Le human iris, with its unique and intricate patterns, has emerged as a powerful tool in modern medicine. Beyond its biological function of controlling light entry into the eye, the iris serves as a distinctive biometric identifier and a window into our health. Medical iris technology is transforming healthcare through enhanced patient identification, disease diagnosis, and secure access to medical information. This article explores how this remarkable technology is changing the medical landscape and what the future holds for iris-based applications in healthcare.Understanding the Medical Iris Concept
The term “Medical Iris” encompasses various applications of iris recognition and analysis in healthcare settings. The iris—the colored part of the eye—contains a complex pattern of features that remain stable throughout a person’s life and are unique to each individual. This uniqueness makes the iris an ideal biometric identifier, more reliable than fingerprints and significantly more accurate than facial recognition.
Medical iris technology utilizes high-resolution imaging and advanced algorithms to capture and analyze these patterns. The technology has two primary applications in healthcare:
- Biometric identification for secure patient recognition and medical record access
- Diagnostic tool for detecting and monitoring various health conditions through iris pattern analysis
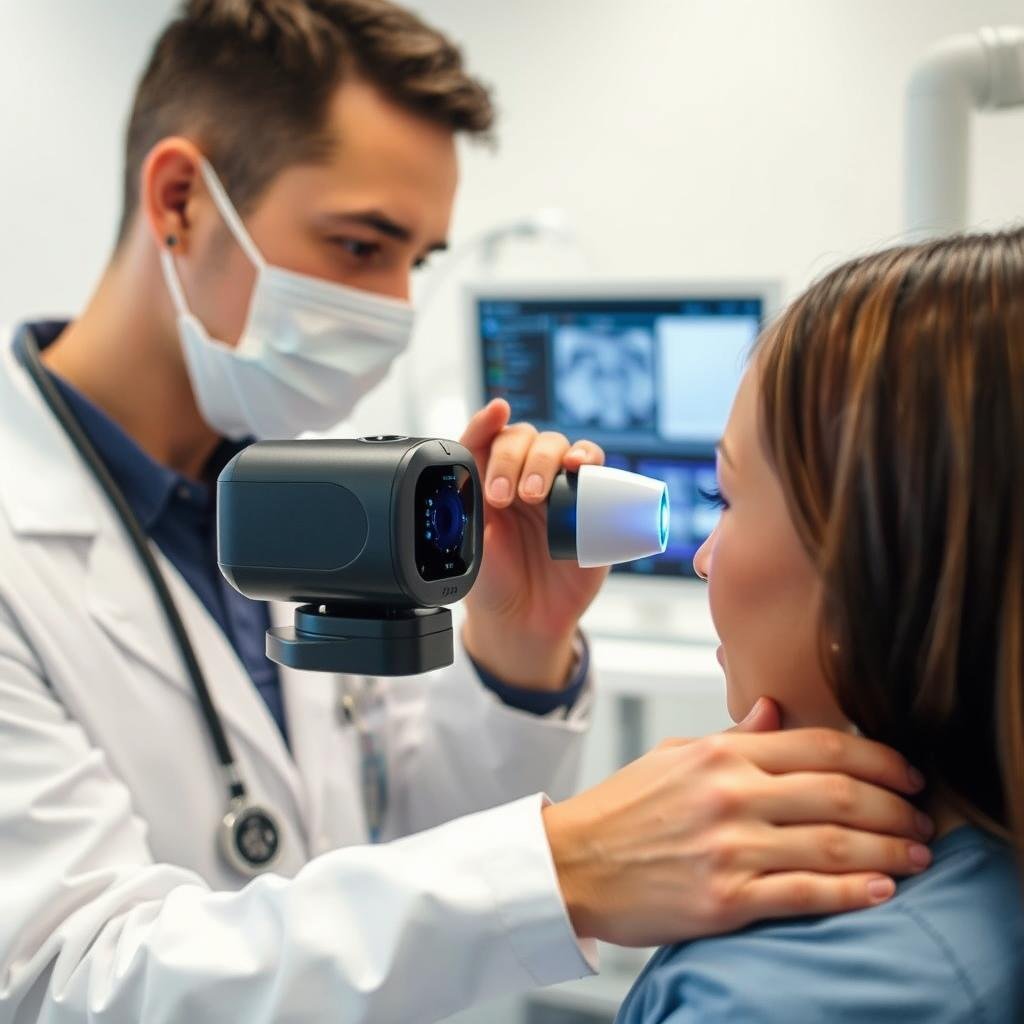
Unlike other biometric systems, iris scanning is non-invasive, requiring only a specialized camera to capture the image. The process takes seconds and provides unparalleled accuracy with error rates as low as 1 in 1.2 million.
Applications of Medical Iris Technology in Modern Healthcare
Patient Identification and Medical Record Management
One of the most widespread applications of medical iris technology is in patient identification. Hospitals and clinics increasingly use iris scanning to accurately identify patients, reducing the risk of medical errors caused by misidentification. According to a study published in the Journal of Healthcare Information Management, implementing iris recognition reduced patient identification errors by 98.5% in participating hospitals.
Disease Diagnosis and Monitoring
The iris contains valuable information about our health. Researchers have discovered correlations between specific iris patterns and various medical conditions. For example:
- Diabetes can cause changes in iris vasculature that are detectable before other symptoms appear
- Hypertension often creates distinctive patterns in the iris
- Certain neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s disease may produce identifiable changes
- Kidney and liver disorders can alter iris pigmentation and structure
These connections allow for early detection and monitoring of disease progression through regular iris scans, potentially revolutionizing preventive medicine.
Secure Access to Medical Information
Healthcare facilities use iris recognition to control access to sensitive areas and information systems. Medical professionals can quickly authenticate their identity to access patient records, medication dispensing systems, and restricted areas. This technology ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive patient information, enhancing privacy and security.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
As telemedicine expands, iris recognition provides a secure method for patient authentication during virtual consultations. This ensures that medical advice and prescriptions are provided to the correct individual, maintaining the integrity of remote healthcare services.
Benefits of Medical Iris Technology
Advantages of Medical Iris Technology
- Exceptional Accuracy: False acceptance rate of less than 0.0001%, far exceeding other biometric methods
- Non-invasive: Requires no physical contact, reducing infection risk and increasing patient comfort
- Speed: Authentication takes 1-2 seconds, streamlining patient processing
- Stability: Iris patterns remain consistent throughout life, unlike other biometrics
- Difficult to Forge: Nearly impossible to replicate, ensuring high security
- Early Disease Detection: Can identify health issues before traditional symptoms appear
- Reduced Medical Errors: Proper patient identification prevents treatment mistakes
Challenges of Medical Iris Technology
- Implementation Cost: Initial investment in equipment and training can be substantial
- Technical Limitations: May have difficulty with certain eye conditions or injuries
- Privacy Concerns: Requires careful data protection and consent management
- Accessibility Issues: May present challenges for individuals with visual impairments
- Integration Complexity: Requires integration with existing healthcare systems
- Standardization Needs: Lack of universal standards across healthcare facilities
- Cultural Acceptance: Some patients may be hesitant about eye scanning technology

Explore the Full Potential of Medical Iris Technology
Want to learn more about how iris-based solutions can enhance patient care and security in your healthcare facility? Our comprehensive guide covers implementation strategies, cost considerations, and success stories.
Télécharger Guide gratuit
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Privacy and Data Security
The collection and storage of biometric data raise significant privacy concerns. Healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures to protect iris scan data from breaches. Additionally, clear consent protocols must be established to ensure patients understand how their biometric information will be used and stored.
Technical Barriers
Despite its advantages, medical iris technology faces several technical challenges:
- Difficulty scanning patients with certain eye conditions like cataracts
- Potential accuracy issues in poor lighting conditions
- Integration challenges with existing healthcare information systems
- Need for standardization across different manufacturers and healthcare facilities
Accessibility and Inclusion
Healthcare systems must ensure that iris-based technologies don’t create barriers for certain populations. Alternative identification methods should be available for individuals with visual impairments or those who cannot use iris scanning for medical or religious reasons.
Conformité réglementaire
Medical iris technology must comply with healthcare regulations like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe. These regulations impose strict requirements on how biometric data can be collected, stored, and used, adding complexity to implementation.
Future Trends in Medical Iris Technology
AI Integration and Enhanced Diagnostics
The integration of artificial intelligence with iris scanning technology promises to dramatically improve diagnostic capabilities. Machine learning algorithms can identify subtle patterns in the iris that may indicate disease, potentially detecting conditions years before traditional symptoms appear. Research at Stanford University has shown that AI-enhanced iris analysis can detect early signs of cardiovascular disease with 85% accuracy.
Portable and Mobile Solutions
The development of smaller, more affordable iris scanning devices is making this technology increasingly accessible. Smartphone-compatible iris scanners and dedicated portable devices allow for iris-based identification and preliminary health screening in remote or underserved areas. These innovations are particularly valuable for:
- Mobile healthcare clinics serving rural communities
- Humanitarian medical missions in developing regions
- Home healthcare services for elderly or immobile patients
- Emergency medical services in disaster zones
Global Standardization Efforts
International organizations are working to establish global standards for medical iris technology. These standards will facilitate interoperability between different systems and ensure consistent quality and security across healthcare facilities worldwide. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has already published several standards related to iris recognition, with healthcare-specific guidelines under development.
Integration with Other Health Technologies
The future of medical iris technology lies in its integration with other health technologies. Combined with electronic health records, wearable health monitors, and genomic data, iris analysis will contribute to a comprehensive picture of patient health, enabling truly personalized medicine.
Real-World Applications of Medical Iris Technology
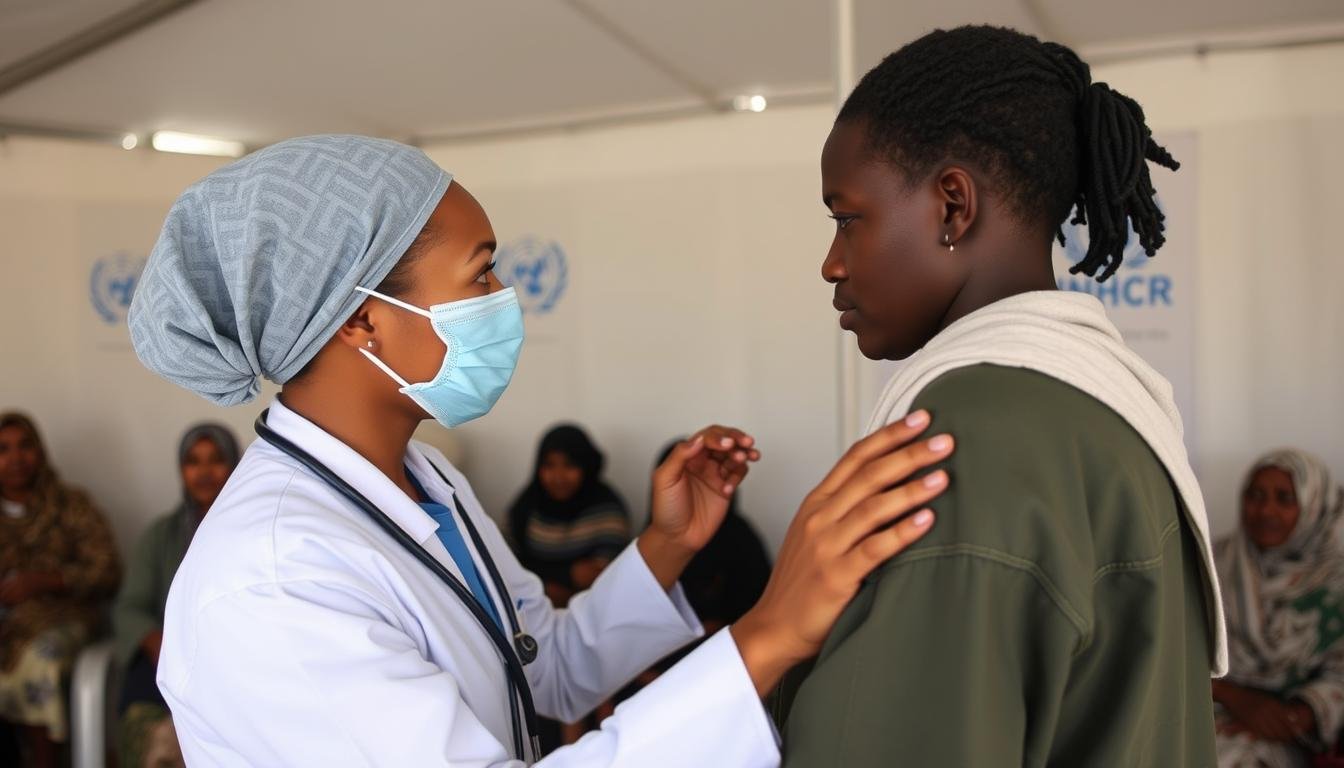
IrisGuard Refugee Healthcare
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) has implemented IrisGuard’s EyeCloud® platform to manage healthcare services for millions of refugees. This system enables secure identification without physical documentation, ensuring that refugees receive their entitled medical care while preventing fraud.
The technology has been deployed in Jordan, Lebanon, and other countries hosting large refugee populations, providing seamless access to healthcare services for vulnerable individuals who often lack traditional identification documents.
Aadhar-Linked Health Records in India
India’s Aadhar biometric identification system, which includes iris recognition, has been linked to healthcare services across the country. This integration allows patients to access their medical records and government health benefits through iris authentication.
The system serves over 1.3 billion citizens, making it the world’s largest biometric identification program. In rural areas with low literacy rates, iris recognition has proven particularly valuable for patient identification.
Iris Diagnostics for Neurological Disorders
Researchers at Emory University have developed an iris-based diagnostic tool for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Their studies have identified specific iris patterns that correlate with neurological changes associated with the disease.
In clinical trials, the technology demonstrated 86% accuracy in identifying patients with early-stage Alzheimer’s, potentially allowing for earlier intervention and treatment before significant cognitive decline occurs.

Stay Updated on Medical Iris Innovations
The field of medical iris technology is evolving rapidly. Subscribe to our newsletter to receive the latest research findings, case studies, and implementation strategies directly to your inbox.
Frequently Asked Questions About Medical Iris Technology
How accurate is iris recognition compared to other biometric methods?
Iris recognition is considered the most accurate biometric identification method available. It has a false acceptance rate of less than 0.0001%, significantly outperforming fingerprint recognition (0.1%) and facial recognition (2-5%). The probability of two irises being identical is approximately 1 in 10^78, making it virtually impossible for the system to confuse two different individuals.
Is iris scanning safe for the eyes?
Yes, iris scanning is completely safe. Modern iris scanners use regular LED light or near-infrared illumination at levels well below safety thresholds. The process is non-invasive and doesn’t require direct contact with the eye. The technology has been thoroughly tested and approved by regulatory bodies worldwide for regular use in healthcare settings.
How are privacy concerns addressed with medical iris data?
Healthcare organizations implementing iris recognition must comply with strict data protection regulations. Best practices include:
- Storing only encrypted templates rather than actual iris images
- Obtaining explicit patient consent before collecting biometric data
- Implementing robust access controls and audit trails
- Establishing clear data retention and deletion policies
- Regular security assessments and compliance audits
Can medical conditions affect the accuracy of iris recognition?
Certain eye conditions can impact iris recognition accuracy. These include:
- Cataracts, which can obscure parts of the iris
- Severe glaucoma that alters iris structure
- Aniridia (absence of the iris)
- Recent eye surgery that may temporarily change iris appearance
However, modern systems are increasingly able to accommodate these conditions through advanced algorithms and alternative scanning methods.
What is the implementation cost for healthcare facilities?
Implementation costs vary based on facility size and integration requirements. A typical mid-sized hospital might invest ,000-0,000 for a comprehensive system including hardware, logiciel d'iridologie, integration, and training. While the initial investment is significant, many facilities report positive ROI within 18-24 months through reduced administrative costs, fewer medical errors, and improved security.
The Future of Healthcare Through the Lens of Medical Iris Technology
Medical iris technology represents a significant advancement in healthcare, offering unprecedented accuracy in patient identification while opening new frontiers in disease diagnosis and monitoring. As the technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, we can expect to see wider adoption across healthcare systems worldwide.
The integration of iris recognition with artificial intelligence, portable devices, and comprehensive health information systems promises to transform patient care, making it more personalized, secure, and efficient. While challenges remain—particularly in the areas of privacy, accessibility, and standardization—the potential benefits for patient outcomes and healthcare operations are substantial.
For healthcare organizations considering implementation, the key is to balance technological innovation with ethical considerations, ensuring that iris-based solutions enhance the patient experience while maintaining the highest standards of privacy and security. As we look to the future, medical iris technology stands as a powerful example of how biometric innovation can advance the core mission of healthcare: improving and saving lives.
Ready to Explore Medical Iris Solutions for Your Organization?
Our team of experts can help you understand the implementation process, cost considerations, and potential benefits for your specific healthcare setting.
Demander une consultation