Iridology is the study of the iris, the colored part of the eye, as a way to identify potential health conditions and genetic predispositions. This alternative health practice analyzes patterns, colors, and other characteristics of the iris to evaluate a person’s overall health status. While controversial in conventional medicine, iridology has gained popularity among holistic health practitioners who believe the eyes can reveal valuable insights about the body’s systems and functions.
Iridology Definition: Understanding the Basics
Iridology, pronounced eye-rid-ology, is defined as the study of the iris structure and its pigmentation patterns as they relate to revealing information about a person’s health. Practitioners believe that the iris connects to every organ and tissue in the body through the nervous system and can reflect changes in these tissues through its appearance.
The fundamental iridology definition centers on the concept that the iris serves as a “mappa” of the body, with different zones corresponding to specific organs and systems. According to iridology theory, this colored part of the eye can display signs of accumulated toxins, inflammation, and inherent strengths or weaknesses in various bodily systems.



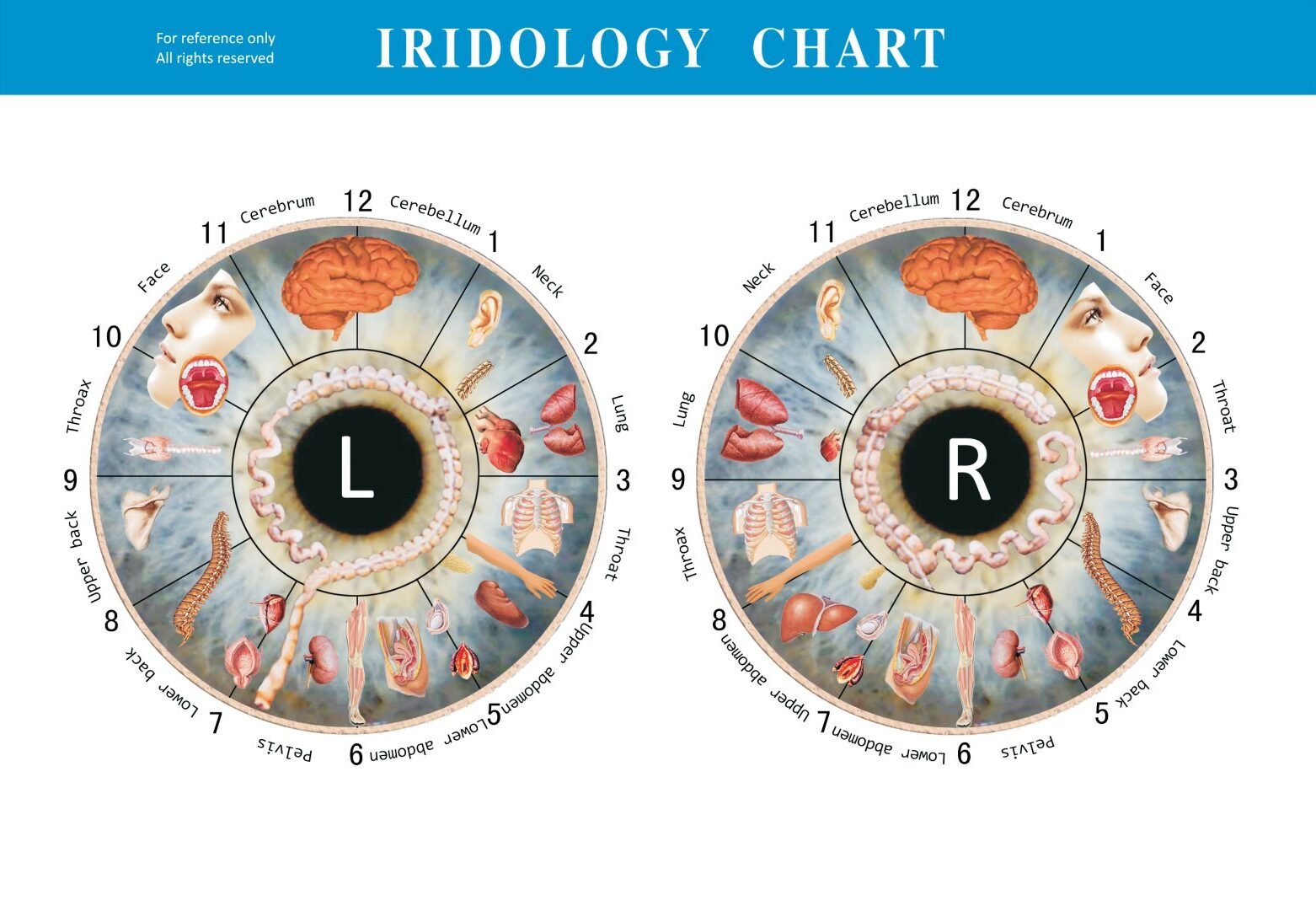
Iridology chart showing how different sections of the iris correspond to various body organs and systems
Principi fondamentali dell'iridologia
Iridology is based on several key principles that guide how practitioners interpret what they observe in the iris. Understanding these foundational concepts provides insight into how this practice approaches health assessment.
The Iris as a Reflex Map
The primary principle of iridology is that the iris contains a detailed reflex map of the body. Each area of the iris corresponds to specific organs and body systems through neurological connections. Iridologists use specialized charts that divide the iris into approximately 80-90 zones, each representing different parts of the body.
Valutazione costituzionale
Iridologists believe they can determine a person’s inherent constitutional strengths and weaknesses by analyzing the structure of iris fibers. Dense, tightly packed fibers may indicate strong genetic constitution, while loose, separated fibers might suggest inherited weaknesses in certain areas.

Four Main Assessment Factors
Iridology evaluates health based on four primary factors that practitioners analyze in the iris:
- Blood circulation patterns reflected in iris coloration
- Condition of the nervous system shown through iris fiber structure
- Lymphatic system status indicated by specific markings
- Nutritional status and metabolic function revealed through pigmentation
Segni e segni dell'iride
Specific features in the iris are interpreted as signs of particular health conditions:
- Lesions or breaks in iris fibers may indicate tissue damage
- White rings around the iris (arcus senilis) might suggest cholesterol issues
- Dark spots could indicate toxin accumulation
- Color changes may reflect inflammation or chemical imbalances
- Radial lines might show stress in specific organs
- Pigment clusters could reveal genetic predispositions
Historical Origins of Iridology
The practice of iridology has roots that stretch back centuries, though its modern form developed primarily in the 19th century. Understanding its historical development provides context for how this alternative health practice evolved.

Dr. Ignaz von Peczely, Hungarian physician considered the father of modern iridology
Antichi inizi
References to examining the eyes for health assessment appear in ancient Egyptian, Chinese, and Indian texts dating back over 3,000 years. These early practices recognized that changes in the eyes could reflect health conditions, though they lacked the systematic approach of modern iridology.
The Birth of Modern Iridology
The foundations of contemporary iridology began with Dr. Ignaz von Peczely, a Hungarian physician in the 1800s. As a child, von Peczely noticed changes in an owl’s iris after the bird suffered a broken leg. This observation sparked his interest in the connection between iris markings and physical trauma or disease.
In 1881, von Peczely published his first book on iris diagnosis, Discoveries in the Field of Natural Science and Medicine: Instruction in the Study of Diagnosis from the Eye, which included the first modern iridology chart mapping iris zones to body organs.
Development and Expansion
Nils Liljequist, a Swedish homeopath, independently developed similar theories after observing changes in his own iris following medical treatments. His work, published in 1893, contributed significantly to the field’s development.
In the 20th century, iridology gained popularity in the United States through the work of Dr. Bernard Jensen, a chiropractor who refined iridology techniques and created detailed iris charts that are still used by many practitioners today.
Modern Iridology Practice
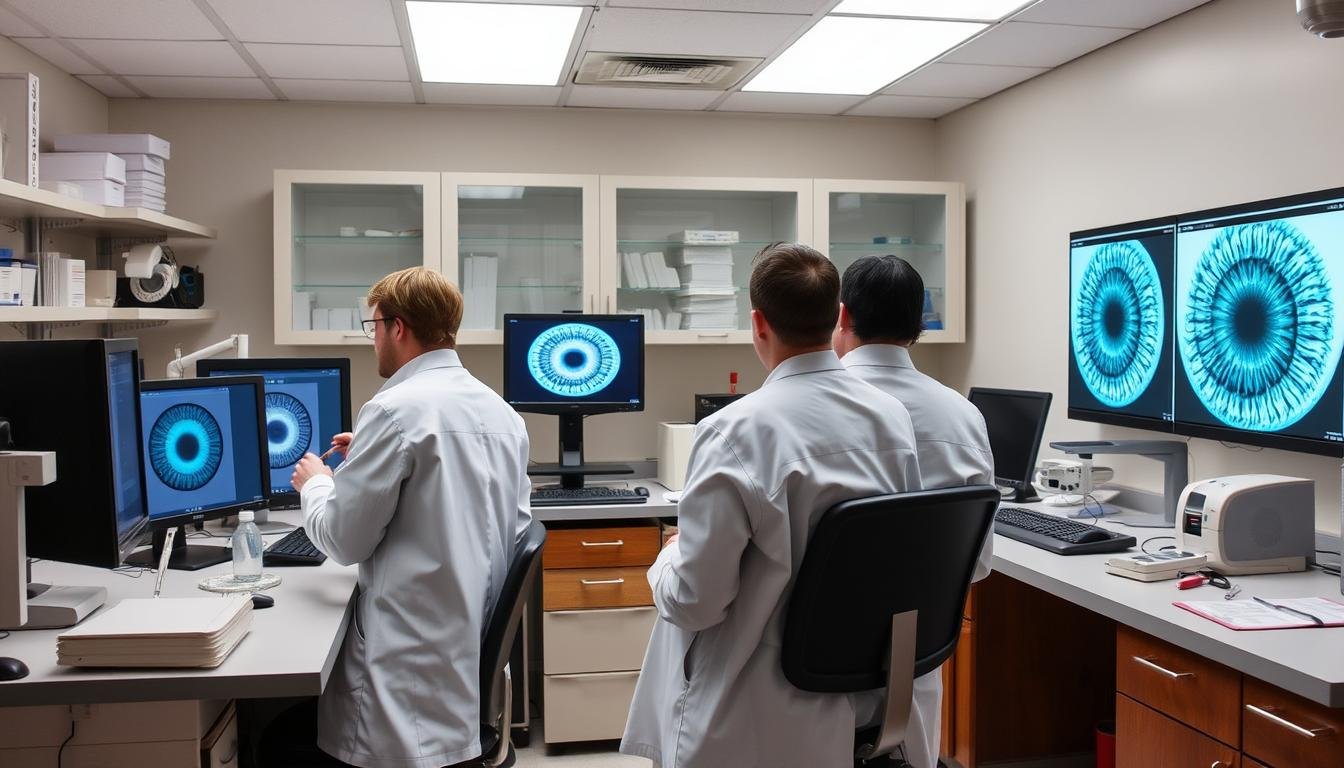
Today’s iridology has evolved with technology and standardized approaches. Modern practitioners use specialized equipment and follow systematic methods to conduct their analyses.

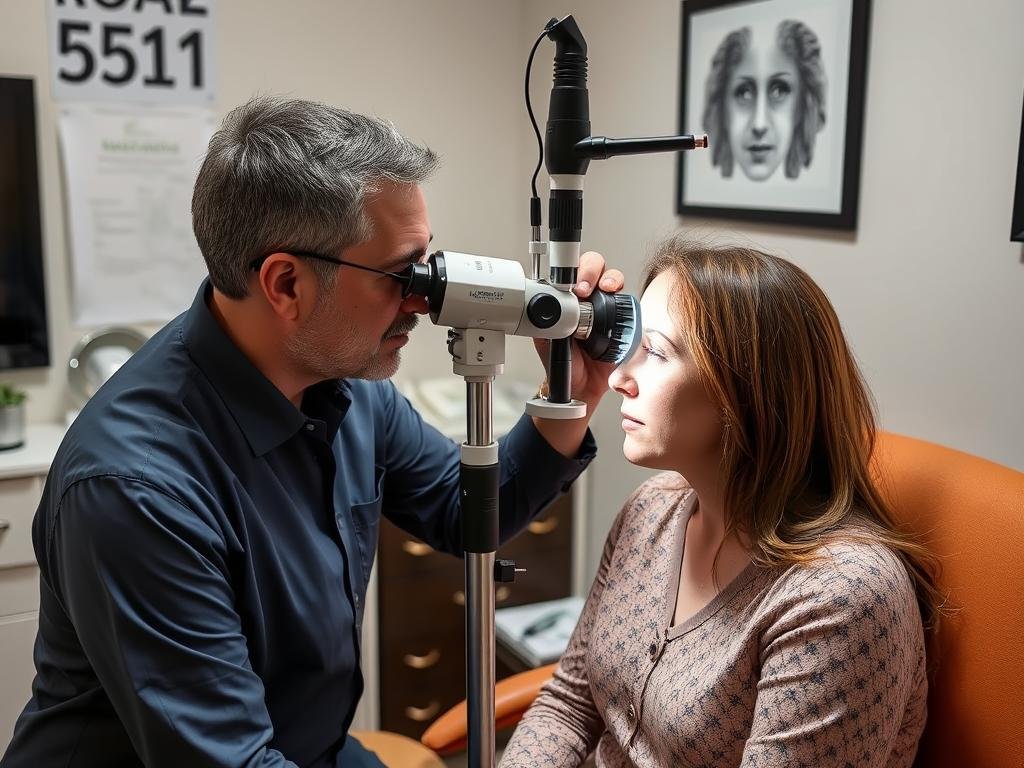
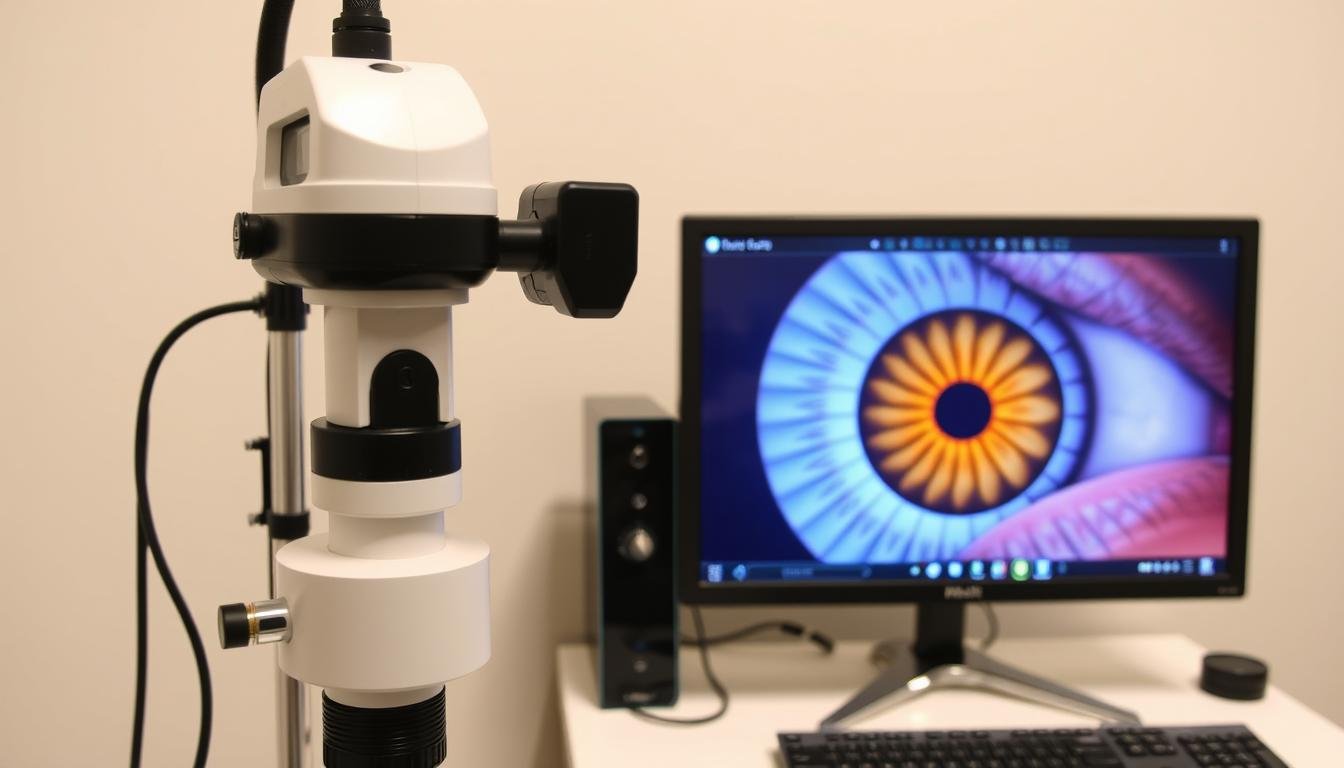
Modern digital iridology equipment capturing high-resolution iris images for detailed analysis
Processo d'esame
A typical iridology examination involves several steps:
- The practitioner takes high-resolution photographs of both irises using specialized cameras or digital iriscopes
- These images are often magnified 10-30 times their actual size for detailed analysis
- The iridologist examines the structure, color, and markings in each zone of the iris
- Findings are compared against standardized iridology charts
- The practitioner develops an assessment based on observed patterns
Types of Iridology Analysis
Modern iridology encompasses several approaches to analysis:
Iridologia costituzionale
Focuses on inherited traits and genetic predispositions visible in the iris structure. This approach helps identify inherent strengths and weaknesses in a person’s health profile.
Comprehensive Iridology
Combines constitutional analysis with examination of acquired markings to provide a complete health assessment, including both genetic factors and lifestyle influences.
Interested in Learning More About Eye Health?
Discover how comprehensive eye exams can provide insights into your overall health and detect potential issues early.
Explore Eye Exam Resources
Applications of Iridology
Practitioners apply iridology in various contexts, though its applications differ significantly from conventional medical diagnostics. Understanding how iridology is used helps clarify its role in alternative health practices.

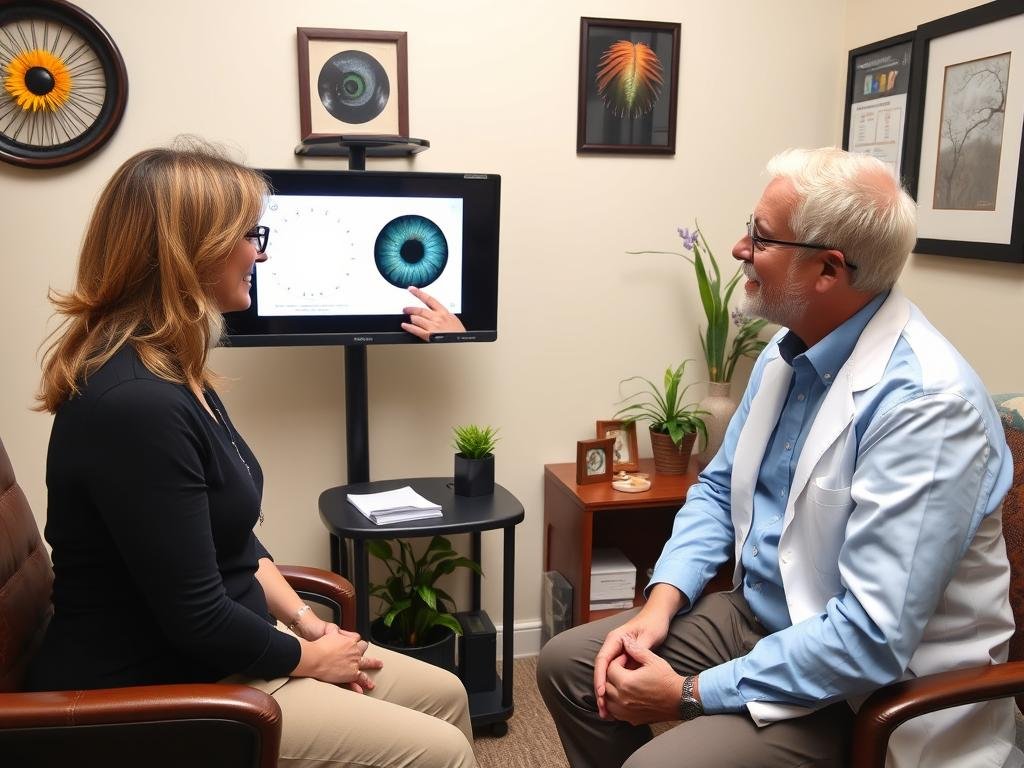
Iridologist discussing analysis findings with a client during a health consultation
Valutazione della salute
The primary application of iridology is as a health assessment tool. Practitioners use it to:
- Identify potential areas of weakness or congestion in body systems
- Detect signs of inflammation or toxin accumulation
- Valutare i fabbisogni e le carenze nutrizionali
- Evaluate stress patterns and their impact on specific organs
- Determine constitutional strengths that can support healing
Complementary Health Approach
Iridology is typically used alongside other alternative health practices rather than as a standalone diagnostic method. It often informs:
- Nutritional and dietary recommendations
- Herbal and supplement protocols
- Detoxification programs
- Lifestyle modification suggestions
- Preventative health strategies
- Personalized wellness plans
Limitations in Application
It’s important to note that iridology has significant limitations in its applications:
- It cannot diagnose specific diseases or medical conditions
- It does not replace conventional medical testing or diagnosis
- It cannot detect acute conditions requiring immediate medical attention
- It should not be used to prescribe pharmaceutical medications
Prospettiva scientifica sull'iridologia
The scientific and medical communities have extensively examined iridology’s claims, and it’s important to understand their perspective when considering this practice.

Scientific research examining the validity of iridology claims through controlled studies
Risultati della ricerca
Multiple scientific studies have investigated iridology’s effectiveness as a diagnostic tool:
- A systematic review published in Ricerca Med complementare (1999) examined four controlled studies and found no evidence supporting iridology as a valid diagnostic method
- Ricerca pubblicata su Archivi di oftalmologia (2000) concluded that iridology lacked scientific merit as a health assessment tool
- Multiple blind trials have shown that iridologists could not consistently identify patients with known diseases by examining their irises
Medical Community Position
The consensus among conventional medical practitioners regarding iridology includes:
Medical Concerns About Iridology
- Mancanza di meccanismo anatomico o fisiologico per spiegare come gli organi interni influenzerebbero l'aspetto dell'iride
- Potential for missed or delayed diagnosis of serious conditions if relying on iridology
- Absence of standardized, reproducible diagnostic criteria
- Risk of unnecessary treatments based on inaccurate assessments
Balanced Perspective
While scientific evidence does not support iridology’s diagnostic claims, some researchers note:
- The iris does contain rich information about a person’s genetic makeup
- Some systemic conditions can cause visible changes in the eyes (though not necessarily in the patterns described by iridology)
- The holistic approach of considering the whole person rather than isolated symptoms has value
Considerations When Exploring Iridology
If you’re interested in iridologia, there are several important factors to consider before pursuing this alternative health practice.

Researching iridology practitioners and their qualifications is essential before booking a consultation
Practitioner Qualifications
When selecting an iridologist, consider:
- Training and certification from recognized iridology organizations
- Years of experience practicing iridology
- Additional health credentials (many iridologists are also naturopaths, nutritionists, or other health practitioners)
- Client testimonials and reviews
- Transparency about limitations and scope of practice
Integration with Conventional Care
For a balanced approach to health:
- Maintain regular check-ups with your primary healthcare provider
- Do not discontinue prescribed medications without consulting your doctor
- Inform all healthcare providers about complementary approaches you’re pursuing
- Use iridology as a complementary tool rather than a replacement for medical care
- Seek immediate medical attention for acute or serious symptoms
Setting Realistic Expectations
Understanding what iridology can and cannot offer helps establish appropriate expectations:
Potenziali benefici
- Insights into constitutional tendencies
- Early awareness of potential health imbalances
- Personalized wellness suggestions
Limitazioni
- Non è possibile diagnosticare malattie specifiche
- Not a substitute for medical tests
- Results interpretation varies between practitioners
Conclusion: Iridology in Context
Iridology offers an intriguing perspective on health assessment through examination of the iris. While its fundamental definition centers on analyzing the colored part of the eye to evaluate health status, the practice exists in a space between traditional healing arts and modern healthcare approaches.
The scientific community remains skeptical of iridology’s diagnostic claims due to lack of supporting evidence in controlled studies. However, many individuals find value in the holistic perspective it provides, particularly when used as one component of a comprehensive wellness approach rather than as a standalone diagnostic method.
Whether you’re curious about iridology or considering a consultation, approaching this practice with informed expectations is essential. Understanding both its historical context and current limitations allows for a balanced perspective on what iridology can realistically offer as a complementary health assessment tool.

Each iris is as unique as a fingerprint, with patterns that remain largely stable throughout life
Explore Your Eye Health Options
Whether you’re interested in conventional eye care or alternative approaches like iridology, making informed decisions starts with quality information.