Iridologie Ce este În ultimii ani, interesul pentru practicile de medicină alternativă a crescut semnificativ pe măsură ce oamenii caută abordări complementare ale asistenței medicale convenționale. Printre aceste practici, iridologia se remarcă ca o metodă fascinantă care pretinde că evaluează starea de sănătate prin examinarea irisului ochiului. Ca o hartă care dezvăluie terenul sănătății corpului tău, iridologia are atât adepți devotați, cât și critici sceptici. Acest ghid cuprinzător explorează ce este iridologia, rădăcinile sale istorice, modul în care practicienii o folosesc și dezbaterea în curs despre eficacitatea ei.
Ce este Iridologia?
Iridologia este o tehnică de medicină alternativă care implică examinarea modelelor, culorilor și a altor caracteristici ale irisului pentru a determina informații despre sănătatea sistemică a unei persoane. Practicanții iridologiei, cunoscuți sub numele de iridologi, cred că fiecare zonă a irisului corespunde unui anumit organ sau sistem din corp, creând în esență o hartă care reflectă starea întregului corp.
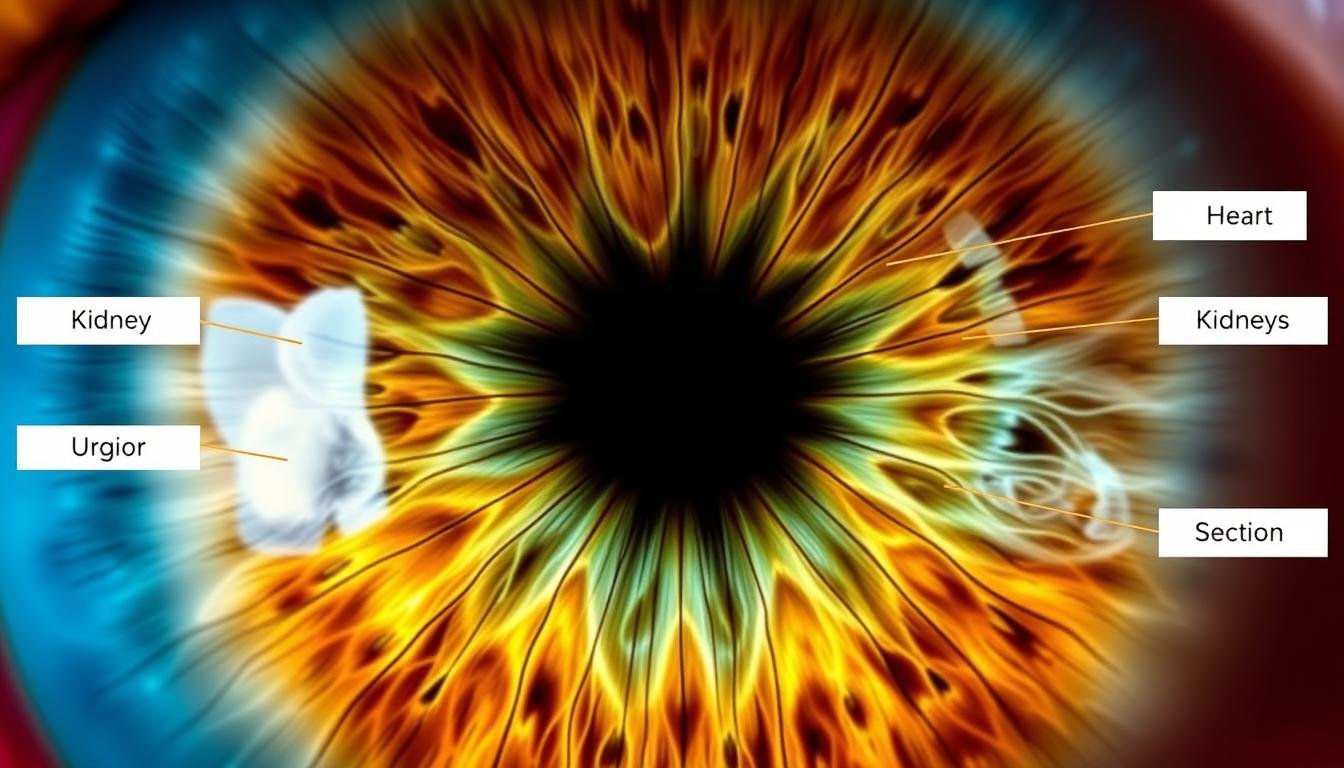
O diagramă de iridologie care cartografiază zonele irisului către sistemele și organele corporale corespunzătoare
Gândește-te la iridologie ca citirea unei hărți specializate a corpului în care partea colorată a ochiului servește ca un teren detaliat al sănătății tale. Așa cum un cartograf ar putea identifica munții, râurile și văile pe o hartă, un iridolog caută marcaje, modificări de culoare și modele în irisul tău pentru a identifica potențiale probleme de sănătate sau slăbiciuni constituționale.
Practica se bazează pe teoria conform căreia irisul este conectat la fiecare organ și țesut prin intermediul sistemului nervos și prezintă modificări ale pigmentării și structurii pe măsură ce diferite părți ale corpului experimentează schimbări de sănătate. Iridologii folosesc aceste informații nu pentru a diagnostica anumite boli, ci mai degrabă pentru a identifica zonele de potențial îngrijorare sau slăbiciune.
Rădăcinile istorice ale iridologiei
Originile iridologiei sunt adesea urmărite încă din secolul al XIX-lea, deși unii susținători susțin că forme de analiză a irisului au existat în civilizațiile antice, inclusiv în Egipt, China și India, cu mii de ani în urmă.

Ignaz von Peczely, medicul maghiar creditat cu fondatorul iridologiei moderne
Iridologia modernă este cel mai frecvent atribuită lui Ignaz von Peczely, un medic maghiar în anii 1800. Potrivit relatărilor populare, în copilărie, von Peczely a observat o dungă întunecată în ochiul unei bufnițe al cărui picior i-a rupt accidental. El a observat mai târziu că acest semn s-a schimbat pe măsură ce piciorul bufniței s-a vindecat, ceea ce i-a stârnit interesul pentru legătura dintre semnele irisului și sănătatea fizică.
În 1881, von Peczely a publicat prima sa carte pe acest subiect, “Descoperiri în domeniul științelor naturale și medicinei: instrucțiuni în studiul diagnosticului din ochi,” care a inclus prima diagramă de iris cunoscută care mapa regiunile corpului către zone specifice ale irisului.
Practica a fost dezvoltată în continuare la începutul secolului al XX-lea de Bernard Jensen, un chiropractician american care a creat o diagramă de iris mai detaliată, care este încă utilizată pe scară largă astăzi. Munca lui Jensen a ajutat la popularizarea iridologiei în Statele Unite și a stabilit multe dintre principiile pe care le urmează practicienii moderni.
Principiile de bază ale iridologiei
Iridologia se bazează pe câteva principii fundamentale care ghidează modul în care practicienii interpretează ceea ce observă în iris:

Prim-plan al unui iris care arată modelele și marcajele detaliate analizate în iridologie
Zonele de iris și corespondența corporală
Fundamentul iridologiei este conceptul că irisul este împărțit în zone, fiecare corespunzând diferitelor părți ale corpului. Folosind un diagramă de iridologie, practicienii cartografiază aceste conexiuni pentru a interpreta constatările.
| Zona Iris | Zona corporală corespunzătoare | Poziția pe diagrama irisului |
| Sus dreapta | Creier, cap, sinus | Poziția ora 12 |
| Dreapta Jos | Sistemul digestiv, colon | Poziția ora 6 |
| Partea stângă | Coloana vertebrală, inimă | Poziția de la ora 3 |
| Partea dreaptă | Ficat, vezica biliară | Poziția de la ora 9 |
| Inel interior | Stomacul, Intestinul Subțire | Cercul central |
| Inelul exterior | Piele, circulație, sistem limfatic | Marginea exterioară |
Interpretarea culorilor și modelelor
Iridologii analizează diferite caracteristici ale irisului, inclusiv:
- Variațiile de culoare și schimbările de pigmentare
- Caracteristici structurale precum fibrele și criptele
- Pete întunecate sau pete
- Zone albe sau înnorate
- Inele sau cercuri
- Liniile radiale care se extind de la pupilă
Se crede că fiecare dintre aceste caracteristici indică diferite condiții de sănătate. De exemplu, o pată întunecată poate sugera inflamație sau leziuni tisulare în zona corespunzătoare a corpului, în timp ce o zonă tulbure albă poate indica congestie sau aciditate.

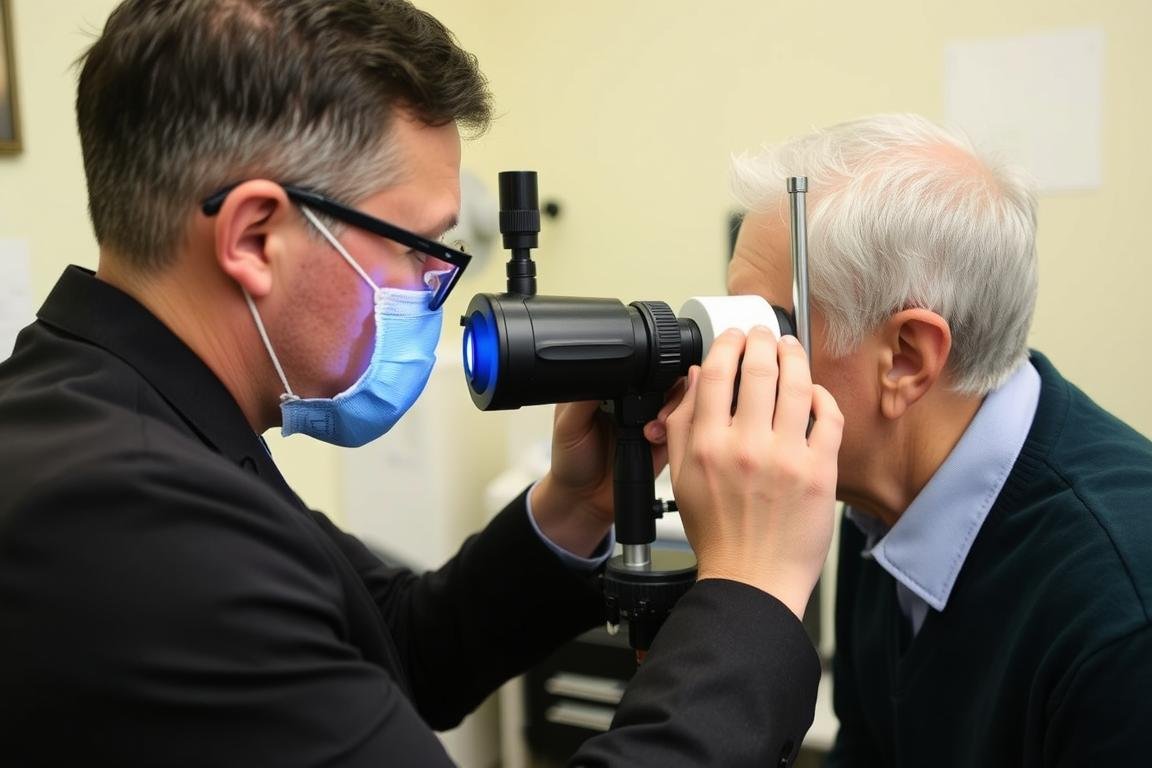
Un iridolog care examinează irisul unui pacient folosind echipamente specializate
Evaluare constituțională
Iridologia subliniază, de asemenea, conceptul de evaluare constituțională - identificarea punctelor forte și a punctelor slabe inerente în sistemele corpului unei persoane. Practicanții cred că structura de bază a irisului, care se formează înainte de naștere, dezvăluie predispoziții genetice și trăsături inerente care pot influența sănătatea de-a lungul vieții.
Cum se practică iridologia
O sesiune tipică de iridologie urmează o abordare structurată pentru examinarea și interpretarea irisului:

Iridologia modernă folosește adesea fotografia digitală pentru analiza detaliată a irisului
Procesul de examinare
- Iridologul preia mai întâi un istoric de sănătate detaliat de la client.
- Practicianul examinează ambii irisi folosind echipamente specializate, cum ar fi un penlight, lupa sau o cameră digitală cu iris.
- Pot fi realizate fotografii de înaltă rezoluție pentru o analiză mai detaliată.
- Iridologul compară observațiile cu o diagramă de iridologie.
- Constatările sunt discutate cu clientul, evidențiind adesea zonele de potențial îngrijorare.
Iridologii moderni folosesc frecvent tehnologia digitală, inclusiv camere specializate și software care pot îmbunătăți și analiza imaginile irisului cu o precizie mai mare decât metodele tradiționale.
Aplicații comune ale iridologiei în sănătatea holistică
Iridologia este folosită în primul rând ca instrument de evaluare în cadrul practicilor de sănătate holistice, mai degrabă decât ca metodă de tratament independentă. Aplicațiile sale includ:

Descoperirile iridologiei conduc adesea la recomandări personalizate de nutriție și stil de viață
Evaluarea preventivă a sănătății
Mulți practicieni folosesc iridologia ca instrument preventiv, susținând că poate identifica potențiale probleme de sănătate înainte de a se manifesta ca simptome fizice. Această abordare a sistemului de avertizare timpurie urmărește să abordeze dezechilibrele subiacente înainte ca acestea să devină condiții mai grave.
Identificarea punctelor slabe constituționale
Iridologia este adesea folosită pentru a identifica ceea ce numesc practicienii “slăbiciunile constituționale”— zone sau sisteme ale corpului care pot fi mai vulnerabile la stres sau boli. Aceste informații ajută la ghidarea strategiilor de sănătate preventive adaptate nevoilor individuale.

Suplimente pe bază de plante și nutritive recomandate în mod obișnuit pe baza evaluărilor iridologie
Instrument de evaluare complementară
Iridologia este utilizată de obicei împreună cu alte metode de evaluare, mai degrabă decât în mod izolat. Practicienii combină adesea analiza irisului cu alte abordări, cum ar fi:
- Evaluarea nutrițională
- Consultatie medicina pe baza de plante
- Evaluarea stilului de viață
- Alte metode de diagnostic holistic
Pe baza constatărilor combinate, practicienii pot recomanda modificări ale dietei, suplimente pe bază de plante, protocoale de detoxifiere sau modificări ale stilului de viață pentru a aborda preocupările identificate.
Perspectivă științifică și controverse
În timp ce iridologia are mulți susținători în comunitatea medicinei alternative, se confruntă cu critici semnificative din partea instituțiilor științifice și medicale:

Cercetările științifice asupra iridologiei au produs rezultate mixte în ceea ce privește eficacitatea acesteia
Lipsa validării științifice
Principala critică la adresa iridologiei este lipsa de dovezi științifice care să susțină afirmațiile sale fundamentale. Mai multe studii controlate nu au reușit să demonstreze că iridologii pot:
- Detectați afecțiunile medicale existente prin examinarea irisului
- Faceți distincția între indivizii sănătoși și cei cu diagnostice confirmate
- Produceți analize consistente atunci când examinați același iris de mai multe ori
Un studiu citat frecvent, publicat în Jurnalul Asociației Medicale Americane în 1979, a constatat că iridologii nu au putut detecta bolile renale la pacienți atunci când examinează fotografiile irisului lor. Studii similare au produs rezultate comparabile pentru alte afecțiuni.
Argumente care susțin iridologia
- Susținătorii citează succesul anecdotic în identificarea problemelor de sănătate
- Unii practicieni susțin că este valoros ca parte a unei evaluări holistice
- Poate încuraja măsurile preventive de sănătate și conștientizarea de sine
- Neinvaziv și, în general, inofensiv ca instrument de evaluare
Critici științifice
- Lipsa unor studii controlate care să susțină eficacitatea
- Nu există un mecanism fiziologic stabilit care să conecteze irisul de organe îndepărtate
- Potențial de diagnosticare greșită sau de îngrijire medicală adecvată întârziată
- Rezultate inconsecvente între diferiți practicieni
Poziția organizațiilor medicale
Organizațiile medicale majore, inclusiv Academia Americană de Oftalmologie și organisme internaționale similare, nu recunosc iridologia ca metodă de diagnostic validă. Aceste organizații subliniază că, în timp ce irisul poate dezvălui anumite afecțiuni ale ochilor, nu există dovezi suficiente că poate indica în mod fiabil tulburări în alte părți ale corpului.
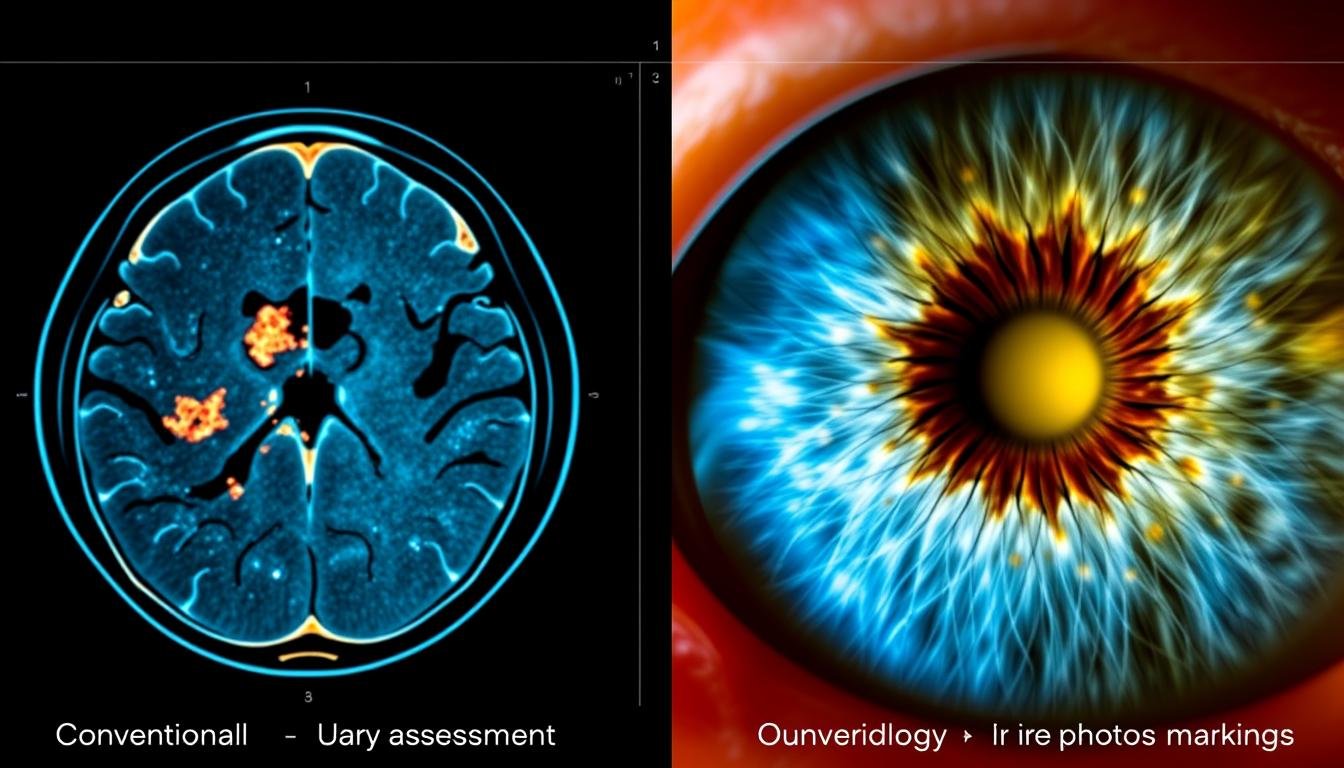
Studiu de caz: Riscul de diagnosticare greșită

Comparație între diagnosticul medical convențional și abordările de evaluare a iridologiei
O preocupare semnificativă în ceea ce privește iridologia este potențialul de diagnosticare greșită sau de îngrijire medicală adecvată întârziată. Luați în considerare acest scenariu ipotetic, dar realist:
O femeie de 45 de ani cu oboseală persistentă a consultat un iridolog care a identificat “slăbiciunea constituțională” în zona tiroidiană pe baza semnelor irisului. Iridologul a recomandat suplimente din plante și modificări ale dietei. După șase luni fără ameliorare, ea a căutat îngrijiri medicale convenționale și a fost diagnosticată cu anemie feriprivă, care a necesitat un tratament complet diferit.
Adaptat după cazuri raportate în literatura medicală
Acest caz subliniază importanța utilizării iridologiei, dacă este deloc, ca o evaluare complementară, mai degrabă decât un înlocuitor pentru diagnosticul medical bazat pe dovezi. Cei mai mulți practicieni responsabili ai iridologiei recunosc aceste limitări și recomandă clienților să mențină, de asemenea, îngrijire regulată cu furnizorii de asistență medicală convențională.
Concluzie: Locul iridologiei în sănătatea holistică

O abordare echilibrată a sănătății încorporează adesea mai multe perspective și metode de evaluare
Iridologia rămâne o practică controversată care ocupă o poziție incertă între artele tradiționale de vindecare și asistența medicală modernă. În timp ce dovezile științifice nu susțin în prezent multe dintre afirmațiile sale fundamentale, unii indivizi găsesc valoare în perspectiva holistică pe care o oferă.
Pentru cei interesați să exploreze iridologia, este recomandabilă o abordare echilibrată:
- Considerați iridologia ca unul dintre multele instrumente potențiale de evaluare, mai degrabă decât o metodă de diagnostic definitivă
- Menține îngrijirea regulată cu furnizorii de asistență medicală convențională, în special pentru simptome grave sau persistente
- Abordați deciziile privind sănătatea cu gândire critică și înțelegerea atât a potențialelor beneficii, cât și a limitărilor practicilor alternative
- Căutați practicieni care recunosc limitările iridologiei și lucrează împreună cu, nu în opoziție cu medicina convențională
Fie că este privită ca o fereastră perspicace asupra sănătății corpului sau ca o practică alternativă interesantă, dar nedovedită, iridologia continuă să-i fascineze pe cei care explorează peisajul divers al abordărilor holistice ale sănătății. Ca și în cazul multor practici complementare, valoarea sa finală poate sta în experiența individului și în abilitatea practicianului de a o folosi ca parte a unei abordări cuprinzătoare a bunăstării.
Explorați mai multe despre evaluarea holistică a sănătății
Doriți să aflați mai multe despre diferitele abordări ale evaluării holistice a sănătății? Descărcați ghidul nostru gratuit pentru practicile complementare de sănătate și descoperiți cum diferite metode de evaluare pot funcționa împreună pentru o înțelegere mai cuprinzătoare a bunăstării dumneavoastră.
Descărcați ghid gratuit