قراءة علم القزحية-Have you ever wondered how the eye can reveal insights about your overall health? Iridology is a fascinating practice that examines the patterns and colors of the iris to assess systemic well-being. This non-invasive method uses detailed iris charts, mapping over 60 zones that correspond to specific organs and systems in the human body.
Originating in the 19th century, this technique has evolved into a modern tool used by practitioners worldwide. While it lacks scientific validation, many believe it offers valuable information about potential health imbalances. Unlike clinical diagnostics, iridology is gentle and focuses on prevention rather than treatment.
In this guide, we’ll explore the techniques, claimed benefits, and scientific debates surrounding this practice. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or simply curious, this comprehensive overview will provide you with a deeper understanding of how the eye connects to the body.

الوجبات السريعة الرئيسية
- Iridology analyzes iris patterns to assess systemic health.
- It uses non-invasive methods with detailed iris charts.
- Over 60 zones in the iris correspond to specific organs.
- Practiced globally despite limited scientific validation.
- Focuses on prevention and holistic well-being.
What is Iridology Reading?
The human eye holds more secrets than meets the eye. Iridology is the study of the قزحية and its pigmentation abnormalities to assess health. This practice has been used for centuries to identify potential imbalances in the human body.
The Basics of Iridology
Iridologists examine the قزحية for patterns, colors, and marks. These features are believed to reflect the state of various organs and systems. Modern charts divide the iris into over 60 zones, each corresponding to a specific part of the body.
History and Origins of Iridology
The practice dates back to the 19th century. Ignaz von Peczely, a Hungarian physician, developed the first iris chart in 1880. He observed التغييرات in an owl’s iris after it suffered an injury. Later, Nils Liljequist expanded on this work, linking iris patterns to anatomical structures.
How Iridology Works
Iridologists use tools like magnifiers and slit lamps to analyze the قزحية. They follow bilateral mapping, where the right iris reflects the right side of the body, and the left corresponds to the left. Over time, practitioners track pigment التغييرات to monitor health trends.
A 1957 German study analyzed 4,000 iris photos but yielded inconclusive results. Despite this, many continue to find value in this holistic approach.
| منطقة القزحية | Corresponding Organ |
|---|
| Upper Right | Brain |
| Lower Left | Liver |
| Center | قلب |
| Outer Ring | Skin |
Techniques Used in Iridology Reading
The iris is a window into the body’s health, offering clues through its unique patterns. Iridologists use specialized tools and methods to examine this delicate part of the eye. By analyzing its colors, marks, and zones, they gain insights into systemic health.
Examining the Iris: Tools and Methods
To study the iris, practitioners rely on tools like 10x magnifiers, flashlights, and DSLR cameras with macro lenses. These devices help capture detailed images of the eye’s structure. Digital photography has become a standard, offering clearer visuals compared to analog methods.
Iridologists also use slit lamps for precise examination. This allows them to observe subtle changes in the iris’s texture and color. These tools ensure accuracy in identifying potential health concerns.
Understanding Iridology Charts
Iridology charts are essential for mapping the iris. They divide the eye into over 60 zones, each linked to a specific organ or system. For example, the liver zone is located at the 6 o’clock position, while the lymphatic system is near the limbus.

مخطط القزحية الرسم البياني للعين اليمنى -الرسم البياني للأياصة -العين اليمنى
العين اليمنى يعكس الجانب الأيمن جسم.
| موضع الساعة (العين اليمنى) | يتوافق العضو/النظام | تفاصيل |
|---|
| 1:CLOCK - 2:CLOCK | الوجه الأيمن | يتوافق مع الأعضاء التناسلية اليسرى ، وتشمل الرحم ، والمباضات (أنثى) أو الخصيتين (ذكر). |
| الساعة 2 - الساعة 3 | الحلق الأيمن
| تتضمن المفاصل اليسرى الصحي في Ringflectks ، وتشمل الركبتين والوركين والمرفقين والكتفين. |
| الساعة 3 - الساعة 4 | اليمين العلوي الظهر
| يتوافق مع العمود الفقري ، صحة العمود الفقري ، المحاذاة ، والمرونة. |
| الساعة 4 - الساعة 5 | المثانة اليمنى | Ringflects المثانة ونظام البول الجانبي الأيمن. |
| 5 - 6 - 6 | الحوض الصحيح | تركت Ringpresents القولون والأمعاء الدقيقة والصحة الجهاز الهضمي. |
| 6 - 7 - 7 | يمين البطن السفلي
| تركت الثرثرة الكلى ، التركيز على الترشيح ، إزالة السموم ، وتوازن السوائل. |
| الساعة 7 - الساعة 8 | اليمين العلوي البطن
| أعضاء معدة الذروة والأعضاء الجهاز الهضمي على الجانب الأيسر. |
| الساعة 8 - الساعة 9 | الصدر الأيمن | يتوافق مع الكبد الجانبي الأيسر ، وإزالة السموم المسؤولة وإنتاج الصفراء. |
| الساعة 9 - الساعة 10 | الرئة اليمنى | Ringpresents القلب الأيسر ، تؤثر على صحة القلب والأوعية الدموية. |
| الساعة 10 - 11 صباحًا | الرقبة اليمنى | رنين اليسار في الرئة ، صحة الجهاز التنفسي ، ووظيفة بريا. |
| الساعة 11 - الساعة 12 | الدماغ اليمين
| يتوافق مع دماغ نصف الكرة الأيسر والصحة العقلية والوظائف المعرفية. |
| الساعة 12 - من الساعة 1 | الدماغ اليمين
| يتوافق مع دماغ نصف الكرة الأيسر والصحة العقلية والوظائف المعرفية. |
مخطط القزحية اليسرى - مخطط القزحية - العين اليسرى
عين اليسار يعكس الجانب الأيسر جسم.
| موضع الساعة (العين اليسرى) | يتوافق العضو/النظام | تفاصيل |
|---|
| 1:CLOCK - 2:CLOCK | اليسار الرقبة
| يتوافق مع الأعضاء التناسلية اليمنى ، وتشمل الرحم ، والمبيض (أنثى) أو الخصيتين (ذكر). |
| الساعة 2 - الساعة 3 | الرئة اليسرى | تتضمن المفاصل الصحيحة الصحيحة في الركبتين ، الركبتين ، الوركين ، المرفقين ، والكتفين. |
| الساعة 3 - الساعة 4 | ترك الصدر | يتوافق مع العمود الفقري ، صحة العمود الفقري ، المحاذاة ، والمرونة على الجانب الأيمن. |
| الساعة 4 - الساعة 5 | غادر البطن العلوي
| رنين المثانة ونظام البول الجانبي الأيسر. |
| 5 - 6 - 6 | ترك البطن السفلي
| Ringpresents القولون الأيمن والأمعاء الدقيقة والصحة الهضمية. |
| 6 - 7 - 7 | اليسار الحوض
| رنين اليمين الكلى ، التركيز على الترشيح ، إزالة السموم ، وتوازن السوائل. |
| الساعة 7 - الساعة 8 | ترك أسفل الظهر
| رنين المعدة والأعضاء الجهاز الهضمي على الجانب الأيمن. |
| الساعة 8 - الساعة 9 | ترك الظهر العلوي
| يتوافق مع الكبد الجانبي الأيمن ، وإزالة السموم المسؤولة وإنتاج الصفراء. |
| الساعة 9 - الساعة 10 | اليسار الحلق
| Ringpresents القلب الأيمن ، تؤثر على صحة القلب والأوعية الدموية. |
| الساعة 10 - 11 صباحًا | الوجه الأيسر | رنين الرئة اليمنى وصحة الجهاز التنفسي ووظيفة بريا. |
| الساعة 11 - الساعة 12 | اليسار الدماغ | يتوافق مع دماغ نصف الكرة الأيمن ، والصحة العقلية ، والوظائف المعرفية. |
| الساعة 12 - من الساعة 1 | اليسار الدماغ | يتوافق مع دماغ نصف الكرة الأيمن ، والصحة العقلية ، والوظائف المعرفية. |

These charts help iridologists interpret the iris’s features systematically. By referencing these zones, they can pinpoint areas of concern and track changes over time.
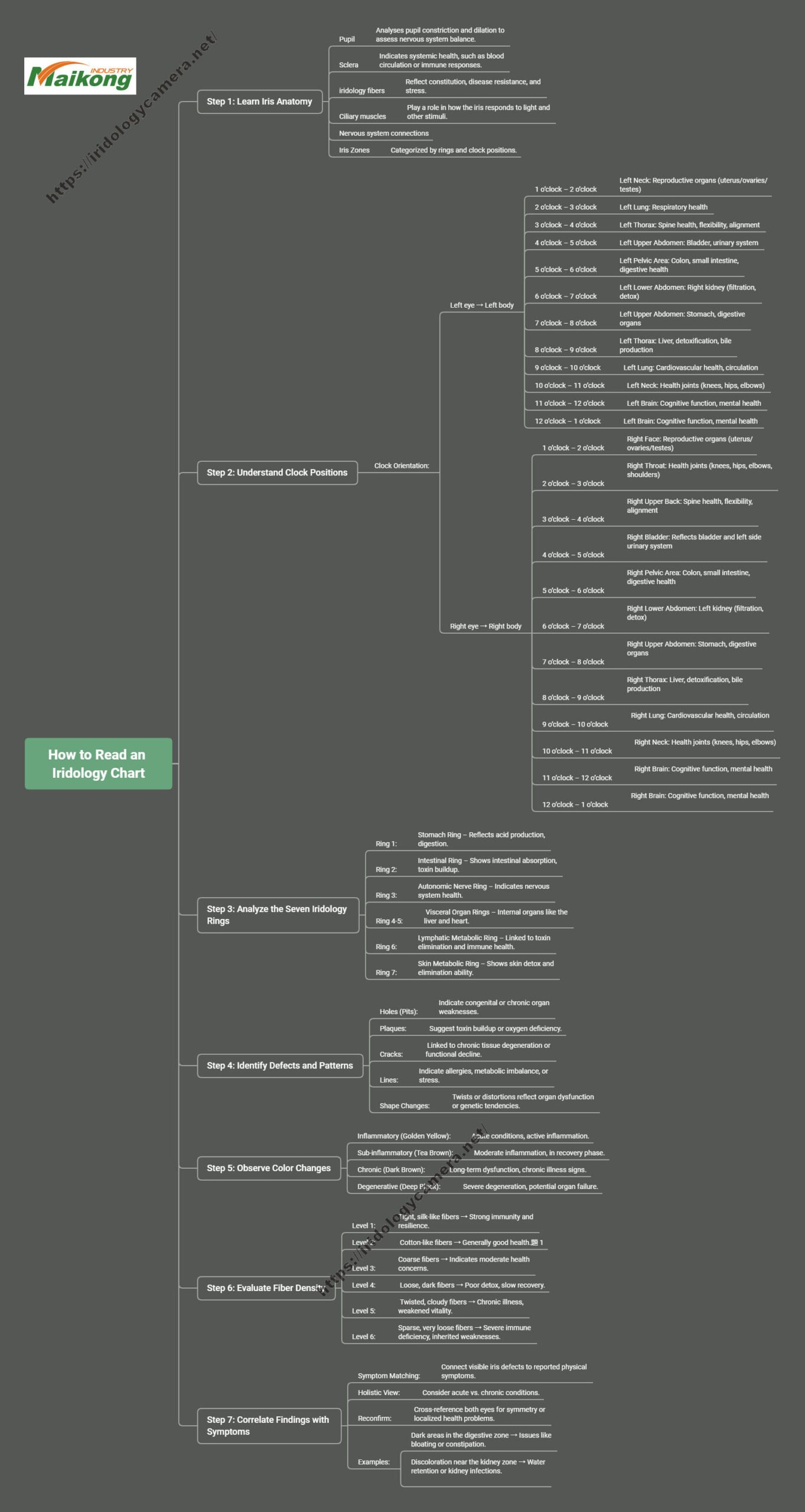
Step 1: Learn Iridology Anatomy and Structure
Iridology is divided into sections that reflect different organs and systems. To begin, I study pupilو sclera, and Iridology fibers, which provide essential clues.
| Key Areas | وصف | Purpose |
|---|
| Pupil | Central part eye | Helps assess nervous system reactions and stress. |
| الصلبة | White part eye | Indicates immune response and systemic health. |
| Iridology Fibers | Colored fibers forme Iridology | Shows constitution, health resilience, or weaknesses. |
Step 2: Understand Clock System and Organ Correlation
Iridology is mapped use clock system, where each hour position reflects different organ or system. العين اليمنى represents الجانب الأيسر body, while عين اليسار mirrors right side.
| موقف الساعة | Right Eye (Organ) | Left Eye (Organ) |
|---|
| 12-1 o’clock | Physiological Brain | Psychological Brain |
| 1-2 صباحا | Face | Neck |
| 2-3 jOclock | Throat | Lungs |
| 3-4 أونوك | Upper Back | Thoracic Cavity |
| 4-5 صباحا | Lower Back | Upper Abdomen |
| 5-6 صباحا | Pelvis | Lower Abdomen |
Knowe these organ correspondences helps pinpoint concern dure Iridology examination.
Step 3: Analyze Seven Iridology Ring
Iridology is divided into 7 Ring, each represente different physiological functions.
| Re Number | اسم | موقع | What Reflects |
|---|
| 1 | Stomach Ring | At pupil-Iridology boundary | Stomach health and digestive function. |
| 2 | Intestinal Ring | Surrounde stomach Ring | Intestinal absorption and toxin elimination. |
| 3 | Autonomic Nerve Ring | Just outside intestinal Ring | Nervous system balance in controlle organs. |
| 4-5 | Visceral Organ Reflex Ring | Surrounde autonomic nerve Ring | Health major organs like liver, lungs, and heart. |
| 6 | Lymphatic Metabolic Ring | Between visceral and skin Ring | Detoxification and lymphatic efficiency. |
| 7 | Skin Metabolic Ring | Outermost Iridology Ring | Skin health and ability to eliminate toxins. |
Step 4: Identify and Interpret Key Defects
Certain defects in Iridology, such ثقوبو cracks, and lines, provide critical insights.
| Defect | وصف | What Indicates |
|---|
| Holes (Pits) | Small depressions in Iridology | Weakness or chronic issues in corresponde organs. |
| Plaques | Flat, discolored areas | Toxin accumulation or poor oxygenation in tissues. |
| Cracks | Irregular fissures | Long-term degeneration or imbalances. |
| Lines | Fine radial streaks | Allergies, poor metabolism, or nervous tension. |
Step 5: Observe Color Changes and Stages Health
Iridology color changes reveal different stages inflammation and organ health deterioration.
| منصة | لون | Indication | Surface Appearance |
|---|
| Inflammatory | Golden Yellow | Active inflammation in affected organs. | Raised surface |
| Sub-Inflammatory | Tea Brown | Moderate inflammation below surface. | Sub-surface |
| مزمن | بني غامق | Reduced organ function and chronic conditions. | Sunken surface |
| التنكسية | Deep Black | Severe tissue degeneration or potential tumor formation. | Deeply sunken surface |
Step 6: Evaluate Iridology Fiber Density
density Iridology fibers reflects person’s immune strength و resilience.
| Density Level | وصف | Health Implications |
|---|
| Level 1 | Tight, silk-like fibers | Strong immunity and high disease resistance. |
| Level 2 | Cotton-like density | Stable health with moderate resilience. |
| Level 3 | Coarse, fabric-like | Weaker constitution, prone to chronic issues. |
| Level 4 | Loose, linen-like fibers | Poor detoxification, chronic imbalances. |
| Level 5 | Twisted, disorganized fibers | Chronic weaknesses and vulnerability to illness. |
| Level 6 | Sparse, extremely loose fibers | Severe immune deficiency, often hereditary. |
Step 7: Correlate Findes with Symptoms
Finally, I compare Iridology findes with client’s symptoms to create holistic picture health. example, if I observe dark areas in digestive zones and client reports bloate or constipation, I can suggest further diagnostic or dietary changes.
Table 1: Six Key Iridology Phenomena
A perfect Iridology h no cracks, holes, or twisted fibers. shows even color and structure, similar to new piece silk fabric. When Iridology changes, often reflects organ dysfunction أو imbalance, indicate sub-health conditions. Below six key phenomena:
| Phenomenon | وصف | Impact on Health |
|---|
| 1. Holes (Pits) | Appear three-dimensional. More holes suggest weaker constitution, often linked to genetic weaknesses. | Open pits easier to treat, while closed pits indicate more severe, harder-to-heal organ issues. |
| 2. Plaques | Flat spots, often cause by long-term antibiotic use. | Common in weak or oxygen-deprived tissue areas, indicate toxin buildup أو reduced circulation. |
| 3. Cracks | Visible irregular fissures. | Often linked to organ degeneration, with symptoms such pain or reduced functionality. |
| 4. Lines | Fine radial lines, often pale in color. | May indicate allergic tendenciesو nervous tension, or poor metabolism. |
| 5. Color Changes | Iridology color shifts dure different health phases (see next table). | Reflects stages اشتعال و organ decline. |
| 6. Fiber Density | Iridology fibers categorized into six density levels (see density table). | Indicates immunityو muscle elasticity, and disease resistance. |
Table 2: Iridology Color Changes by Disease Stage
| منصة | لون | Indication | Surface Appearance |
|---|
| Inflammatory | Golden Yellow | Indicates active اشتعال in body. | Raised surface |
| Sub-Inflammatory | Tea Brown | Less intense, showe moderate level inflammation. | Below surface |
| مزمن | بني غامق | Reflects organ dysfunction or reduced capacity. | Sunken surface |
| التنكسية | Deep Black | Suggests severe organ damage and possible tissue degeneration or tumor formation. | Deeply sunken |
Table 3: Iridology Fiber Density Levels
Fiber density in iridology reveals person’s immunityو resilience, and ability to recover. Variations indicate different constitutional strengths.
| مستوى | وصف | Health Implications |
|---|
| Level 1 | Tight, silk-like fibers | Strong immunity, resilience, and high disease resistance. |
| Level 2 | Cotton-like density | Generally good health, moderate resilience. |
| Level 3 | Coarse fabric-like | Weaker constitution, potential chronic or stress-related health issues. |
| Level 4 | Linen-like, darker fibers | Poor resilience, may indicate long-term imbalances. |
| Level 5 | Twisted, loose fibers | Indicates chronic weaknesses; disorganized fibers suggest poor detoxification and health challenges. |
| Level 6 | Sparse, extremely loose | Reflects severe immune deficiency أو inherited disorders, with high vulnerability to illness. |
Table 4: Seven Iridology Res
Each re around Iridology corresponds to specific system in body. From pupil outward, seven Iridology res provide insight into organ function.
| Re Number | اسم | موقع | What Reflects |
|---|
| 1 | Stomach Re | At pupil-Iridology boundary | Reflects stomach health, digestion, and acidity levels. |
| 2 | Intestinal Re | Outer third Iridology | Indicates intestinal absorption, elimination, and toxin processe. |
| 3 | Autonomic Nerve Re | Just outside intestinal re | Shows balance between nervous system regulation and internal organ function. |
| 4-5 | Visceral Organ Reflex Res | Outside autonomic nerve re | Reflects conditions internal organs such الكبد و قلب. |
| 6 | Lymphatic Metabolic Re | Between visceral and skin res | Indicates lymphatic detoxification and metabolic efficiency. |
| 7 | Skin Metabolic Re | Outermost Iridology re | Reflects health skin and its ability to eliminate waste. |
Table 5: Iridology Clock Positions and Organ Correlation
In iridology, each clock position Iridology relates to specific organs. Memorize these helps identify health issues with precision.
| موقف الساعة | Right Eye (Organ) | Left Eye (Organ) |
|---|
| 12-1 o’clock | Physiological Brain | Psychological Brain |
| 1-2 صباحا | Face | Neck |
| 2-3 jOclock | Throat | Lungs |
| 3-4 أونوك | Upper Back | Thoracic Cavity |
| 4-5 صباحا | Lower Back | Upper Abdomen |
| 5-6 صباحا | Pelvis | Lower Abdomen |
| 6-7 jOclock | Lower Abdomen | Pelvis |
| 7-8 jOclock | Upper Abdomen | Lower Back |
| 8-9 | Thoracic Cavity | Upper Back |
| 9-10 صباحا | Lungs | Throat |
| من 10 إلى 11 | Neck | Face |
| 11-12 صباحا | Psychological Brain | Physiological Brain |
Tips Learne Iridology
| Tip | Advice |
|---|
| 1. Memorization | Familiarize yourself with Iridology -organ map and seven res. |
| 2. Practical Study | Observe multiple Iridology cases to reinforce your understande patterns and signs. |
| 3. Holistic View | Analyze both left and right Iridology together to get complete health overview. |
These tables provide comprehensive guide to mastere iridology step by step.

Conditions Detected Through Iridology Reading
By examining the iris, practitioners can identify early signs of various health conditions. This non-invasive method provides insights into systemic imbalances, helping to address potential issues before they escalate. Below, we explore specific conditions that may be detected through iris analysis.
Hypertension and Cardiovascular Issues
Concentric rings in the iris are often linked to hypertension risk. These patterns may indicate increased دم pressure or arterial plaque buildup. Early detection allows for proactive measures to prevent cardiovascular disease.
Liver and Gallbladder Problems
Scleral yellowing is a common sign of gallbladder dysfunction. Discoloration in the liver zone of the iris may also suggest stress or toxicity. Identifying these signs can guide treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Digestive System Disorders
Radial furrows near the pupil often point to gastric inflammation. Discoloration in the digestive zone may indicate conditions like leaky gut syndrome. Addressing these problems early can improve overall digestive health.
Inflammation and Immune System Health
“Lymphatic rosary” patterns in the iris are associated with immune suppression. Changes in iris topography may predict autoimmune flare-ups. Monitoring these signs helps in managing chronic disease and supporting immune function.
| علامة القزحية | Potential Condition |
|---|
| Concentric Rings | Hypertension |
| Scleral Yellowing | Gallbladder Dysfunction |
| الأخاديد الشعاعية | Gastric Inflammation |
| الوردية اللمفاوية | Immune Suppression |
Controversies and Criticisms of Iridology
قراءة علم القزحية-While iridology has gained attention, its validity remains a topic of debate. Critics argue that the practice lacks scientific backing, while supporters believe it offers valuable health insights. This section explores the controversies surrounding iridology, including its scientific validity, common misconceptions, and potential risks.
Scientific Research and Validity
Numerous studies have questioned the accuracy of iridology. A 1979 JAMA study found 0% accuracy in detecting kidney disease. Similarly, a 2005 Münstedt trial showed no correlation between iris patterns and cancer. These findings challenge the reliability of iridology as a diagnostic tool.
Edzard Ernst’s 2000 review of 77 studies concluded that iridology lacks consistent evidence. While some practitioners claim the iris reflects systemic health, research suggests otherwise. This raises concerns about its use in clinical settings.
Common Misconceptions
One widespread belief is that the iris provides fixed genetic indicators, known as “iris constitutions.” However, biometric studies show that the iris remains stable over time, contradicting claims of diagnostic changes. This undermines the idea that iris patterns can predict health trends.
Another misconception is that iridology can replace traditional medical diagnosis. While it may offer supplementary information, it should not be used as a standalone diagnostic method. Relying solely on iridology can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
Potential Risks and Misdiagnoses
One major risk is delayed diagnosis of serious conditions like cancer. Patients may rely on iridology instead of seeking medical advice from a doctor. This can result in untreated illnesses and worsened health outcomes.
Additionally, iridology often leads to unnecessary supplement regimens. Patients may spend money on treatments for conditions they don’t have. This highlights the need for regulatory oversight in the practice of iridology.
In the U.S. and Canada, certification for iridologists is largely unregulated. This lack of oversight increases the risk of misdiagnosis and unethical practices. Patients should approach iridology with caution and consult licensed healthcare providers for accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
فهم eye’s role in health assessment can open new perspectives. While analyzing iris patterns may offer insights, it should never replace traditional medical diagnostics. A 2015 Australian government review found no evidence supporting its accuracy, and iris recognition technology disproves theories of structural changes over time.
We recommend using this method as a supplemental tool alongside evidence-based practices. For actionable results, consult a doctor or ophthalmologist, especially for scleral changes. Annual eye exams remain the gold standard for preventive care, ensuring early detection of potential issues.
By integrating holistic approaches with modern medicine, patients can achieve a balanced perspective on their health. Always prioritize proven methods for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
التعليمات
ما هو القزحية؟
Iridology is a practice that examines the iris to identify potential health conditions. It is based on the idea that changes in the iris can reflect issues in different parts of the body.
How does iridology work?
Practitioners use tools like magnifying lenses and specialized charts to analyze the iris. They look for patterns, colors, and markings that may indicate health concerns.
What conditions can iridology detect?
It is believed to identify issues like hypertension, liver problems, digestive disorders, and immune system imbalances. However, its effectiveness is debated in the medical community.
هل علم القزحية مثبت علميا؟
While some studies explore its potential, iridology lacks widespread scientific validation. Many medical professionals consider it a complementary tool rather than a diagnostic method.
Are there risks associated with iridology?
Misdiagnosis is a potential risk if relied upon exclusively. It is essential to consult a licensed healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
What tools are used in iridology?
Practitioners often use magnifying lenses, cameras, and iridology charts to examine the iris and interpret its markings.
Can iridology replace traditional medical diagnosis?
No, iridology should not replace conventional medical practices. It is best used as a supplementary tool alongside professional healthcare advice.