Iridology-Respiratory System-A Comparative Analysis of Symptoms in Nose Zone, Nasal Cavity, and Paranasal Sinus Cases

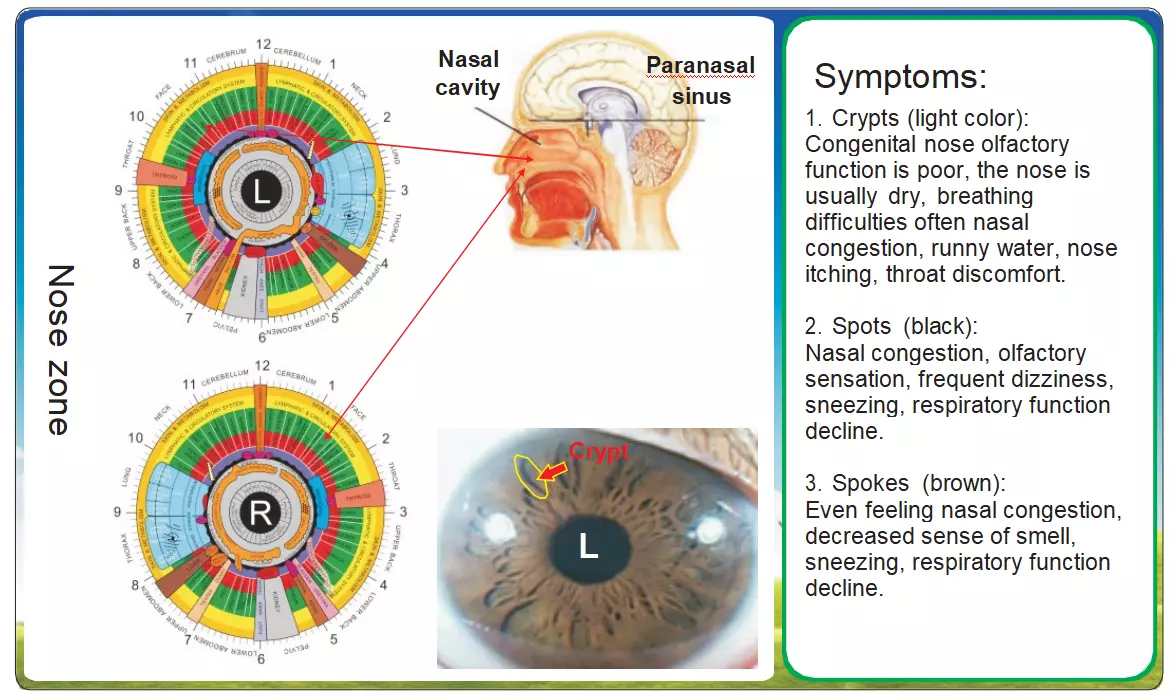
Nose Zone
Iridologie–The nose zone encompasses external nasal structures and their associated functions. Pathological changes here often manifest through visible signs and sensory disruptions.
Crypts (Light Color):
- Symptoms: Congenital olfactory dysfunction is prevalent, characterized by persistently dry nasal passages. Patients frequently experience difficulty breathing, chronic nasal congestion, watery rhinorrhea, pruritus (itching) in the nasal vestibule, and throat irritation.
- Pathophysiology: Hypoplasia of olfactory epithelium or reduced mucus secretion may underlie these symptoms. The dryness exacerbates mucosal irritation, leading to compensatory throat discomfort.
Spots (Black):
- Symptoms: Persistent nasal obstruction, diminished olfactory acuity, recurrent dizziness, paroxysmal sneezing, and declining respiratory efficiency.
- Pathophysiology: Melanin deposits or chronic inflammation (e.g., allergic rhinitis) may cause pigmentation. The obstruction disrupts airflow, reducing odorant molecule absorption and triggering reflexive sneezing.
Spokes (Brown):
- Symptoms: Intermittent nasal congestion, progressive anosmia/hyposmia, sneezing fits, and compromised respiratory function.
- Pathophysiology: Brown discoloration suggests hemosiderin deposits or chronic sinusitis. The intermittent nature points to cyclical mucosal edema, impairing both olfaction and ciliary clearance.
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity, lined with respiratory and olfactory mucosa, is prone to structural and functional anomalies.
Crypts (Light Color):
- Symptoms: Congenital defects often correlate with underdeveloped turbinates or septal deviations, exacerbating dryness and congestion.
- Extension: Secondary infections (e.g., bacterial rhinitis) may arise due to stagnant mucus.
Spots (Black):
- Symptoms: Blackened areas indicate fungal colonization (e.g., Aspergillus) or pollution-induced metaplasia, worsening obstruction and hyposmia.
- Extension: Chronic hypoxia from obstruction may contribute to dizziness.
Spokes (Brown):
- Symptoms: Brown streaks suggest mucosal atrophy or granulomatous inflammation, further reducing mucociliary activity.
Paranasal Sinus
The paranasal sinuses, air-filled cavities, are critical for resonance and mucus drainage.
Crypts (Light Color):
- Symptoms: Hypoplastic sinuses (e.g., maxillary sinus) may predispose to recurrent infections, presenting with pressure pain and postnasal drip.
Spots (Black):
- Symptoms: Fungal ball (Mycetoma) or neoplasms can cause localized black spots, accompanied by frontal headaches and purulent discharge.
Spokes (Brown):
- Symptoms: Chronic sinusitis with polyp formation often exhibits brownish mucosal thickening, leading to persistent congestion and anosmia.
| Région | Fonctionnalité | Symptômes | Pathological Insight |
|---|
| Nose Zone | Crypts (Light) | Congenital poor olfaction, dryness, congestion, watery rhinorrhea, itching | Hypoplastic olfactory epithelium, reduced mucus secretion |
| Spots (noir) | Nasal obstruction, hyposmia, dizziness, sneezing | Melanin deposits, chronic inflammation (e.g., allergies) |
| Rayons (marron) | Intermittent congestion, anosmia, sneezing | Hemosiderin deposits, cyclical edema |
| Nasal Cavity | Crypts (Light) | Dryness, recurrent infections | Turbinate hypoplasia, septal deviation |
| Spots (noir) | Fungal colonization, obstruction | Aspergillus infection, pollution-induced metaplasia |
| Rayons (marron) | Mucosal atrophy, reduced ciliary function | Granulomatous inflammation |
| Paranasal Sinus | Crypts (Light) | Pressure pain, postnasal drip | Hypoplastic sinuses (e.g., maxillary) |
| Spots (noir) | Fungal ball, headaches, purulent discharge | Mycetoma, neoplastic growth |
| Rayons (marron) | Chronic congestion, polyps | Mucosal thickening, polyp formation |