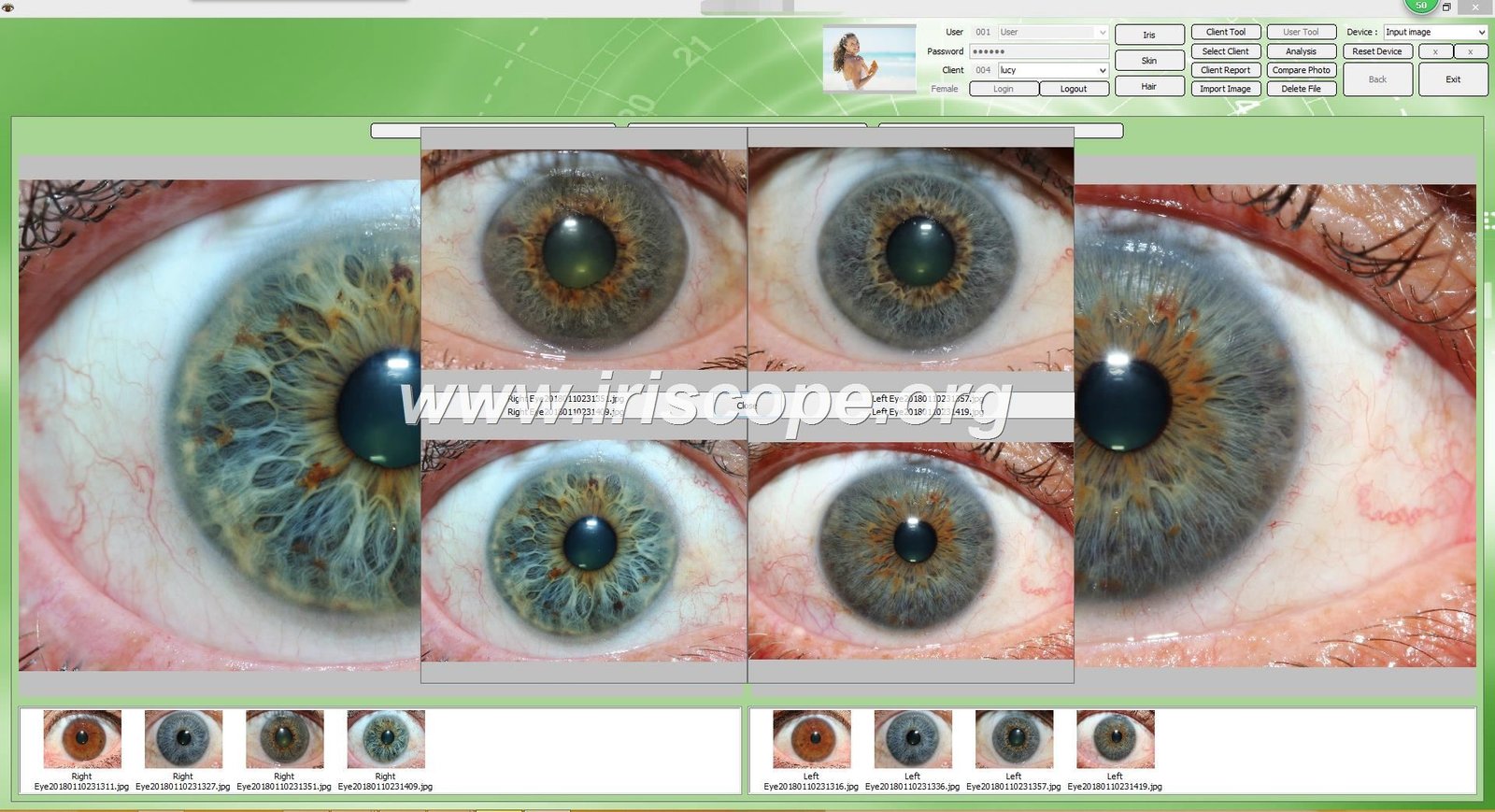
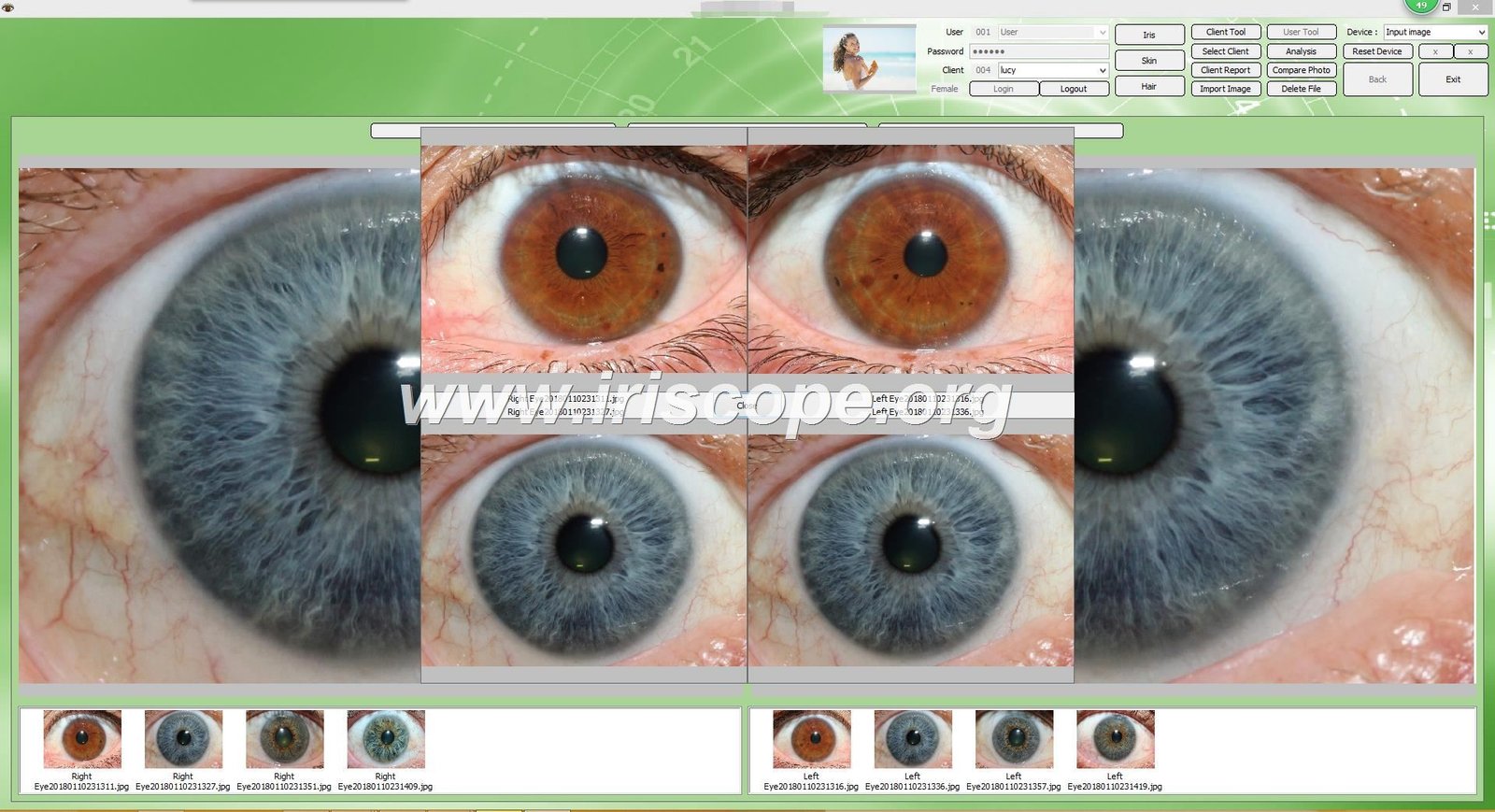
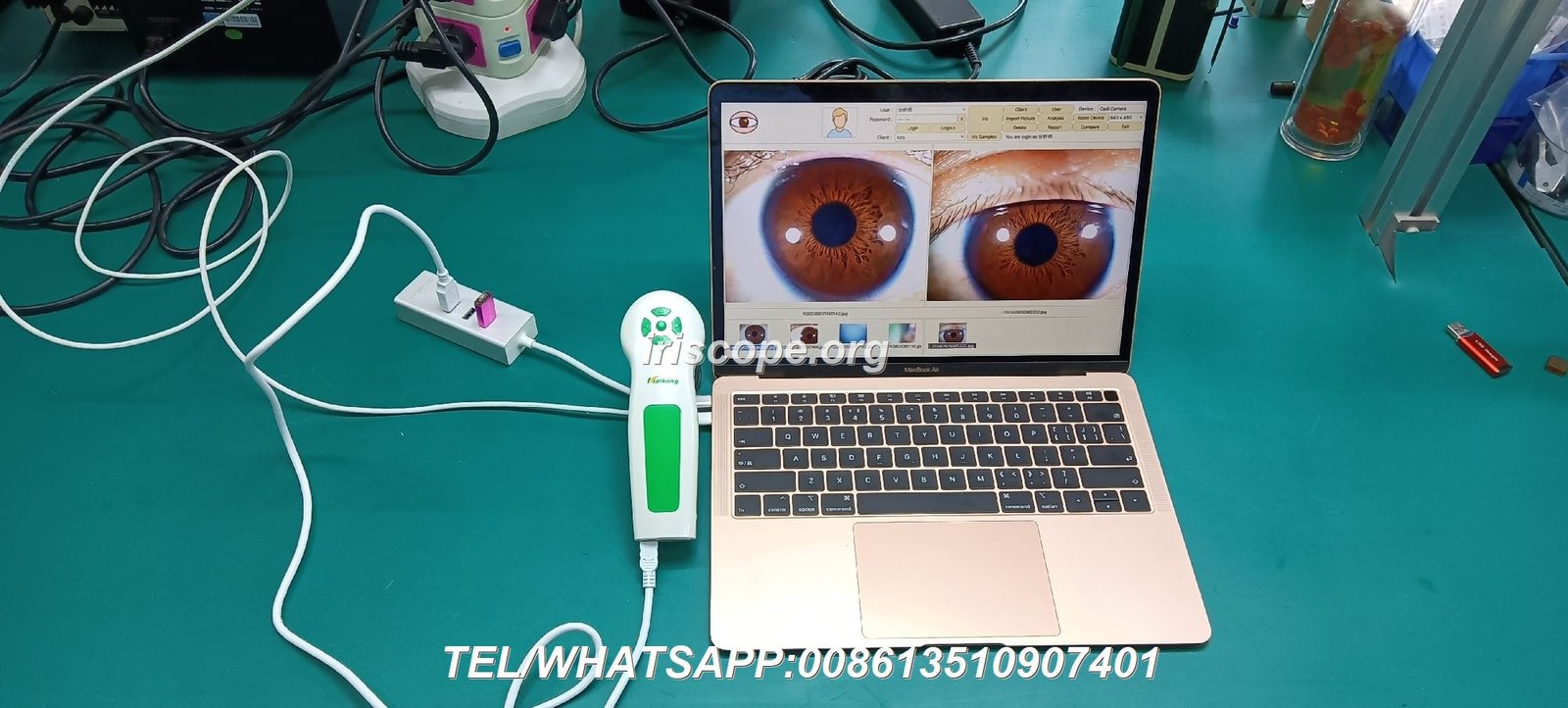
The relationship between cancer iridology and health assessment has garnered attention in alternative medicine circles for decades. As practitioners examine the intricate patterns of the iris for potential signs of cancer, the demand for professional-grade equipment continues to grow. This comprehensive guide explores how cancer iridology works, its historical context, scientific perspectives, and the professional tools that support practitioners in their analysis.What Is Cancer Iridology and How Does It Work?
Cancer iridology refers to the practice of examining the iris (the colored part of the eye) to detect potential signs of cancer or cancer predisposition in the body. This specialized branch of iridology is based on the premise that specific areas of the iris correspond to different organs and systems, with changes in iris patterns potentially indicating health changes in corresponding body parts.




Iridology chart mapping iris zones to body organs and systems
Iridologists who focus on cancer detection typically look for specific markers in the iris:
- Very dark spots or markings in specific organ-related zones
- Unusual discolorations that may indicate tissue changes
- Structural abnormalities like lacunas (pits) in cancer-prone areas
- Color changes that might suggest inflammatory or degenerative processes
Using specialized equipment like كاميرات علم القزحية و iriscopes, practitioners capture high-resolution images of the iris, which they then analyze using برامج علم القزحية and reference against detailed مخططات علم القزحية.
معدات علم القزحية المهنية
MAIKONG offers state-of-the-art iridology cameras and software designed specifically for professional practitioners. With over 20 years of research and development experience, our equipment provides the precision and clarity needed for detailed iris analysis.
استكشف كاميرات علم القزحية لدينا
Historical Context of Iridology in Cancer Detection
The practice of examining the eyes for signs of illness dates back thousands of years, with records suggesting its use as early as 3,000 BCE. However, modern iridology as we know it began taking shape in the 19th century.
Evolution of Cancer Iridology Through the Years
The specific application of iridology for cancer detection evolved alongside general iridology practice. Key historical developments include:
Early Foundations: Philippus Meyeus first described iridological principles in his 1665 work “Chiromatica Medica,” though he didn’t specifically focus on cancer detection.
19th Century Development: Ignaz von Peczely, often considered the father of modern iridology, began developing systematic approaches to iris analysis in Hungary, establishing some of the foundational principles still used in cancer iridology today.
20th Century Advancement: Bernard Jensen significantly popularized iridology in the United States during the 1950s, including techniques for identifying potential cancer markers in the iris.
Modern Practice: Contemporary cancer iridology incorporates advanced imaging technology and software analysis to enhance the precision of iris examinations, allowing for more detailed observation of potential cancer indicators.

Modern iridology examination using professional digital equipment
Scientific Perspective on Cancer Iridology
The scientific community has conducted several studies examining the efficacy of iridology for cancer detection. It’s important to understand both the claims and the scientific evidence when considering cancer iridology.
Research Studies and Findings
Several clinical studies have investigated iridology’s effectiveness in detecting cancer:
| يذاكر | سنة | Participants | Cancer Type | Results |
| Münstedt et al. | 2005 | 110 (68 with cancer, 42 without) | Breast, ovary, uterus, prostate, colorectal | Iridologist correctly identified only 3 cancer cases |
| Herber et al. | 2008 | 58 (29 with cancer, 29 without) | Colorectal | 50-53% detection rate (similar to random chance) |
| Simon et al. | 1979 | 143 patients | Various | Iridologists could not reliably detect disease |
“Iridology is based on intriguing possibilities, but, to date, evidence-based studies do not support its safety and utility. Some researchers are considering improving the accuracy of the practice by using computer-aided diagnostics.”
– Clinical Advisor Journal
While conventional medicine does not currently recognize iridology as a validated diagnostic method for cancer, many practitioners continue to use it as a complementary assessment tool, particularly with the aid of advanced technology.

Detailed iris examination showing tissue patterns analyzed in cancer iridology
Cancer Iridology in Professional Practice
Professional iridologists who focus on cancer detection typically follow a structured approach to iris analysis, utilizing specialized equipment and methodologies.
Equipment Used in Professional Cancer Iridology
Accurate iris analysis requires professional-grade equipment:
كاميرات علم القزحية
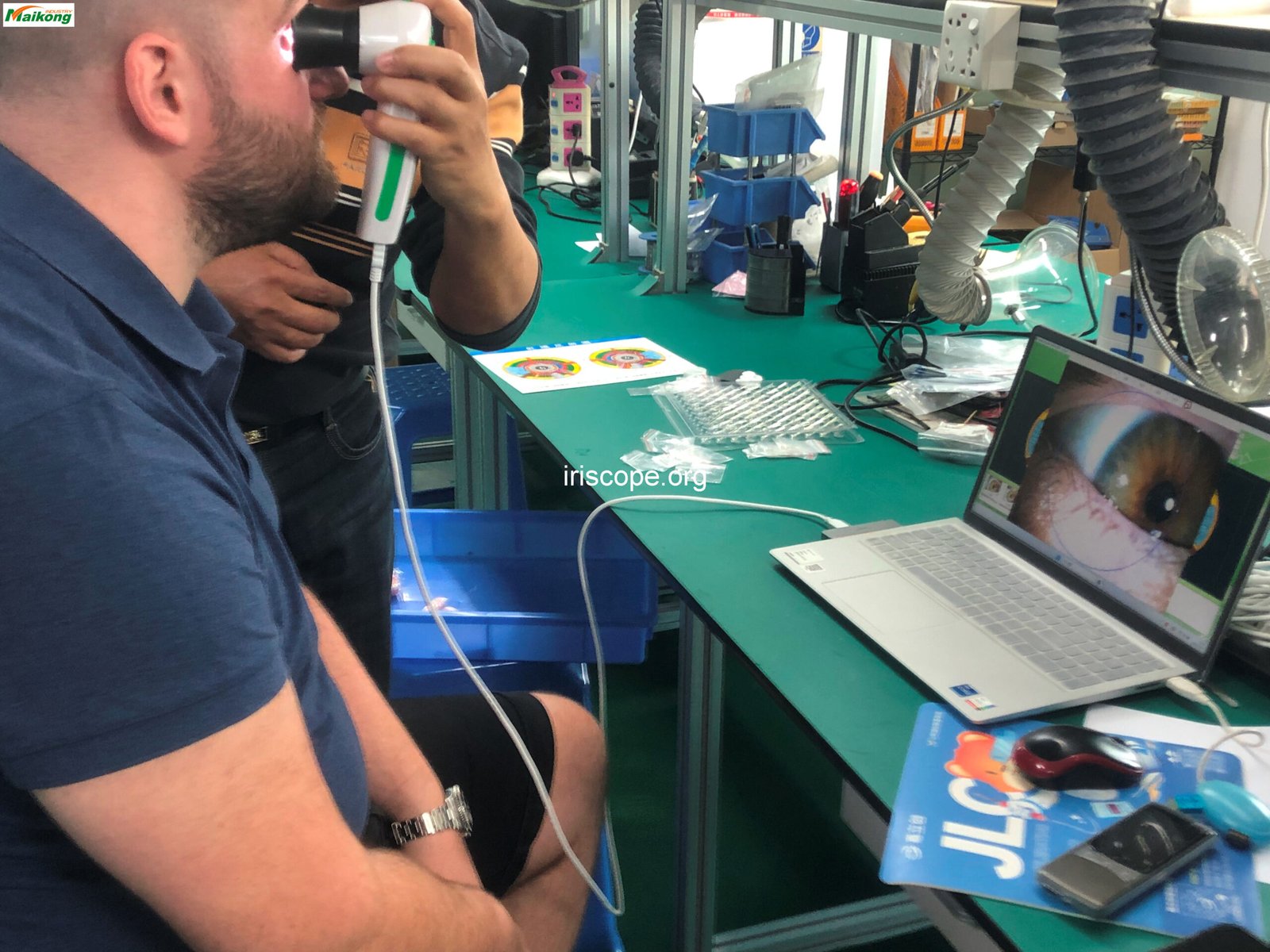
High-resolution digital cameras specifically designed to capture detailed iris images. MAIKONG’s كاميرات علم القزحية feature advanced optics and lighting systems for capturing the subtle details necessary for cancer marker identification.
Iriscopes
Specialized microscopes for examining the iris in detail. Our iriscope models provide magnification options ranging from 10x to 50x, allowing practitioners to observe minute iris changes potentially associated with cancer.
برامج القزحية
Digital analysis programs that help process and interpret iris images. MAIKONG’s برامج علم القزحية includes specialized modules for cancer marker identification and tracking changes over time.

MAIKONG professional iridology camera system in clinical use
Examination Process for Cancer Detection
Professional iridologists typically follow these steps when examining the iris for potential cancer indicators:
- Patient History: Gathering relevant health information and family cancer history
- التقاط الصور: Taking high-resolution photographs of both irises using specialized equipment
- Systematic Analysis: Examining specific zones of the iris corresponding to cancer-prone organs
- Marker Identification: Looking for dark spots, lacunas, or discolorations that may indicate abnormal tissue changes
- التحليل المقارن: Comparing findings against established iridology charts and previous examinations
- Recommendations: Suggesting further conventional medical testing if concerning markers are identified
Specific Markers in Cancer Iridology
Iridologists who specialize in cancer detection look for specific signs and patterns in the iris that may indicate potential cancer development or predisposition.
Common Iris Signs Associated with Cancer
According to iridology practitioners, these iris characteristics may warrant further investigation:


Comparison of normal iris patterns (left) versus patterns showing potential cancer markers (right) according to iridology
Dark Spots and Pigmentation
Very dark or black spots in specific organ zones may indicate tissue damage or abnormal cell activity. These are particularly concerning when found in zones corresponding to cancer-prone organs like the breast, prostate, or colon.
Lacunas and Structural Changes
Pit-like formations or structural abnormalities in the iris fiber may suggest tissue degradation. A notable case mentioned by practitioners involved identifying a large lacuna in the lung area of a heavy smoker, who was subsequently diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer.
اختلافات الألوان
Unusual color changes or discolorations in specific iris zones may indicate inflammatory or degenerative processes that could potentially be related to cancer development.
Lymphatic Rosary Signs
White markings arranged in a circular pattern may indicate lymphatic system issues, which some iridologists associate with increased cancer susceptibility when found in conjunction with other concerning markers.
ملاحظة مهمة: While iridologists identify these patterns as potential cancer indicators, it’s crucial to understand that iridology should not replace conventional medical diagnosis. If concerning markers are identified during an iridology session, patients should be referred for appropriate medical testing and evaluation.
Case Studies in Cancer Iridology
Practitioners of cancer iridology often share case studies where iris analysis has contributed to early detection or assessment. These anecdotal reports provide insight into how iridology is applied in practice, though they should be considered alongside the scientific research.


Iridologist analyzing digital iris images using specialized software
Practitioner Observations
Some iridologists report cases where iris examination revealed concerning markers that led to further medical investigation:
Lung Cancer Case Study
A practitioner described examining a heavy smoker who showed a large lacuna (pit) in the iris zone corresponding to the right lung. The patient was referred for medical testing, which reportedly detected early-stage lung cancer that had been asymptomatic. While such cases are compelling, they represent anecdotal evidence rather than controlled scientific studies.
Breast Cancer Monitoring
Some iridologists report monitoring changes in the breast-corresponding iris zones of patients with family histories of breast cancer. They suggest that changes in these areas sometimes precede detectable tumors, though scientific validation of these observations is lacking.
Colorectal Cancer Screening
Practitioners have described cases where specific iris signs in the intestinal zone prompted recommendations for colonoscopy, sometimes resulting in the discovery of precancerous polyps. Again, these represent individual case reports rather than systematic studies.
Medical Disclaimer: These case studies represent anecdotal reports from iridology practitioners and have not been validated through controlled scientific studies. Iridology should be considered a complementary approach rather than a replacement for conventional medical cancer screening and diagnosis.
Professional Equipment for Cancer Iridology
High-quality equipment is essential for accurate iris analysis, especially when looking for subtle markers that might indicate cancer predisposition or development.
MAIKONG Professional Iridology Solutions
With over 20 years of research and development experience, MAIKONG has established itself as a leading manufacturer of professional iridology equipment used by practitioners worldwide.

MAIKONG’s comprehensive iridology system for professional practitioners
Advanced Iridology Cameras
Our كاميرات علم القزحية feature high-resolution optics, specialized lighting systems, and ergonomic designs for capturing detailed iris images. These cameras are specifically calibrated to detect the subtle color variations and structural details that may indicate cancer-related changes.
Comprehensive Software Analysis
ماكونج برامج علم القزحية includes specialized modules for cancer marker identification, allowing practitioners to analyze iris images with precision. The software supports comparison of current and previous images to track changes over time.
Detailed Iridology Charts
Our مخططات علم القزحية provide comprehensive mapping of iris zones to body organs and systems, with specific attention to cancer-prone areas. Available for both العين اليمنى و عين اليسار analysis.
Equip Your Practice with Professional Tools
MAIKONG offers complete iridology systems designed for professional practitioners. Our equipment is used in clinics worldwide for comprehensive iris analysis.
طلب معلومات المنتج
Practical Applications of Cancer Iridology
While scientific validation remains limited, many practitioners incorporate cancer iridology into their practice in specific ways that complement conventional medical approaches.

Iridologist discussing findings and recommendations with a patient
Complementary Assessment Approach
Most responsible practitioners position iridology as a complementary tool rather than a replacement for conventional cancer screening:
Appropriate Uses
- As an additional screening tool alongside conventional methods
- For monitoring general health patterns in high-risk individuals
- To encourage preventative health measures based on potential predispositions
- As part of a holistic health assessment approach
Inappropriate Uses
- As a replacement for conventional cancer screening
- For definitive cancer diagnosis
- To delay seeking conventional medical care
- As the sole basis for treatment decisions
Integration with Conventional Medicine
The most effective approach integrates iridology with conventional medical care:
- التقييم الأولي: Iridology may be used as part of a comprehensive health assessment
- Referral Protocol: If concerning markers are identified, patients are referred for appropriate medical testing
- Collaborative Care: Iridologists work alongside medical professionals rather than in opposition
- يراقب: Regular iris examinations may complement medical monitoring for high-risk patients
Professional Approach: Responsible iridologists emphasize that their practice is not intended to diagnose cancer but rather to identify potential areas of concern that warrant further investigation through conventional medical channels.
Global Perspective on Cancer Iridology
The practice and acceptance of cancer iridology varies significantly around the world, with different countries taking diverse approaches to its regulation and integration into healthcare systems.

International iridology practitioners sharing knowledge and techniques
Regional Variations in Practice and Acceptance
Iridology’s integration into healthcare systems varies by region:
| Region | الوضع التنظيمي | Integration Level | Common Applications |
| الولايات المتحدة | Unregulated, considered alternative medicine | Limited, primarily in alternative health clinics | Complementary assessment, wellness monitoring |
| Europe (Germany, Russia) | More accepted, some formal training programs | Moderate integration with naturopathic medicine | Preventative health screening, complementary assessment |
| Asia (China, India) | Often integrated with traditional medicine systems | Higher integration in some regions | Holistic health assessment, constitutional analysis |
| أمريكا اللاتينية | Varies by country, often accepted as complementary | Moderate to high in some countries | General health screening, preventative guidance |
MAIKONG serves practitioners across these diverse regions, providing equipment that meets the specific needs of different practice styles and regulatory environments. Our iriscopio models are particularly popular in Spanish-speaking countries, where iridology has gained significant acceptance.
Global Distribution Network
MAIKONG supplies professional iridology equipment to practitioners worldwide. Interested in becoming a distributor or finding a representative in your region?
تعرف على فرص التوزيع
Conclusion: The Future of Cancer Iridology
The field of cancer iridology continues to evolve, with technological advancements potentially bridging some gaps between traditional practice and scientific validation. While scientific evidence remains limited, the integration of advanced imaging technology and computer analysis may offer new possibilities for this alternative assessment method.

Advanced digital analysis technologies are shaping the future of iridology practice
For practitioners interested in incorporating iridology into their practice, professional-grade equipment and proper training are essential. MAIKONG remains committed to advancing the field through continued research and development of cutting-edge iridology tools that meet the highest standards of precision and reliability.
Whether you’re an established iridologist looking to upgrade your equipment or a healthcare practitioner interested in exploring iridology as a complementary assessment tool, MAIKONG offers comprehensive solutions backed by over two decades of industry experience.
Contact MAIKONG for Professional Iridology Solutions
Discover how our professional iridology equipment can enhance your practice. With global distribution and expert support, we’re here to help you provide the best possible care for your patients.
بريد إلكتروني: لوسي@iriscope.org
التواصل عبر الواتس اب
Visit Our Contact Page