Iridologie définie
Iridologie définie
L'iridologie est définie comme la science et l'étude de la couleur et de la structure de l'iris pour déterminer la faiblesse des tissus et la prédisposition du corps à la faiblesse. La science de l'iridologie n'est pas utilisée pour le diagnostic. Il s'agit d'un outil utilisé comme moyen d'évaluation des conditions et des niveaux de santé. Les débuts de l'iridologie ont été cités dans de nombreuses régions du monde et remontent à l'époque des premiers Chaldéens (1000 av.J.-C.) La première référence documentée à l'analyse d'Iris peut être créditée au médecin Philippus Meyens, qui a écrit un livre intitulé «Chiromatica Medica», publié en 1670, qui décrivait les caractéristiques réflexives de l'iris. En 1786, Christaen Haertels a publié son «De Oculo et Signo» traduit du sens «l'œil et ses signes» et avec cela, la signification des signes oculaires gagnait de la crédibilité. L'œil a été examiné à des fins diagnostiques depuis des siècles. Les examens des patients malades. Iris et son marquage, ont publié une œuvre en deux volumes qui a été traduite en ENGILSH et appelée «diagnostic de l'œil». En Amérique, un chiropraticien, le Dr Bernard Jensen, est salué comme l'iridologue le plus accompli de ces dernières années et est connu pour sa philosophie de guérison et ses écrits dans le domaine de l'iridologie. Les médecins en Russie, en Allemagne et en France connaissent davantage la technique iridologique que ceux qui pratiquent en Amérique du Nord. En termes de science, l'expérimentation dans l'évaluation de l'iris est relativement nouvelle et ne doit pas être utilisée isolément mais comme système complet couplé à des antécédents médicaux et à d'autres résultats.

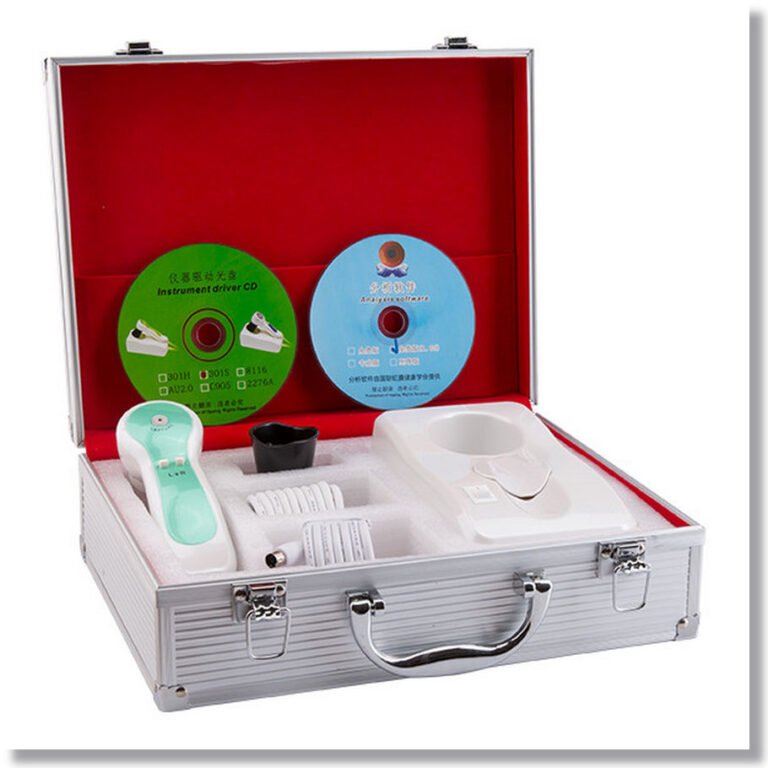
Essential elements to look for in best iridology camera
Essential elements to look for in best iridology camera
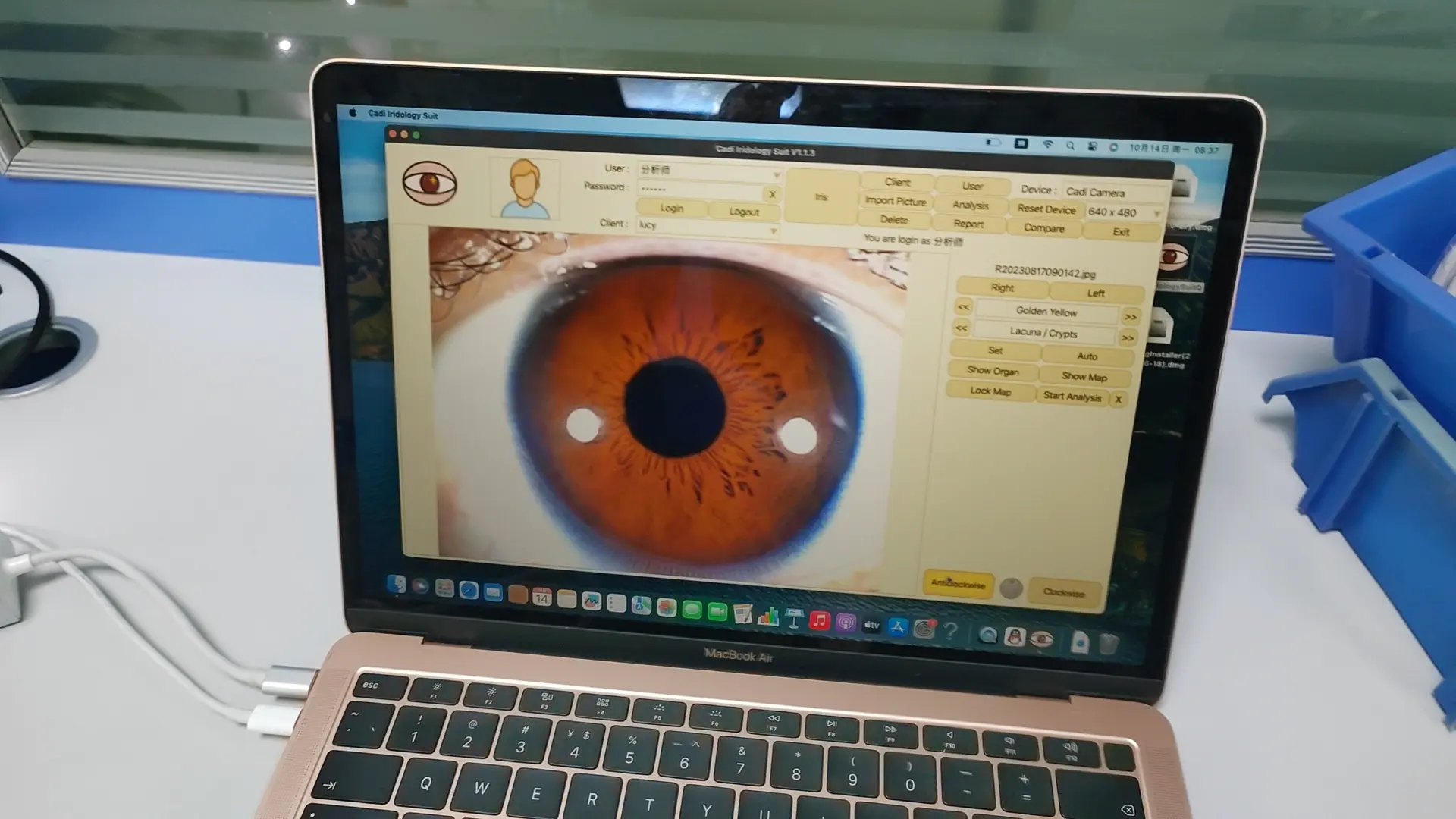
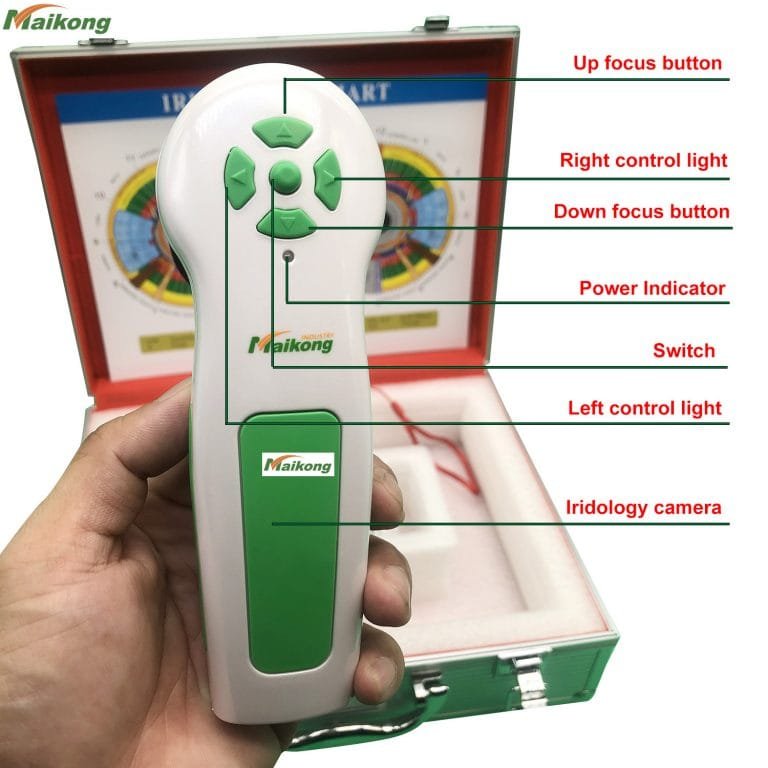
Notre système de fibre optique d'éclairage froid minimise l'irritation du client et donne un éclairage précis pour une exposition optimale et une vraie couleur à chaque fois. Il comprend un ajustement d'intensité variable pour permettre même aux yeux les plus sombres d'afficher chaque détail sans perte de contraste! De plus, nos lumières évitent les élèves pour éviter de mettre des artefacts dans cette zone d'évaluation vitale.
Opération facile. Obtenez une concentration parfaite avec facilité.
L'une des caractéristiques les plus importantes à considérer est l'éclairage. Notre système d'éclairage fixe assure une analyse comparative facile. Option d'éclairage latéral incluse.
Notre concepteur a eu plus de 30 ans d'expérience clinique en tant que ND et iridologue qui apporte avec lui une compréhension approfondie de ce dont les iridologues professionnels ont besoin.
Nous n'utilisons que des caméras de modèle de haute qualité et des matériaux de qualité professionnelle. La plupart de nos systèmes de caméras incluent un logiciel d'analyse de pointe dans le prix.
Tous nos caméras répondent aux critères photographiques de l'Iridology. En fait, nous ouvrons la voie à Iris Photography!

Conclusion for iridology
Conclusion for iridology:
Iridology is an excellent example of pseudoscience in medicine, displaying many of the core features. It was invented by one individual based upon a single observation and emerging from a culture of quackery and pseudoscience. It follows a pre-scientific notion of biology – the homunculus model. It lacks any basis in anatomy, physiology, or any other basic science. Its practitioners are mostly “alternative” practitioners who use the technique as a cold reading. And the research clearly shows that iridology has absolutely no effect – it does not provide any useful information at all.
Quiconque utilise ou promeut l’iridologie est donc un praticien pseudo-scientifique. Toute profession qui soutient l’iridologie n’est pas fondée sur la science et doit être considérée avec méfiance.

Qu’est-ce que l’iridologie ?
Qu’est-ce que l’iridologie ?
Iridology (also known as iridodiagnosis or iridiagnosis) is an alternative medicine technique whose proponents claim that patterns, colors, and other characteristics of the iris can be examined to determine information about a patient’s systemic health. Practitioners match their observations to iris charts, which divide the iris into zones that correspond to specific parts of the human body. Iridologists see the eyes as “fenêtres” into the body’s state of health.
Iridologists claim they can use the charts to distinguish between healthy systems and organs in the body and those that are overactive, inflamed, or distressed. Iridologists claim this information demonstrates a patient’s susceptibility towards certain illnesses, reflects past medical problems, or predicts later health problems.
As opposed to evidence-based medicine, iridology is not supported by quality research studies and is widely considered pseudoscience. The features of the iris are one of the most stable features on the human body throughout life.[disputed – discuss] The stability of iris structures is the foundation of the biometric technology which uses iris recognition for identification purposes.
In 1979, Bernard Jensen, a leading American iridologist, and two other iridology proponents failed to establish the basis of their practice when they examined photographs of the eyes of 143 patients in an attempt to determine which ones had kidney impairments. Of the patients, forty-eight had been diagnosed with kidney disease, and the rest had normal kidney function. Based on their analysis of the patients’ irises, the three iridologists could not detect which patients had kidney disease and which did not.
The iris is the greenish-yellow area surrounding the transparent pupil (showing as black). The white outer area is the sclera, the central transparent part of which is the cornea.Iridologists generally use equipment such as a flashlight and magnifying glass, cameras or slit-lamp microscopes to examine a patient’s irises for tissue changes, as well as features such as specific pigment patterns and irregular stromal architecture. The markings and patterns are compared to an iris chart that correlates zones of the iris with parts of the body. Typical charts divide the iris into approximately 80–90 zones. For example, the zone corresponding to the kidney is in the lower part of the iris, just before 6 o’clock. There are minor variations between charts’ associations between body parts and areas of the iris.
According to iridologists, details in the iris reflect changes in the tissues of the corresponding body organs. One prominent practitioner, Bernard Jensen, described it thus: “Les fibres nerveuses de l'iris répondent aux changements dans les tissus corporels en manifestant une physiologie réflexe qui correspond à des changements et des emplacements tissulaires spécifiques.” This would mean that a bodily condition translates to a noticeable change in the appearance of the iris, but this has been disproven through many studies. (See section on Scientific research.) For example, acute inflammatory, chronic inflammatory and catarrhal signs may indicate involvement, maintenance, or healing of corresponding distant tissues, respectively. Other features that iridologists look for are contraction rings and Klumpenzellen, which may indicate various other health conditions.
Sept anneaux Zones/anneaux de l'iris et région/organe du corps qui l'accompagnent
Inner: Stomach.
Second: Small and large intestine.
Third: Circulation of blood and lymph.
Fourth: Internal organs and endocrine system.
Fifth: Musculoskeletal system.
Outer: Skin and organs of elimination.