The practice of iridology has a rich and fascinating history spanning centuries. From ancient observations to modern diagnostic techniques, iridologistas have developed a unique approach to understanding health through the iris of the eye. This comprehensive guide explores the origins, evolution, and key figures who shaped this alternative health practice, while examining how modern iridologistas continue to develop and apply these techniques today.O que é um Iridologista?

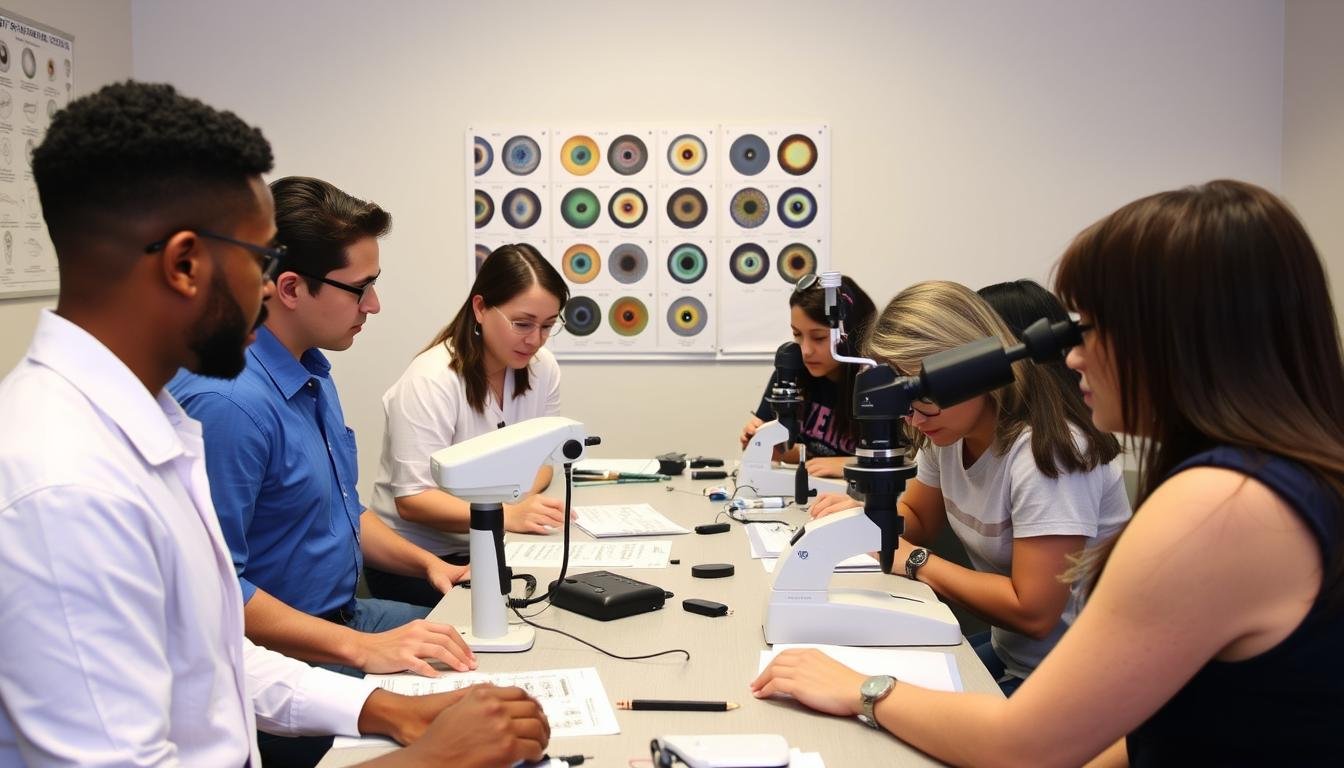
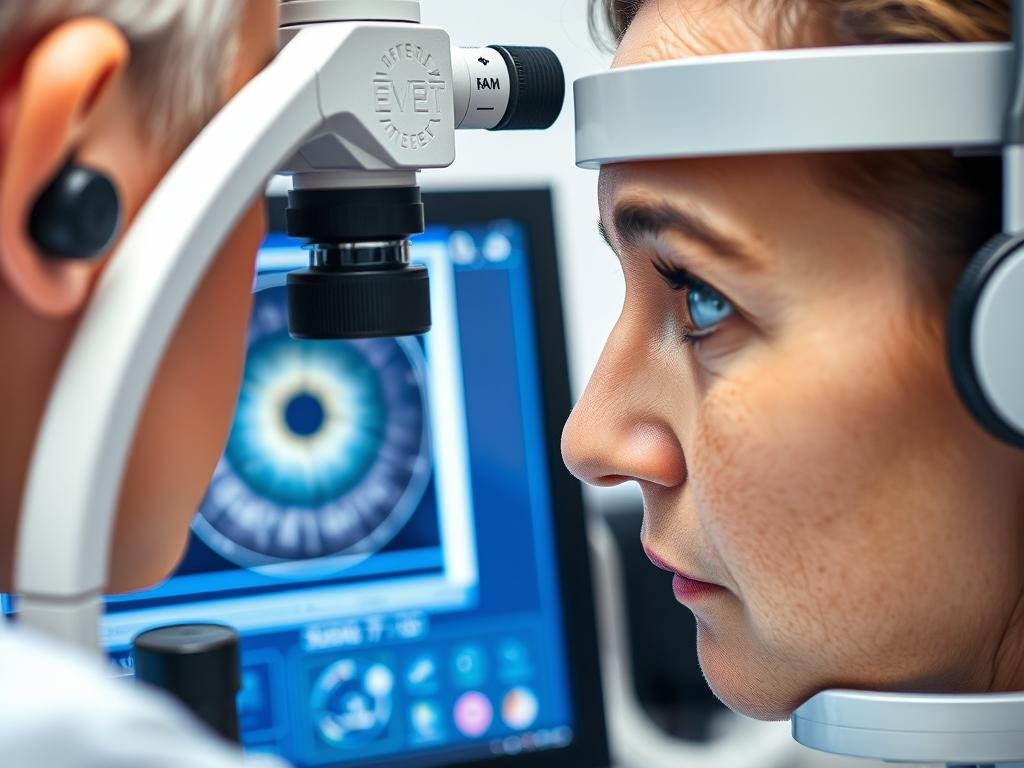
Um iridologista examining a patient’s iris using specialized equipment
Um iridologista is a practitioner who analyzes patterns, colors, and other characteristics in the iris of the eye to determine information about a person’s health. Based on the theory that the iris connects to every organ and tissue via the nervous system, iridologistas believe that these connections are reflected in the iris through distinctive signs and marks.
Unlike conventional eye doctors who focus on eye health and vision correction, iridologistas use the iris as a diagnostic tool to identify potential health issues throughout the entire body. They analyze the iris using specialized charts that divide it into zones, each corresponding to different organs and body systems.
“The eyes are not only the windows to the soul but also a map to understanding the body’s past, present, and potential future health conditions.” – Bernard Jensen, pioneering iridologista
In alternative medicine, iridologistas often work alongside other holistic practitioners or may integrate iridology with other healing modalities such as naturopathy, herbalism, or nutritional therapy. Their primary goal is to identify signs of inflammation, toxin accumulation, and organ weaknesses before they manifest as serious health problems.
The Diagnostic Methods of Iridologistas
Moderno iridologistas employ several diagnostic techniques and tools to analyze the iris effectively:



Iridology chart used by iridologistas para mapear zonas da íris para sistemas corporais
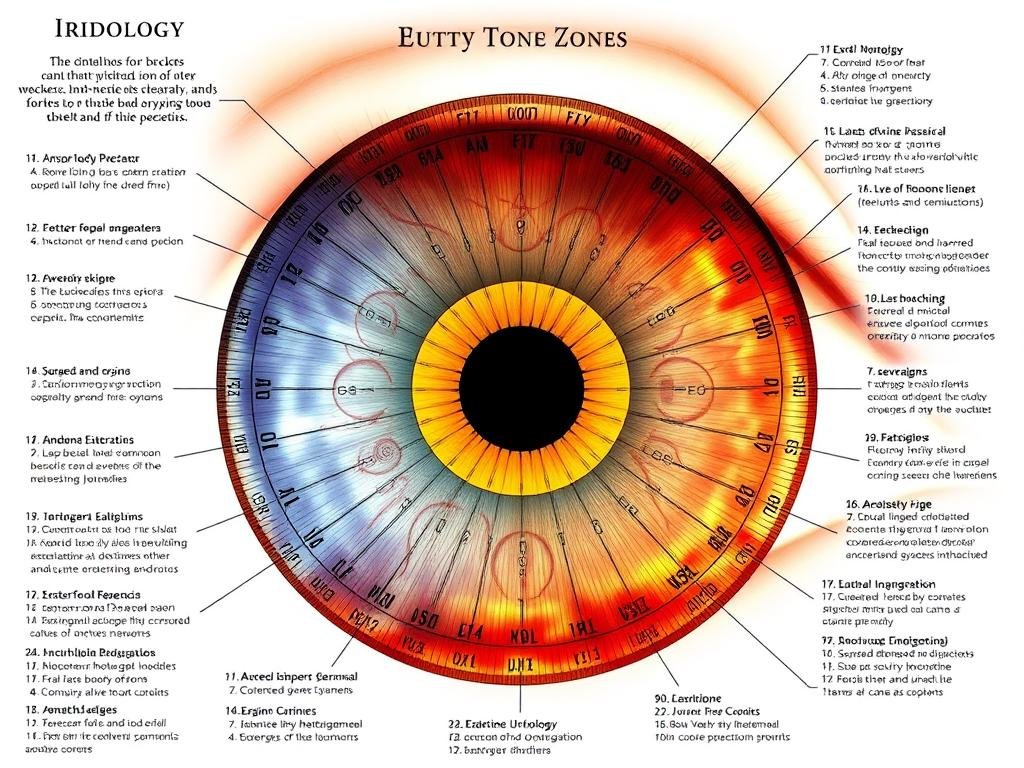
Mapeamento de íris
The foundation of an iridologist’s practice is the iris chart or map. These charts divide the iris into approximately 80-90 zones, each corresponding to different organs and systems in the body. The right iris is generally associated with the right side of the body, while the left iris corresponds to the left side.
Iridologistas carefully examine each zone for signs like color changes, dark spots, rings, and structural patterns that may indicate health conditions in the corresponding body areas.
Equipment and Technology
Profissional iridologistas use specialized equipment to examine the iris in detail:
- Iriscopes – specialized microscopes designed specifically for iris examination
- High-resolution digital cameras with macro lenses
- Slit lamps – providing focused illumination
- Computer software for iris analysis and record-keeping
These tools allow for detailed documentation and comparison of iris changes over time.
During a typical session, an iridologista will first take photographs or directly examine both irises under magnification. They then analyze the iris structures, noting any abnormalities according to iridology principles. Based on their findings, they may recommend dietary changes, herbal supplements, detoxification protocols, or lifestyle modifications to address potential health imbalances.
Origins of Iridology and Early Iridologistas
The practice of examining the iris for health insights has ancient roots, with evidence suggesting early forms of iris analysis in various cultures around the world. However, the systematic development of iridology as we know it today began to take shape in the 19th century.

Ancient manuscript depicting early eye examination techniques that preceded modern iridology
Some historical records suggest that forms of iris analysis existed in ancient Egypt, with hieroglyphics indicating possible connections between eye markings and health. Similarly, ancient Chinese and Greek texts contain references to examining the eyes for diagnostic purposes, though these were not as systematized as modern iridology.
The first documented reference to a form of iridology appears in Philippus Meyeus’ book Médico cromático, published in 1665. In this work, Meyeus described how changes in the iris could indicate health issues before physical symptoms appeared elsewhere in the body.
However, it wasn’t until the 19th century that iridology began to develop into a more structured practice, thanks to the work of several pioneering iridologistas.
Dr. Inácio de Peczely – The First Modern Iridologista

Dr. Ignaz von Peczely, considerado o pai da iridologia moderna
The most widely recognized founder of modern iridology is Dr. Ignaz von Peczely (1826-1911), a Hungarian physician. The origin story of his discovery has become somewhat legendary in iridologista circles.
As a child, von Peczely reportedly caught an owl that broke its leg while struggling to escape. At that moment, he noticed a dark streak appear in the owl’s iris. This observation sparked his curiosity about the connection between body injuries and changes in the iris.
Years later, as a physician, von Peczely began systematically studying this phenomenon in his patients. He observed that specific injuries and diseases corresponded to particular markings in the iris. In 1881, he published his findings in the book Descobertas no campo das ciências naturais e da medicina: instruções no estudo do diagnóstico ocular.
Von Peczely developed the first comprehensive iris chart, mapping the iris into zones that corresponded to different organs and body systems. This chart became the foundation upon which future iridologistas would build their practice.
Nils Liljequist’s Contributions to Iridologista Prática
Working independently and unaware of von Peczely’s research, Swedish homeopath Nils Liljequist (1851-1936) made similar discoveries about the iris. His interest in iris analysis stemmed from personal experience – after receiving medications containing quinine and iodine for malaria and other conditions, he noticed changes in his own iris coloration.

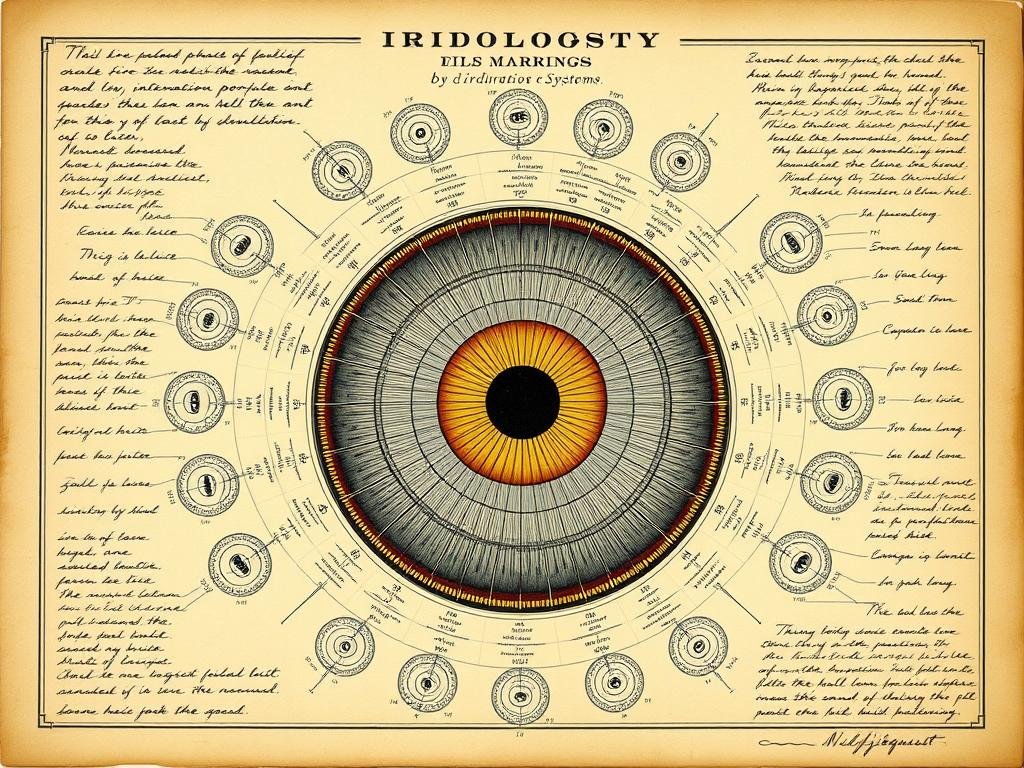
Early iridology chart developed by Nils Liljequist showing iris markings and their significance
Liljequist documented these changes meticulously and published his observations in Sobre o diagnóstico ocular (About Eye Diagnosis) in 1893. His work particularly focused on how drug deposits affected the iris, noting that medications could cause specific discolorations.
The contributions of both von Peczely and Liljequist were remarkable because they developed similar theories and iris charts independently, lending credibility to the foundational concepts of iridology. Their work established the core principles that iridologistas still use today:
- The iris connects to all organs and tissues via the nervous system
- Changes in the body are reflected in specific areas of the iris
- The iris can reveal inherent strengths and weaknesses in the body
- Iris markings can indicate past, present, and potential future health conditions
These early iridologistas laid the groundwork for what would become a global alternative health practice in the 20th century.
20th Century Developments in Iridologista Prática
The 20th century saw significant advancements in iridology, with new practitioners building upon the foundational work of von Peczely and Liljequist. During this period, iridology spread globally and became more systematized as a practice.
In the early 1900s, German iridologista Pastor Emanuel Felke further developed iridology techniques and integrated them with other natural healing methods. His approach, combining iridology with homeopathy, became known as the “Felke cure.” He established several natural healing clinics in Germany where iridology was a primary diagnostic tool.
Around the same time, Dr. Henry Edward Lane brought iridology to America and published Iridologia: o diagnóstico do olho in 1904, helping to popularize the practice in the United States.
Bernardo Jensen – Popularizing Iridologista Techniques

Dr. Bernard Jensen, who standardized modern iridologista técnicas
Perhaps the most influential figure in modern iridology was Dr. Bernard Jensen (1908-2001), an American chiropractor and nutritionist. Jensen studied under various European iridologistas before developing his own comprehensive approach to iris analysis.
In the 1950s, Jensen created a detailed iris chart that expanded on previous work, mapping the iris into more specific zones. His chart is still widely used by iridologistas today and is considered the standard in the field. Jensen’s approach emphasized the connection between iris signs and nutritional deficiencies, making dietary recommendations a central part of his practice.
Jensen é autor de vários livros sobre iridologia, incluindo A ciência e a prática da iridologia (1952) and Iridologia: a ciência e a prática nas artes da cura (1982). These comprehensive works helped standardize iridology practices and brought the field to a wider audience.
“The iris never lies. It’s a recording of what’s been going on in the body.” – Dr. Bernard Jensen
Jensen also established the first major iridology school in the United States, training thousands of practitioners and elevating the professional standards of iridologistas. His emphasis on scientific documentation and systematic analysis helped bring more credibility to the practice.
Technological Advancements for Iridologistas

Modern digital iriscope used by contemporary iridologistas
The latter half of the 20th century brought significant technological advancements that transformed how iridologistas practice. These innovations included:
Improved Imaging Technology
The development of high-resolution cameras and specialized iriscopes allowed iridologistas to capture detailed images of the iris. These tools provided much clearer visualization of iris structures than was previously possible with simple magnifying glasses.
Digital photography further revolutionized the field, enabling iridologistas to document iris changes over time and compare images with precision.
Computer Analysis
The introduction of computer software designed specifically for iris analysis represented a major advancement. These programs could:
- Enhance iris images for better visibility of details
- Map iris zones automatically
- Compare current images with previous ones to track changes
- Generate detailed reports based on iris findings
By the end of the 20th century, iridology had evolved from a relatively simple observational practice to a more sophisticated system utilizing advanced technology. Modern iridologistas could document their findings with greater precision and maintain detailed records of their patients’ iris changes over time.
Despite these technological advances, the core principles established by the early pioneers remained fundamental to iridologista practice. The iris chart, though refined and expanded, still followed the basic mapping concept introduced by von Peczely and developed by Jensen.
How to Become a Certified Iridologista Hoje

Students learning iris analysis techniques in an iridologista certification program
For those interested in pursuing a career as an iridologista, there are several educational paths available today. While iridology is not regulated by governmental medical boards in most countries, there are reputable certification programs that provide comprehensive training.
Explore Professional Iridology Certification
Ready to deepen your understanding of iridology and gain professional credentials? Our comprehensive certification program provides the skills and knowledge needed to practice as a qualified iridologista.
Discover Certification Options
Most iridology training programs include the following components:
| Training Component | Descrição | Duração Típica |
| Foundational Theory | History of iridology, basic principles, iris topography, and constitutional types | 40-60 hours |
| Análise da íris | Detailed study of iris signs, markings, colors, and their interpretations | 80-100 hours |
| Clinical Practice | Supervised practice sessions analyzing real iris photographs and case studies | 50-100 horas |
| Treinamento de equipamentos | Learning to use iriscopes, cameras, and analysis software | 20-30 hours |
| Complementary Studies | Basic anatomy, physiology, nutrition, and natural remedies | 60-100 hours |
Several organizations offer respected certification programs for aspiring iridologistas:
- Associação Internacional de Profissionais de Iridologia (IIPA)
- Associação Nacional de Pesquisa em Iridologia (NIRA)
- Guild of Naturopathic Iridologists International (GNI)
- Institute of Applied Iridology
- Bastyr University (offers courses in iridology as part of naturopathic programs)
Muitos iridologistas also pursue additional education in complementary fields such as naturopathy, nutrition, herbalism, or other holistic health practices. This integrated approach allows practitioners to offer more comprehensive health guidance based on their iris analysis findings.

Moderno iridologista using digital equipment for precise iris analysis
Continuing education is an important aspect of an iridologist’s career, as the field continues to evolve with new research and technological advancements. Most certification programs require ongoing education to maintain credentials.
A Perspectiva Científica sobre Iridologista Práticas
While iridology has a dedicated following among alternative health practitioners, it’s important to understand how the conventional medical and scientific communities view this practice.

Scientific research examining claims made by iridologistas
The scientific community has conducted several studies to evaluate the efficacy and validity of iridology as a diagnostic tool. Most of these studies have not supported the fundamental claims made by iridologistas.
Argumentos de apoio
- A íris contém milhares de terminações nervosas conectadas ao cérebro através do nervo óptico
- Some health conditions do cause visible changes in the eyes (though not necessarily in the iris patterns)
- Anecdotal success stories from patients who have benefited from iridologista consultations
- Potential value as a complementary assessment tool when used alongside conventional diagnostics
Perspectivas críticas
- Lack of consistent scientific evidence supporting diagnostic accuracy
- Controlled studies have not shown iridologistas can reliably identify specific diseases
- No proven physiological mechanism explaining how internal organs would affect iris patterns
- Risk of missed or delayed diagnosis if used instead of conventional medical testing
Several peer-reviewed studies have examined the diagnostic accuracy of iridology. A notable study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 1979 tested the ability of iridologistas to detect kidney disease by examining photographs of irises. The study found that the iridologistas could not distinguish between healthy individuals and those with kidney disease.
Similar studies have been conducted for other conditions with comparable results. A systematic review published in 2000 examined all available controlled studies of iridology and concluded that “a validade da iridologia como ferramenta diagnóstica não é apoiada por avaliações científicas.”
“While the historical development of iridology is fascinating, and many practitioners are sincere in their beliefs, we must acknowledge that conventional medicine requires evidence-based validation of diagnostic methods.”
– Revista de Medicina Alternativa e Complementar
Despite these scientific challenges, many iridologistas continue to practice and report positive outcomes for their clients. Some suggest that the benefits may come from the holistic health advice that often accompanies an iridology session, such as improved nutrition and lifestyle changes, rather than from the iris analysis itself.
It’s worth noting that some medical professionals have taken an interest in exploring potential correlations between iris characteristics and certain genetic predispositions, suggesting there may be some aspects of iridology worthy of further scientific investigation.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Iridologistas Through History
The history of iridology and the contributions of pioneering iridologistas represent a fascinating chapter in the development of alternative health practices. From the early observations of Ignaz von Peczely to the systematic approach of Bernard Jensen, iridologistas have built a unique system of analysis that continues to attract interest worldwide.
While scientific validation remains a challenge for the field, the historical significance of iridology cannot be denied. The practice has evolved considerably over the centuries, adapting new technologies and refining its methodologies while maintaining its core principles.
For those interested in holistic approaches to health, understanding the historical context and development of iridology provides valuable perspective. Whether viewed as a complementary assessment tool or approached with scientific skepticism, the story of iridology and its practitioners offers insights into humanity’s ongoing quest to understand the connections between different aspects of health and the body.
Deepen Your Knowledge of Iridology
Whether you’re considering becoming an iridologista or simply want to learn more about this fascinating field, we offer comprehensive resources to support your journey.
Explore Iridology Resources
Perguntas frequentes sobre Iridologistas
What qualifications should I look for when choosing an iridologista?
Ao selecionar um iridologista, look for certification from recognized organizations such as the International Iridology Practitioners Association (IIPA) or the Guild of Naturopathic Iridologists. Additionally, consider their years of experience, client testimonials, and whether they have complementary training in fields like nutrition or naturopathy.
How does an iridologist’s approach differ from conventional medical diagnosis?
Um iridologista takes a holistic approach, looking for patterns in the iris that may indicate constitutional weaknesses or tendencies rather than diagnosing specific diseases. Conventional medical diagnosis relies on symptoms, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to identify specific pathologies. Iridologistas often focus on prevention and identifying potential health issues before they manifest as clinical symptoms.
Pode iridologistas detect all health conditions through iris analysis?
Não, iridologistas do not claim to detect all health conditions. The practice is considered most useful for identifying constitutional tendencies, potential weaknesses in certain organs or systems, inflammation, and toxin accumulation. Acute conditions, infections, and many specific diseases require conventional medical diagnosis. Most responsible iridologistas recommend working in conjunction with conventional healthcare providers.
Quanto tempo leva para se tornar um certificado iridologista?
O tempo necessário para se tornar um certificado iridologista varies depending on the program. Basic certification courses may take 3-6 months of part-time study, while comprehensive programs can take 1-2 years. Many practitioners continue their education throughout their careers, adding specialized knowledge and techniques to their practice.
What is the relationship between eye color and an iridologist’s análise?
Iridologistas consider eye color an important factor in their analysis. They classify eyes into different constitutional types: blue (lymphatic), brown (hematogenic), and mixed (biliary). Each type is believed to have different inherent strengths and weaknesses. For example, blue-eyed individuals may be more prone to lymphatic and respiratory issues, while brown-eyed people might have more challenges with blood, liver, and digestive functions according to iridology theory.
Sobre o autor
This article was written by Dr. Sarah Chen, a certified iridologista with over 15 years of experience in the field. Dr. Chen holds certifications from the International Iridology Practitioners Association and has trained with leading iridologistas across Europe and North America. She maintains a holistic health practice where she integrates iridology with nutritional counseling and herbal medicine.