<<Illustration of Iridology>> – Chapter 2: Eye Structure and Iris Functions
Chapter 2: Eye Structure and Iris Functions
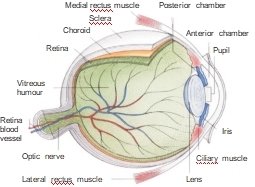
2.1 The Structure of an Eye
The eye is the most vital organ for human perception, with approximately 80% of knowledge and memory in the brain acquired through vision.
The eye is a visual system organ—a hollow, spherical structure situated within the skull’s orbit. It comprises three layers enclosed by various anatomical structures:
- The outermost layer (fibrous tunic): Cornea and sclera
- The middle layer (vascular tunic/uvea): Iris, ciliary body, and choroid
- The innermost layer: Retina
The Outermost Layer: Cornea and Sclera
- Cornea: A transparent frontal portion covering the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. It lacks blood vessels (avascular) and functions primarily to refract light, focusing most incoming light into the eye. The canal of Schlemm marks the junction between the cornea and sclera.
- Sclera: The white, collagen-rich outer layer covering most of the eyeball, providing structural protection and maintaining the eye’s shape.
The Middle Layer: Iris, Ciliary Body, and Choroid
- Iris: A circular, pigmented muscular diaphragm controlling pupil size (2.5–4 mm diameter) to regulate light entry. Its colour determines eye colour.
- Ciliary Body: A ring-shaped tissue extending from the choroid, containing muscles and connective tissue. It connects to the lens via zonular fibres, adjusting lens shape for retinal focus.
- Choroid: A vascular layer between the retina and sclera, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the retina’s outer layers. Its dark pigment minimises internal light reflection, preventing visual distortion.
The Innermost Layer: Retina A sensory membrane lining the eyeball’s posterior, converting light into neural signals for visual perception.
2.2 What Is the Iris?
The iris is the foremost part of the uvea, in front of the lens of the eye. It is a thin, circular  structure which controls the diameter and size of the pupil from around 2.5 mm to 4 mm in its center. The surface of the iris has crypts of Fuchs, radial stripes and wrinkles, called the iris texture. Different iris texture features record different body condition or status, so the iris has its uniqueness in reflexing body healthy.
structure which controls the diameter and size of the pupil from around 2.5 mm to 4 mm in its center. The surface of the iris has crypts of Fuchs, radial stripes and wrinkles, called the iris texture. Different iris texture features record different body condition or status, so the iris has its uniqueness in reflexing body healthy.
2.3 The Structure of the Iris
The iris comprises three layers:
- Anterior Layer: Lacks epithelium; projects as dilator muscles.
- Stroma: A pigmented fibrovascular layer with blood vessels, nerves, and pigment granules (varies by eye colour).

- Posterior Layer (Iris Pigment Epithelium): A two-cell-thick, heavily pigmented layer blocking stray light from reaching the retina.
2.4 The colour of iris
The iris is usually strongly pigmented, with the color typically ranging between brown, hazel, green, gray, or blue. The pigment that contributes to human iris color is the dark pigment melanin.
So, the quantity of melanin pigment is a main factor in determining the eye color.
Iris color is due to variable amounts of eumelanin (brown/black melanins) and pheomelanin (red/yellow melanins) produced by melanocytes. More of the former is found in brown-eyed people and of the latter in blue and green-eyed people. Iris color is a combined effects of texture, pigmentation, fibrous tissue and blood vessels within the iris stroma. The genetics of eye color are complicated, and color is determined by multiple genes.
Changes of eye colors, lightening or darkening, during early childhood, puberty, pregnancy, and sometimes after serious trauma do represent cause for a plausible argument stating that some eyes can or do change, based on chemical reactions and hormonal changes within the body. Eye color changes can be a warning sign of certain diseases, such as Fuch’s heterochromic iridocyclitis, Horner’s syndrome or pigmentary glaucoma.








2.5Features of iris
The functions of iris are to control the opening size of the pupil in order to control the amount of light entering the eye. It also control the thickness of the lens for focusing. These are why the brain can have a clear and sharp image to interact with the environment either in day or night. Not only these, iris also reflex the healthiness of the body.
2.6Iris and Healthy
The eyes are not only for us to observe the world, but also a mean for observing the health of the body. Eye is a magical mirror, which will reflect the health information of the body through various forms on the iris surface such as unnatural colourings, crypts (lesion, lacunae), spokes (radial furrows, radii solaris), pigment spot etc.. It is easy and reliable to find out the unhealthy body information appeared on the iris surface, such as psychological, physiological and physical changes.
For examples:
1)The tissue on the iris forming a crypt means that the corresponding organ is weak and is facing of a potential health risk.
2)There are more than three concentric rings on the iris, reflecting that the psychological stress is high, the body may have pain and poor sleeping quality.
In short, the signs on the iris are the distress signals from the body. If we know the signals, it can be dealt with or be avoided.
TCM Argument: The human body has twelve meridians with direct or indirect relationship with the eyes. Therefore, the doctor observes the iris as a diagnostic criterion for life phenomena, such as the reduction of iris with enlarged pupil and eyes are fixed indicating the end of life, so the iris is closely related to health.