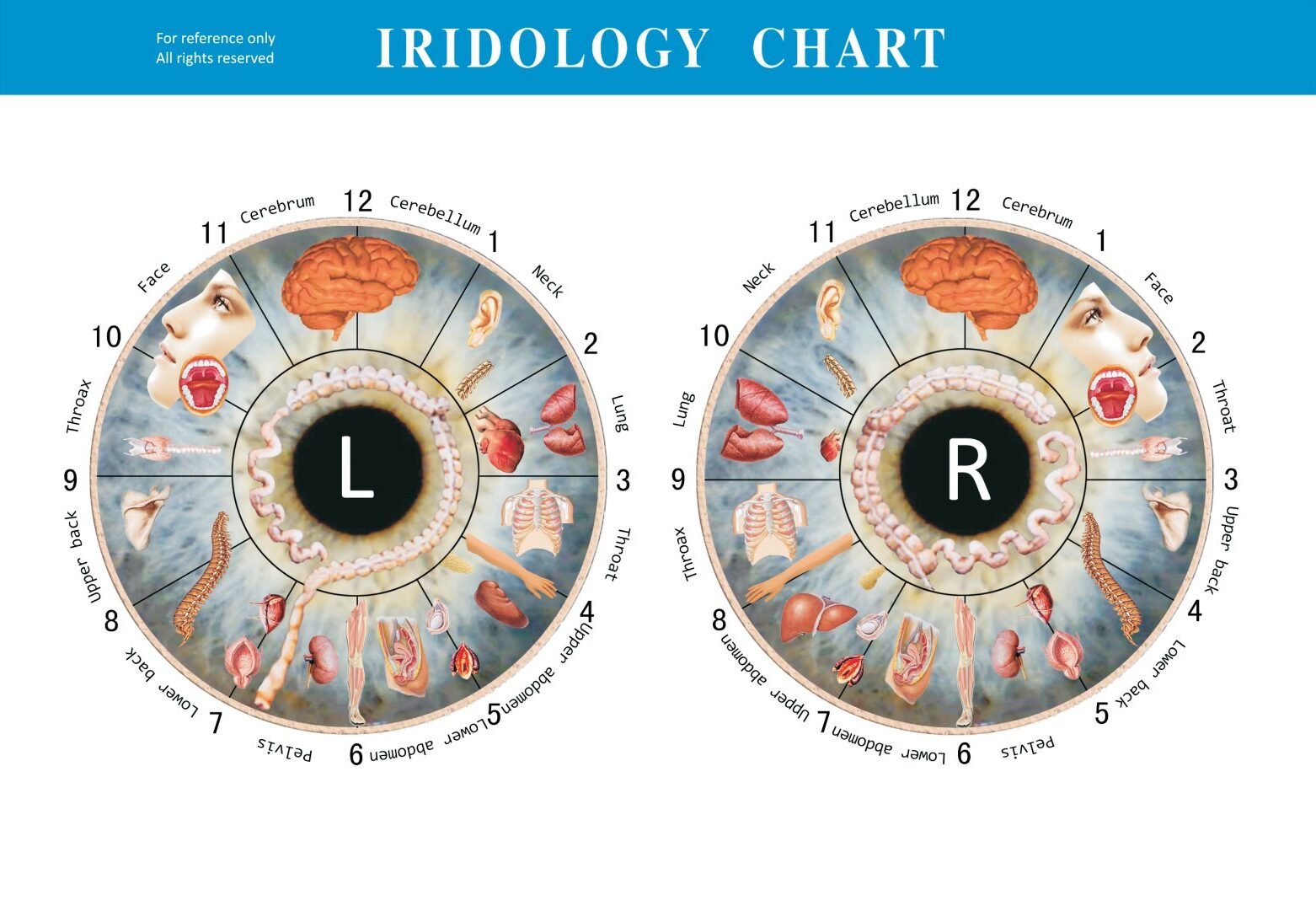
Iridology چارٽس
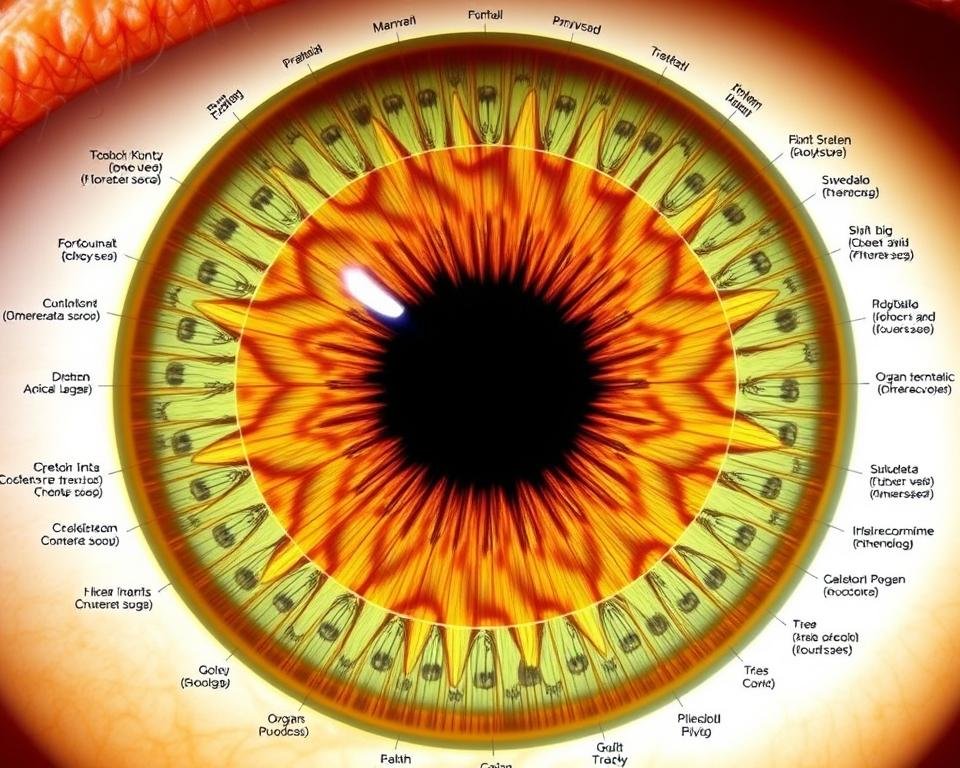
Central to iridology practice is the use of ارڊولوجي چارٽس—detailed maps that divide the iris into approximately 80-90 zones, each corresponding to different organs and body systems. These charts serve as reference guides for practitioners to interpret their observations.
Want to Learn More About Eye Health?
Discover how comprehensive eye exams can provide valuable insights about your overall health and vision.
سکو جامع اکين جي امتحانن بابت
The Theoretical Basis of Iris Analysis
Iridology is founded on several key theoretical principles that explain how the iris might reflect health conditions throughout the body. Understanding these concepts helps clarify the practice’s underlying framework.


Core Principles of Iridology
The practice of iridology is based on several fundamental beliefs:
- Reflex Relationship: The iris is connected to every organ and tissue via the nervous system and energy pathways
- Topographic Correspondence: Specific areas of the iris correspond to specific parts of the body
- Genetic Inheritance: Iris patterns can reveal inherited genetic predispositions to certain conditions
- Health Timeline: The iris can show past, present, and potential future health issues
According to iridology theory, the iris contains thousands of nerve endings connected to the brain via the optic nerve. These connections supposedly create a “map” of the body in the iris, with changes in iris appearance reflecting changes in tissue state throughout the body.
Iridologists believe that the body’s condition is constantly reflected in the iris through:
- Changes in color and structure
- Appearance of spots, clouds, or lesions
- Alterations in fiber patterns
- Development of rings or other formations
Health Conditions and Concerns Addressed by Iridologists
Iridologists claim to identify a wide range of health conditions through iris analysis. While conventional medicine questions these capabilities, practitioners believe they can detect various issues before symptoms manifest.

Common Health Indicators in Iridology
What Iridologists Claim to Identify
- Inflammation and congestion in specific organs
- Digestive system weaknesses and imbalances
- Lymphatic system congestion
- Nervous system stress and tension
- Circulation problems and blood quality issues
- Toxin accumulation in tissues
- Hormonal imbalances
- غذائيت جي گھٽتائي
- Genetic predispositions to certain conditions
Scientific Perspective on These Claims
- Limited scientific evidence supporting these diagnostic capabilities
- Controlled studies have not validated iridology’s diagnostic accuracy
- Conventional medicine relies on specific tests for these conditions
- Iris patterns are largely determined by genetics and remain stable
- Potential for missed diagnoses if relying solely on iridology
- Risk of unnecessary treatments based on misinterpretations
- Delay in seeking conventional medical care for serious conditions
It’s important to note that iridologists typically do not claim to diagnose specific diseases. Instead, they identify areas of weakness or stress in the body that might indicate underlying issues or predispositions to certain conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Iridology Practitioners
What qualifications do iridologists have?
Iridology is not regulated in most countries, so qualifications vary widely. Some practitioners complete certification programs through holistic health schools or iridology associations, while others may be naturopaths, chiropractors, or other alternative health practitioners who have added iridology to their practice. Training programs typically range from weekend workshops to year-long courses.
How much does an iridology session cost?
The cost of an iridology session varies widely depending on location, practitioner experience, and whether it’s combined with other services. Typical sessions range from to 0, with initial consultations often being longer and more expensive than follow-up visits.
Is iridology covered by insurance?
Most conventional health insurance plans do not cover iridology sessions as they are considered alternative or complementary therapies. Some flexible spending accounts (FSAs) or health savings accounts (HSAs) may allow for these expenses, but it’s best to check with your specific provider.
Can iridology diagnose serious medical conditions?
Iridologists generally avoid claiming to diagnose specific diseases, instead focusing on identifying areas of weakness or stress in the body. Scientific research has not supported iridology as an accurate diagnostic tool for serious medical conditions. For any concerning symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a licensed medical doctor.

How long does an iridology session take?
An initial iridology consultation typically lasts between 60 to 90 minutes. This includes the examination of both irises, analysis of findings, explanation of results, and recommendations. Follow-up sessions are usually shorter, ranging from 30 to 45 minutes.
Do I need to prepare for an iridology session?
Most iridologists recommend avoiding wearing contact lenses on the day of your appointment, as they can temporarily affect the appearance of the iris. Some practitioners may ask you to avoid caffeine or alcohol before your session, as these can cause pupil dilation or constriction.
Considering Alternative Health Approaches?
While exploring iridology, it’s important to maintain regular check-ups with qualified healthcare professionals.
Consult with an Eye Care Professional
Iridology Compared to Conventional Eye Care Fields
Understanding how iridology differs from conventional eye care disciplines helps clarify its place in the broader healthcare landscape. Here’s how iridologists compare to optometrists and ophthalmologists:
| پاسو | ارڊولوجسٽ | Optometrist | Ophthalmologist |
| پرائمري فوڪس | Analyzing iris patterns to assess overall health | Vision testing, prescribing corrective lenses, detecting eye conditions | Medical and surgical eye care, treating eye diseases |
| Education Required | Varies widely; certification programs from weeks to months | Doctor of Optometry (O.D.) degree (4 years post-bachelor’s) | Medical Doctor (M.D.) plus specialized residency (8+ years total) |
| Regulatory Oversight | Minimal to none in most countries | Licensed and regulated by state/national boards | Licensed medical doctors with specialty certification |
| Diagnostic Approach | Observes iris patterns to identify potential health issues throughout the body | Uses standardized tests and equipment to assess vision and eye health | Performs comprehensive medical eye exams and specialized diagnostic tests |
| Treatment Capabilities | Typically recommends lifestyle changes, herbs, supplements | Prescribes corrective lenses, manages certain eye conditions | Prescribes medications, performs surgery, treats all eye diseases |
| Scientific Validation | Limited scientific evidence supporting diagnostic claims | Evidence-based practices with established clinical standards | Evidence-based medical and surgical interventions |

While iridologists focus on the iris as a window to overall health, conventional eye care professionals concentrate on the health and function of the eye itself. These approaches reflect fundamentally different perspectives on the role of eye examination in healthcare.
Scientific Perspectives and Controversies
The practice of iridology has generated significant debate within the medical and scientific communities. Understanding both sides of this discussion provides important context for anyone considering iridology.

Research and Evidence
Several scientific studies have examined iridology’s diagnostic claims:
A systematic review published in 1999 in the journal Forsch Komplementärmed examined four case-control studies and concluded that iridology’s efficacy was not supported by scientific evaluations.
A 2000 study published in the Archives of Ophthalmology stated: “Iridology has shown to be of little benefit to anyone. Patients and therapists should be discouraged from utilizing iridology since it has the potential to cause personal and financial harm.”
The scientific community generally points to several key issues with iridology:
- Lack of consistent diagnostic criteria among practitioners
- Failure to demonstrate reproducible results in controlled studies
- Absence of a plausible physiological mechanism to explain how internal organ states would affect iris appearance
- The fact that iris structure is largely determined by genetics and remains stable throughout life
Practitioner Perspective
Proponents of iridology counter these criticisms by arguing:
- Conventional studies may not properly account for the holistic nature of iridology
- Subtle changes in the iris may be missed by researchers not properly trained in iridology
- Iridology is best used as one component of a comprehensive health assessment, not as a standalone diagnostic tool
- Anecdotal evidence from practitioners and clients supports its effectiveness
The controversy highlights the broader tension between evidence-based medicine and alternative health approaches that rely on different epistemological frameworks.
Making Informed Decisions About Iridology
When considering iridology as a health assessment tool, it’s important to approach it with a balanced perspective that acknowledges both its possibilities and limitations.

If You’re Considering Iridology
- Research practitioners thoroughly, looking for proper training and certification
- Maintain realistic expectations about what iridology can and cannot reveal
- Use iridology as a complement to, not a replacement for, conventional medical care
- Discuss any iridology findings with your primary healthcare provider
- Be wary of practitioners making definitive disease diagnoses or promising cures
A Balanced Approach
The most responsible way to engage with iridology is as part of an integrative approach to health. While iridology may offer interesting insights into potential areas of concern, important health decisions should be made in consultation with licensed healthcare professionals.
Remember that even if the scientific evidence for iridology is limited, many people find value in holistic approaches that consider the interconnectedness of body systems and emphasize preventive health measures.
Take Charge of Your Eye Health
Whether you’re curious about iridology or seeking conventional eye care, regular eye examinations are essential for maintaining vision and detecting potential health issues.
Find a Qualified Optometrist Near You
Ultimately, the decision to explore iridology is a personal one. By approaching it with an informed, critical perspective and maintaining open communication with your healthcare team, you can make choices that best support your overall health and wellness goals.